Quiz 2
advertisement

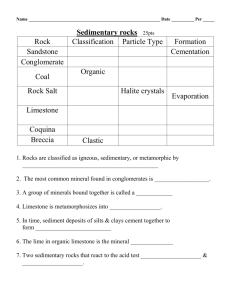
Quiz 2 1. Atoms with the same atomic number but different mass numbers are called: B) isotopes 2. The part of the atom that has a negative charge is referred to as the C) Both A and B are correct. 3. The mass number of an atom is A) the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. 4. One atom of a hypothetical element X has 27 neutrons while another has 29. This would make the two atoms of the element D) isotopes. 5. What type of weak bond results from asymmetry in the charge distribution? D) Van der Waals bond 6. What type of bond forms the strongest chemical bonds and compounds that tend to be strong with great hardness? A) covalent bond 7. In the illustration above, the part of the atom that has a negative charge is referred to as the C) Both A and B are correct. 8. In the illustration above, the part of the atom that has a positive charge is referred to as the D) nucleus. 8. The property of a mineral that relates how heavy it is for its size is referred to as B) density. 9. Which element is the most abundant in Earth's crust? D) oxygen 10. Which type of rocks have been altered by heat and pressure so that a new mineral assemblage and rock fabric has developed? B) Metamorphic rocks 11. Granite and basalt are what type of rocks? A) Igneous rocks 12. Which type of rocks are held together by naturally forming cement? C) Sedimentary rocks 13. An atom that has an excess positive or negative electrical charge caused by the loss or addition of an electron is called a(n) ______. ION 14. The mass number of an atom is the sum of the protons and ______. NEUTRONS 15. The four types of bonding that are important in minerals are ______, covalent, metallic, Van der Waals. IONIC 16. The property of ______ is a mineral's resistance to scratching. HARDNESS 17. Some minerals break along specific directions of weakness in their crystal structures. This property of a mineral to break in this predictable way is referred to as______. CLEAVAGE 18. The _____ of a mineral is the color of the mineral when powdered, which is usually accomplished in soft minerals by rubbing the sample against an unglazed porcelain plate. STREAK 19. _____ and silicon are the two most common elements in Earth's crust. OXYGEN 20. The two most abundant mineral families of Earth's crust are the silicates and the _____. OXIDES 21. Based on their origins, rocks can be divided into three distinct families: _______, sedimentary and metamorphic. IGNEOUS 21. There are 6 protons in the nucleus of a carbon atom. How many neutrons are there in carbon 12, carbon 13, and carbon 14, respectively? 6, 7, 8 22. Weak bond that is easily broken. One side of a “neutral” molecule is slightly positive and the other side slightly negative (assymetrical charge distribution). Van der Waals bonding 23. Charging of atoms positively or negatively so that they would attract. This bond creates minerals with an intermediate hardness. Ionic bonding 24. Clouds of electrons are shared by atoms making minerals malleable and good conductors of electricity. Metallic bonding 25. “Sharing” of electrons. This bond creates minerals that are hard. Covalent bonding 25. What are the four requirements necessary to classify a solid material as a mineral? inorganic, solid, crystalline, naturally occurring 26. Why is color an unreliable way to identify a mineral? Many minerals have the same color 30. Two chemical elements make up 70 percent of Earth's crust by weight. What are the two elements and what family of minerals do they form? Oxygen and Silicon 31. What's the difference between a rock and a mineral? Minerals are the building blocks of rocks. Rocks are an aggregate of minerals. 32. What are the three families of rocks? Igneous, Metamorphic, and Sedimentary 33. The figure below illustrates bonding forming crystal structures of carbon. Indicate why are both minerals completilety different. Molecular arrangement 34. What holds rocks together? In igneous and metamorphic the grains are interlocked, in sedimentary rocks the grains are cemented together. 35. Metamorphic rocks – Rocks that have been altered by exposure to high temperature, high pressure, or both True 36. Igneous rocks – Rocks that form under conditions of low pressure and low temperature near the surface. False 37. Sedimentary rocks – Rocks that form by cooling and solidification of molten rock False