Globe Balloon Activity
advertisement

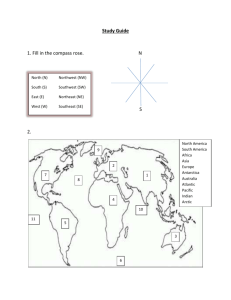
Subject Area(s): Earth Science Associated Unit: none Associated Lesson: none Activity Title: Globe Balloons Header: none Grade Level 6 - 9 Activity Dependency: none Time Required: 1 hr Group Size: 6 Expendable Cost per Group US $2 Summary: Students will learn what longitude and latitude and how to use them to indicate locations. They will also learn about important biological features associated this certain latitudes. This activity may precede other activities where students map features using latitude and longitudinal coordinates. Engineering Connection Structural engineering requires an understanding of how places are located on Earth. Understanding latitude and longitude and high tech equipment used in navigation, such as the Global Positioning System, are important for engineering projects. Engineering Category (1) relates science concept to engineering Level of Inquiry This lesson has guided questions that make students think about the uses of latitude and longitude and abiotic and biotic patterns around the earth associated with them. The level of inquiry can be adjusted according to different student ability. Students will need to put together information from several different maps to find listed features and answer questions about phenomena at different latitudes. Keywords Latitude, longitude, direction, Global Positioning System, desert, rainforest Educational Standards State science: Earth Science 5f.* Students know the interaction of wind patterns, ocean currents, and mountain ranges results in the global pattern of latitudinal bands of rain forests and deserts. 6b. Students know the effects on climate of latitude, elevation, topography, and proximity to large bodies of water and cold or warm ocean currents. 6c. Students know how Earth’s climate has changed over time, corresponding to changes in Earth’s geography, atmospheric composition, and other factors, such as solar radiation and plate movement. 8a. Students know the thermal structure and chemical composition of the atmosphere. Investigation & Experimentation d. Formulate explanations by using logic and evidence. h. Read and interpret topographic and geologic maps. i. Analyze the locations, sequences, or time intervals that are characteristic of natural phenomena (e.g., relative ages of rocks, locations of planets over time, and succession of species in an ecosystem). k. Recognize the cumulative nature of scientific evidence. Pre-Requisite Knowledge Students should be familiar with maps and globes, but do not necessarily have to know what the latitude and longitude lines are. Learning Objectives After this activity, students should be able to: Students will learn what longitude and latitude are, what they are used for, how they appear on a map versus a globe. how to use latitude and longitude to indicate locations. how to write latitude and longitudinal coordinates. some important biological features (deserts and rainforests) associated this certain latitudes. Materials List Each group needs: Balloons (one per student), blue color will simulate the ocean nicely pens (black, green, orange) student worksheet (attached) To share with the entire class: GPS device for show (optional) Introduction / Motivation Vocabulary / Definitions Word Definition latitude Latitude is an angular measurement ranging from 0° at the Equator to 90° at the poles (90° N or 90° S). longitude Imaginary lines that cross the surface of the Earth, running from north to south, measuring how far east or west of the prime meridian a place is located. Global A navigational system involving satellites and computers that Positioning can determine the latitude and longitude of a receiver on Earth System by computing the time difference for signals from different (GPS) satellites to reach the receiver. Hadley A thermal circulation consisting of rising air near the equator cell and sinking air near 30 degrees latitude. Procedure Background The teacher can first ask a student to describe how to get to a location (e.g., his/ her house) from school. Teachers can then talk about how we describe where features are on earth (N, S, E, W). They can point out the latitudes & longitudes on a map in front of the class, indicate the units they are measured in, and that latitude is indicated as N & S of the equator and longitude is indicated as E & W of the prime meridian. Teachers may ask students for ideas on how lat/long are useful (e.g., geography, navigation). If available, the teacher can show/ demonstrate a GPS (Global Positioning System) device and explain how satellites are used to find locations at a specific longitude and latitude. Before the Activity For each group, the teacher should put out in bins 1 balloon per student, pens (black, green, orange), student worksheet (1 per student, attached) With the Students 1. Students can do this activity individually or in partners, but should be encouraged to work with others in their group. Announcing that a couple of prizes (e.g. candy) will be given to the most accurate globes may encourage careful work. 2. Students should follow the directions on the worksheet (attached) and draw and label some major latitudes and longitudes on their balloon using the given maps. 3. Students should then find a desert and rainforest using their maps and draw them at the correct latitude or longitude on their balloon. Attachments Globe_balloon_worksheet Safety Issues This activity has no safety hazards. Troubleshooting Tips Students automatically tend to want to play with the balloons and may break them. Also, they might break if they don’t write gently with their pens. Tell them that they are only getting one and to be careful. Investigating Questions Assessment Pre-Activity Assessment Title: Preliminary questions for students Ask student the following questions: 1) How would you describe getting from your house to school (Answer: student should give directions- turn right/ left/ east/ west/ north/ south) 2) How would you give directions to a remote spot on Earth? (Answer: various ideas) 3) Has anyone heard of the terms “latitude” and “longitude”? Do you know what they are used for? (Answer: they are used as a coordinate system for marking locations on earth) Activity Embedded Assessment Title: Activity The teacher should make sure that students are on task and following instructions. He/she should make sure that the students understand the difference between longitudes and latitudes and how they are measured (longitude is measured in E and W and latitude is measured in N and S). Make sure students are labeling the latitudes and longitudes of the features listed on the worksheet on the balloon. Post-Activity Assessment Title: Class-wide discussion After the activity, the teacher should go around the room and select a few of the most accurately drawn balloons (everything labeled correctly, lat or long. of a desert and rainforest labeled). The students with the best balloons should be awarded a prize (e.g., piece of candy) and the teacher should explain in front of the class why the balloons that were selected is the most accurate ones. He/ she should also reiterate the difference between latitude and longitude and go over the discussion questions on the worksheet. Activity Extensions: none Activity Scaling For lower grades, fewer maps (or a single map with all the information) can be used. The part about finding the latitude or longitude of a rainforest and desert can be omitted. This activity can also be done as a whole-class demonstration. For upper grades, students can do the “Alternative (More Inquiryoriented) thought question” on the worksheet. Additional Multimedia Support Air Current Animation: http://trc.ucdavis.edu/biosci10v/bis10v/media/ch31/global_circ_v2.html References: Earth Science: Geology, the Environment, and the Universe. 2002. The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. New York. Chapter 2 “Latitude and Longitude” explains latitude and longitude as well as mapping and GPS. Websites: Lat/Long: http://geography.about.com/cs/latitudelongitude/a/latlong.htm GPS: http://www.gis2gps.com/GPS/GPSDEF/gpsdef.html Map sources: http://www.worldatlas.com/aatlas/newart/imagee.gif http://www.uefap.com/images/rainfor1.gif http://geology.com/records/sahara-desert-map.gif http://www.newmediastudio.org/DataDiscovery/Hurr_ED_Center/Easterly_W aves/Trade_Winds/Trade_Winds_fig02.jpg Other Owner UCLA SEE-LA GK-12 Program, University of California, Los Angeles Contributors Developer: Brittany Enzmann. This activity was developed as part of the UCLA Science and Engineering of the Environment of Los Angeles (SEE-LA GK-12) program and has been classroom tested in several 9th grade Integrated Coordinates Science classes at University High School in Los Angeles. Copyright © 2009 University of California, Los Angeles. This digital library content was developed by the UCLA SEE-LA GK-12 program under National Science Foundation grant number 0742410.