flitad
advertisement

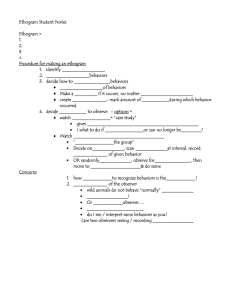
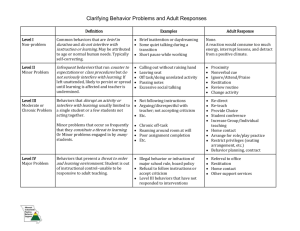
“FLITAD” – Dimensions of concern. FLITAD is used to describe how/what is being seen by an observer when observing a behavior of concern. Each area is designed to aide in behavioral descriptions and analysis of need areas. FLITAD (Frequency, Latency, Intensity, Topography, Accuracy, and Duration) is a useful acronym for remembering the possible dimensions of a problem. Dimensions commonly used are: Frequency: the number of times a behavior occurs; the behavior has definite beginning and ending points and can be tracked using tallies or counts. Often listed as correct words per minute (WPM), correct digits per minute (CDPM), correct responses or behaviorally when looking at how frequent something is happening (ie: head banging, tapping, or off task behaviors) *always under specific time frames/limits Latency: the elapsed time from the presentation of a stimulus and the response/problem; the amount of time that elapses from the end of one event and the beginning of the following event. Examples may include: following directions, how long it takes a student to initiate the requested behavior (ie: start a task, pick up the spoon, answering a question.) Intensity: the strength or force with which a problem is expressed; the magnitude of the behavior; often measured through rubrics, a goal attainment scale, and other observer based ratings. Examples may include: the level of the outburst on a rubric (scale of 1-3) or the level of voice control (scale of loud to soft) Topography: the configuration, form, or shape of a response or problem. How the student looks or acts during the observed behavior. Examples may include: students with sensory issues (the actions or behaviors related to how they look when presented with an item – ie: loud noise acting out vs. behaviors of coping with the noise), correct pencil grip, walking on toes in hallway, behavioral ticks, twitches etc… “FLITAD” Accuracy: the extent to which the problem meets standards/expectations or is correct; the proportion of correct responses to opportunities to respond. Often used with comprehension questions, spelling, letter formation, and master level tasks (ie: folding laundry, taking coat off and putting it away, hallway behaviors, bathroom routines etc…) *Typically not under specific time frames or limits. Duration: the length of time that passes from the time the problem starts to the time the problem stops. Often used when looking at the time it takes or passes for a behavior to cease. Examples may include: tantrums, remaining on task, destruction of materials or property, engaging in peer interaction for social skills.