Understanding by Design Unit Template
advertisement

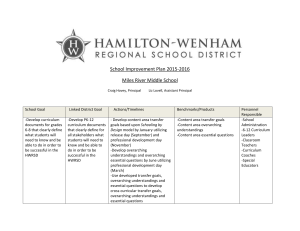
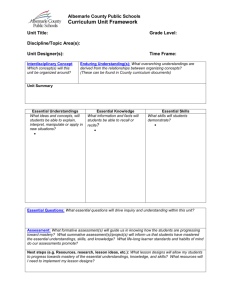
Understanding by Design Unit Template Title of Unit Curriculum Area Developed By Grade Level Time Frame Identify Desired Results (Stage 1) Content Standards Identify one or more content standards. List the strand and objective number. Write out the standard(s). Understandings Overarching Understanding What specifically do you want students to understand? What inferences should students make? Related Misconceptions Identify any misconceptions students may have during this unit. Essential Questions Overarching Overarching EQ’s are openended with no single, correct answer. They are meant to stimulate inquiry, debate and further questions. Topical Topical EQ’s are more unitspecific questions that lead into to specific topical understandings within a unit. Overarching EQ’s are more general. Knowledge (Declarative) Skills (Procedural) Students will know… Students will be able to… What facts, basic concepts, and vocabulary should students know and be able to recall? Skills are what you do with the facts or how you use the facts. They should be written in terms as, “Students will know . . .” Examples: vocabulary, definitions, concepts, laws, formulas, key facts, critical details, sequence and timelines What specific skills and processes should students be able to use? They should be written in terms as, “Students will be able to . . “ Examples: decoding, computation, communication skills (listening, speaking, writing), thinking skills (compare, infer, analyze), research (inquiry, investigate), group skills Assessment Evidence (Stage 2) Performance Task Description -Anchors the unit by providing evidence of student understanding. Goal Role Audience Situation Product/Performance Standards Your task is _____. The goal is to ____. The problem or challenge is ____. The obstacles to overcome are ____. Student’s role in the task. You are ______. You have been asked to ________. Your job is _______. Your clients are ____. The target audience is ______. You need to convince ______. The context you find yourself in is ______. The challenge involves dealing with ______. You will create a ______ in order to ______. You need to develop ______ so that _____. Good place to include the rubric. Your product must meet the following standards:______. A successful result will _______. Other Evidence Examples: informal checks for understanding, observations and dialogues, tests and quizzes, academic prompts, performance tasks, student work samples, peer reviews, student demonstration, visual presentations, etc. Learning Plan (Stage 3) WHERETO: Acronym that summarizes key elements to consider when designing and effective and engaging learning plan. Defines how you will get to the desire learning in Stage 1. Where are your students headed? Where have they been? How will you make sure the students know where they are going? How will you hook students at the beginning of the unit? What events will help students experience and explore the big idea and questions in the unit? How will you equip them with needed skills and knowledge? How will you cause students to reflect and rethink? How will you guide them in rehearsing, revising, and refining their work? How will you help students to exhibit and selfevaluate their growing skills, knowledge, and understanding throughout the unit? How will you tailor and otherwise personalize the learning plan to optimize the engagement and effectiveness of ALL students, without compromising the goals of the unit? How will you organize and sequence the learning activities to optimize the engagement and achievement of ALL students? What are the learning goals for the students? Why are they learning the content? What is required of them to achieve the goal(s), such as performance requirements, evaluative criteria? How will students be engaged in digging into the Overarching Essential Question(s) or Big Idea(s)? Have adequate opportunities to explore and experience the Big Idea(s). Examples may include inquiry, research, problem-solving, experimentation, etc. Have opportunities for students to rethink, revise, and refine their work based on timely feedback. Have an opportunity to evaluate their work and set future goals. How is the learning plan flexible to address the interests and learning styles of all students? How is the learning plan organized and sequenced to maximize engagement and effectiveness for all students? From: Wiggins, Grant and J. Mc Tighe. (1998). Understanding by Design, Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development ISBN # 0-87120-313-8 (ppk)