Cancer Gene Detection Lab: Li-Fraumeni Syndrome & p53
advertisement

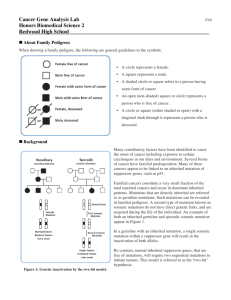
Cancer Gene Detection Lab Review of terms: Germline mutations- Somatic mutations- Tumor suppressor gene- Background: Hereditary forms of cancer include breast cancer (BRCA1 and 2), colon cancer (HNPCC) and LiFraumeni Syndrome (p53). Li-Fraumeni Syndrome is rare, affecting approximately 400 families worldwide, and is characterized by an increased risk for multiple cancers affecting brain, bone, blood, breast, and soft tissues. Another notable feature in family pedigrees include a sarcoma patient and at least two immediate relatives with other cancers before the age of 45, as well as multiple cancers in other family members. The gene that is mutated in Li-Fraumeni Syndrome is p53, a DNA binding protein that is also a tumor suppressor gene. Mutations in p53 that cause Li-Fraumeni Syndrome inhibit DNA binding and result in an inactive protein. The mutant form of p53 is the result of a missense mutation, which leads to a novel SalI recognition site in the central region of the gene. p53 mutations can therefore be diagnosed by performing SalI digests of patient’s DNA. Objective: Use the information provided below to determine if Valerie might have Li-Fraumeni Syndrome. Your job is to: 1. Establish a family pedigree. Be sure to include the name, age and type of cancer under each person’s symbol. 2. Use gel electrophoresis to diagnose Valerie’s p53 genotype (normal/normal, normal/mutant, mutant/mutant) AND to determine whether she inherited a germline mutation in p53. Be sure to include a tracing of your gel as data! Don’t forget labels! Name_________________________ Date ________ Period_______ Score _________ Cancer Detection Lab Family Pedigree: Gel Tracing: Valerie’s p53 genotype: ______________________ Describe whether Valerie inherited a germline mutation, and whether she obtained one or two somatic mutations in her p53 alleles. Does this data lead you to believe that Valerie has Li-Fraumeni Syndrome? Why/why not?