Due Date: 40 minutes
advertisement

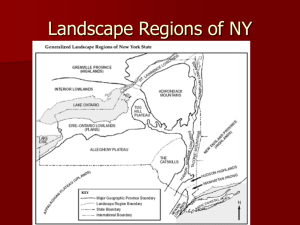
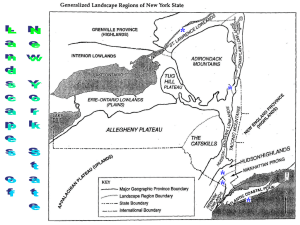
Name: ________________________ Due Date: _____________________ Per: ________ 40 minutes New York State Landscape Regions Purpose: At the end of this activity, you should be able to identify and understand the variety of landscape regions in New York State Introduction: New York State has a greater number of different landscape regions than any other state. The chief reason for this variety of landscape regions is the great variation in age, structure, and resistance to weathering of the bedrock found within the state. Almost all of New York State was affected by the glaciers of the last ice age that ended in New York about 10,000 years ago. As a result, glacial features are observed throughout the state. One of the most important features left by the glaciers is the transported soils (glacial till). New York State can be divided into 10 main landscape regions based on changing topographies and rock structure. Procedure A: 1. Read the passage about each landscape region on the following pages to determine if each is an area of high, middle, or low elevation according to the following criteria: High Middle Low (> 800 m) (200 – 800 m) (< 200 m) = = = red yellow green 2. On Map 1, color each landscape region as high, middle, or low elevation using the colors above. Atlantic Coastal Plain This landscape region is found exclusively on Long Island and consists of sedimentary bedrock formed during the late Mesozoic and Cenozoic Eras. Covered with thick glacial deposits of gravel, sand and clay, it can reach elevations of 110 meters above sea level. The slopes of the hills are gentle, and features along the shore such as beaches and sandbars have been created by waves and ocean currents. On Map 1, label the area “Atlantic Coastal Plain.” Newark Lowlands This region is made up of weak sedimentary rocks, such as conglomerate, red sandstone, and red shale, which have been weathered and eroded to lower elevations than the surrounding landscape regions and has a generally smooth appearance. An igneous intrusion called the Palisades Sill borders the Hudson River. It is very resistant to weathering and forms a cliff that ranges up to 150 meters above sea level. On Map 1, label the area “Newark Lowlands.” VVS Earth Science Landscapes New York State Landscape Regions Page 1 of 7 Hudson Highlands The mountains in this region are in the mature and old-age stages and are made up of Precambrian rocks, such as gneisses, quartzites, and marbles. The rocks are more resistant to weathering than the rocks of the surrounding regions. In the northern parts of the region there are elevations up to 500 meters above sea level with steep slopes. The southern parts have less slope. This landscape region is part of the New England Uplands. On Map 1, label the area “Hudson Highlands.” Taconic Mountains These greatly eroded mountains were originally uplifted in the Paleozoic Era. The rocks are mostly sandstone, shale, and slate and are highly folded and faulted. Today they have moderate elevations (up to about 600 meters above sea level) and gradual changes in slope, so that the topography has the form of rolling hills. On Map 1, label the area “Taconic Mountains.” Hudson-Mohawk Lowlands The rocks of this region are sedimentary rocks of Paleozoic age, such as limestones, shales, sandstones, and dolostones. They have been weathered and eroded by the Mohawk and Hudson Rivers to generally low elevations. More resistant rocks have formed escarpments (steep cliffs) and the walls of the valleys carved by the rivers. South of Albany, the Hudson River has an elevation of sea level and may be considered an inlet of the Atlantic Ocean. On Map 1, label the area “Hudson-Mohawk Lowlands.” Allegheny (Appalachian) Plateau This plateau is made up of sedimentary rocks mostly of Paleozoic age, such as limestones, shales, sandstones, and conglomerates. Significant weathering and erosion by streams and glaciers has resulted in steep slopes and much change in elevation. The Finger Lakes are found in this region and are the remnants of glacial lakes that filled the valleys. Elevations range from about 245 meters to 425 meters above sea level. On Map 1, label the area “Allegheny Plateau.” Catskills The Catskills are not true mountains. They have the appearance of mountains due to weathering and erosion by streams and glaciers resulting in steep slopes and much change in elevation, so that they resemble mountains. Elevations are up to 900 meters above sea level in the Catskills. The Catskills are carved out of the Allegheny Plateau, but are considered a distinct landscape region. On Map 1, label the area “Catskills.” VVS Earth Science Landscapes New York State Landscape Regions Page 2 of 7 Erie-Ontario Lowlands This region is a plain of sedimentary rock of Paleozoic age, such as limestone, shale, sandstone, and dolostone, covered by much glacial till. The northern section is especially smooth because of deposits of sediments from glacial lakes that were the ancestors of Lakes Erie and Ontario. Oneida Lake is the remains of glacial Lake Iroquois which covered most of central New York (Verona is located in this former lake bed). Elevations and slopes are generally small throughout the region. On Map 1, label the area “Erie-Ontario Lowlands.” Tug Hill Plateau This plateau of sedimentary rocks of Paleozoic age has a surface layer very resistant to weathering. The elevation of the plateau is about 600 – 700 meters above sea level. However, steep slopes occur where rivers have cut valleys, such as the Black River Valley that separates this region from the Adirondacks. On Map 1, label the area “Tug Hill Plateau.” Adirondack Mountains These are mature mountains made up of metamorphic rocks of Precambrian age, such as gneisses, quartzites, and marbles. There are moderate elevations in the western section, but the highest elevations in the state (over 1,350 meters above sea level at mountain peaks) occur in the eastern section. Mt. Marcy, at 1,629 meters above sea level, is the highest point in New York State. The landscape is rugged, which much change in elevation; steep slopes, valleys related to faults, and rocks of lesser resistance to weathering. On Map 1, label the area “Adirondack Mountains.” St. Lawrence-Champlain Lowlands This plain is made up of sedimentary rocks of lower resistance to weathering than rocks of the surrounding regions, and therefore has lower elevations. The rocks are Paleozoic limestones, shales, sandstones, and dolostones. The St. Lawrence area is mostly flat and borders the St. Lawrence River. Some steep slopes exist in the Champlain area due to uplift. On Map 1, label the area “St. Lawrence-Champlain Lowlands.” Manhattan Prong This area has a landscape of rolling hills and valleys. Its greatest elevation is approximately 100 meters above sea level. The region is made up of tightly folded metamorphic rocks covered by glacial deposits. On Map 1, label the area “Manhattan Prong.” VVS Earth Science Landscapes New York State Landscape Regions Page 3 of 7 Procedure B: In addition to elevation, the patterns of water drainage on a land surface play an important role in landscape formation. Map 2 shows some of the rivers, streams, and lakes in New York State. 1. Referring to the Generalized Bedrock Geology of New York State map in the ESRT, find and label the following water features on the NYS Drainage Map. Use a blue pencil to trace over and highlight each of the following features. Susquehanna River Mohawk River Genesse River Niagara River Lake Erie Finger Lakes Hudson River Delaware River St. Lawrence River Lake Ontario Lake Champlain Long Island Sound 2. The Hudson River drains into ___________________________________. 3. The Finger Lakes drain into Lake ________________________________. 4. Significant farming occurs on NYS’ Appalacian Plateau. What bodies of water may be affected by the use of pesticides and fertilizers in that part of the state? ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 5. List the names of the major cities/towns that have developed along the Hudson River. ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 6. List the names of the landscape regions that the Hudson River flows through – in order - in its trip from source to mouth. ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ VVS Earth Science Landscapes New York State Landscape Regions Page 4 of 7 Conclusions: Compare the Generalized Bedrock Geology of New York State map in the ESRT with your completed Map 1 and answer the following questions: 1. In the areas of high elevation, what is the bedrock type and geologic age? _________________________________________________________________ 2. In the Atlantic Coastal Plain region what is the bedrock type and geologic age? _________________________________________________________________ 3. The Allegheny Plateau includes the Catskills (a plateau dissected by streams which gives the appearance of being mountains). Describe the bedrock in terms of type and age. _________________________________________________________________ 4. Describe the Erie-Ontario Lowlands in terms of rock type and age. _________________________________________________________________ 5. Describe the Hudson-Mohawk Lowlands in terms of rock type and age. _________________________________________________________________ 6. Describe the Taconic Mountains in terms of rock type and age. _________________________________________________________________ 7. Which regions show evidence that crustal uplift was dominant over erosional forces in the past? _________________________________________________________________ VVS Earth Science Landscapes New York State Landscape Regions Page 5 of 7 Map 1: Landscape regions of New York State VVS Earth Science Landscapes New York State Landscape Regions Page 6 of 7 Map 2: New York Sate Drainage Map VVS Earth Science Landscapes New York State Landscape Regions Page 7 of 7