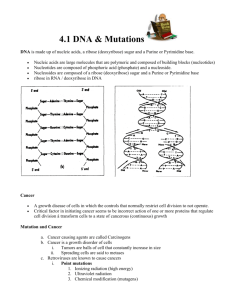
Evidence 1 – DAPI is a fluorescent dye used by scientists to
advertisement

Evidence 1 – DAPI is a fluorescent dye used by scientists to highlight DNA in cells. DAPI is blue under fluorescent light. Below are some pictures taken of DAPI stained cells. Human endothelial cells Bovine Pulmonary Artery Wall Cells Unidentified Bacterial Cells Human Blood Cells Conclusion - The nucleus is not the control center of the cell because bacteria can function with out a nucleus. DNA is the ‘controlling factor’ in the cell DNA is only found inside the nucleus in Eukaryotic organisms Mutation Percentage ( in decimal form) formdecemimal Evidence 2 – Number 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Organism Bacteriophage λ Bacteriophage M13 Bacteriophage T2, T4 Escherichia coli Drosophila melanogaster Caenorhabditis elegans Saccaromyces cervisiae Mus Musculus Neurospora crassa Homo Sapiens Name Virus Virus Virus Prokaryotic Eukaryotic Eukaryotic Prokaryotic Eukaryotic Eukaryotic Eukaryotic Mutations percentage 77,000,000% 72,000,000% 2,400% 54% 34% 23% 22% 18% 7.2% 5% Conclusion – The function of the nucleus is to protect DNA Evidence 3 These results are based off an experiment in which scientists sampled the inside of the nucleus to determine the components of the macromolecules that make up the nucleus. Chemical Name Adenine Cytosine Guanine Phosphate Ribose Thymine Description The A in ATP Nucleic Acid Purine Can form 2 Hydrogen Bonds Nucleic Acid Pyrimidine Can form 3 Hydrogen Bonds The G in GTP (A molecule related to ATP) Nucleic Acid Purine Can form 3 Hydrogen Bonds A component of ATP (Attached to Ribose in ATP) A 5 carbon sugar A component of ATP and related molecules Nucleic Acid Pyrimidine Can form 2 Hydrogen Bonds Conclusion – See vocabulary section for DNA structure Amount Collected (μm) 26 14 14 40 40 26 Evidence 4 Scientists were experimenting with different DNA stains other than DAPI. They found that when they used Pyronin Y they stained another substance called RNA. The picture below shows a group of cells that were stained with both DAPI (blue) and Pyronin Y (Red in high concentrations, orange in low concentrations) Conclusion: The location of RNA in the cell is _____________________________________________________ The location of DNA in the cell is _____________________________________________________ Evidence 5 In 1953 Watson and Crick discovered the structure of DNA. (We did this as a class, the results are summarized on the vocabulary page. In addition to figuring out the structure of DNA these two scientists also noticed that DNA is like a zipper – in it can be split into a two single strands by separating the hydrogen bonds between the base pairs. Check out this video http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0CMIgZQakHY Evidence 6 The nuclear membrane is similar to the cell membrane. Materials that cannot diffuse or squeeze through the membrane must use proteins to move in and out of the nucleus. The proteins of the nuclear membrane only allow a single strand of genetic information through. Bonus Evidence 7 Proteins are large molecules that are made from smaller molecules called amino acids. There are twenty amino acids that make up all proteins. Large proteins such as hemoglobin contain as many as 574 amino acids. Vocabulary DNA – Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid, doubled stranded genetic material Purine – A double ring Nitrogenous base Pyrimidine – A single ring nitrogenous base Prokaryote – Bacteria, singled cell organisms that lack a nucleus Eukaryote – single or multi celled organism that contains a membrane bound organelles Virus – A non living macromolecule that is made of a protein coat surrounding DNA. Hydrogen Bond – An attraction between two molecules (or parts of molecules). This is weaker than a chemical bond Base Pair – Two nucleic acids that interact in DNA A–T G–C Sugar phosphate backbone – The repeating ribose – phosphate – ribose – phosphate pattern that connects nucleic acids ( nitrogenous bases) together RNA – Ribose Nucleic Acid a single stranded piece of genetic material Structure of RNA Structure of DNA AMP