Rocks Study Guide
advertisement

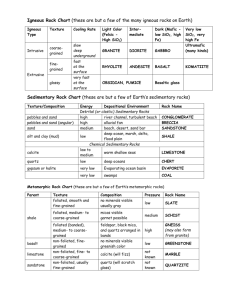
Name:_________________________ Date of test:_____________ Doc:_____________ Rocks Study Guide Be sure to review your labs, notes, textbook, and graphic organizers. You will have a lab practical portion to the test. This is used to help you study, it is not the only thing you should study. 1. What is a rock?__a mixture of minerals. It is solid, and naturally made 2. What are the 3 types of rocks? ____Igneous________ ___Sedimentary___ __Metamorphic____ 3. Match the 3 types of rocks to the way that they are produced: Word bank: Igneous Metamorphic Sedimentary a. ___Igneous____Produced from melted or molten rock cooling. Volcanic. Magma or lava cooling. b. __Sedimentary_Produced from lots of weathered and eroded rocks or organisms that have been deposited, compressed, and cemented together. The process of gluing sediments into stone is called lithification. c. ___Metamorphic__Produced from adding heat and or pressure to existing rocks to produce a new rock called a daughter rock. 4. Label the rock cycle and be able to explain what is going on. Word bank: Igneous Melted rocks Metamorphic Sedimentary Sediment Igneous Weathering & erosion Cooling crystallization Sediments Melted rocks (lava & magma) Deposition, compaction, cementation (lithification) Melting Sedimentary Metamorphic Heat Pressure One type of rock can become ANY other type of rock. Igneous Rock 5. How are igneous rocks formed? ____The cooling and crystallization of lava and magma________ 6. Why can’t you find fossils in igneous rock?__The lava/magma would melt them.______________ ______ Mineral Content- Felsic vs Mafic: 7. __Mafic________rocks are dense and have little silica, but lots of magnesium and iron. They are usually a DARK color. 8. ___Felsic________rocks are less dense and have lots silica and feldspar. They are usually a LIGHT color. Origin, cooling rate & Texture: quickly glassy very quickly slowly porphyritic large Word bank: coarse-grained fine grained coarse-grains on a fine background small 9. Intrusive rocks form from the cooling of magma within the earth’s crust. This magma cools __Slowly________ and as a result ____Coarse_-grained (LARGE crystals) forms. 10. Extrusive rocks form from the cooling of lava on the surface of earth’s crust. A. Lava flowing down the side of a volcano cools __quickly___ and as a result ___fine__-grained (small crystals) forms. B. Lava that cools in the air cools __VERY quickly___ and as a result has a __glassy__ texture which means that no crystals are visible. Note: pumice and scoria look like rocky sponges. They do not look like glass, but are still glassy because they have no visible crystals. 11. Porphyritic rocks started cooling slowly and ended cooling quickly. As a result they have a porphyritic texture which is described as having both ___large and small crystals___. 12. Be able to look at a rock and tell its mineral content, origin, cooling rate, and texture. Mineral content: Mafic (dark) or felsic (light) Origin Cooling Rate Texture Intrusive slow Extrusive Fast or REALLY fast Fine-grained or glassy Porphyritic Slow then fast CoarseBOTH large grained & small (small or none) (large) crystals 13. What is the relationship between origin and crystal size? _The longer it takes to cool, the larger the crystal size, to intrusive rocks are always coarse grained and extrusive rocks are always fine or glassy_ Reread your igneous rock notes and try to draw the volcano diagram you drew. Sedimentary Rock 14. Sedimentary rocks are formed by the LITHIFICATION of sediments. List and describe the 5 steps. Step Description 1. WEATHERING Breaking rock into small sediments. Can be chemical or mechanical. Ex. Abrasion, ice wedging, animals and plants, acid rain etc. 2. EROSION Moving sediments to a new area by wind, water, gravity etc. 3. DEPOSITION When sediments settle into a new area. 4. COMPACTION Pressing and squeezing sediments together. 5. CEMENTATION Minerals fill in the spaces between sediments and glue / cement them into a rock. 15. The law of superposition states that layers that are deeper down must have been deposited first and are therefore older than the layers above them. In the diagram below which letter layer is the oldest?__C______ newest?___A____ 16. What is stratification and why can it happen?___Layers of sediments deposited over time. Older layers deposited first and newer layers get deposited on top of them._____________ 17. Is there a relationship between the type of sedimentary rock and if it is stratified?__No, not all stratified rocks are the same type. Ex. Coal is organic and stratified and sandstone is clastic and stratified. Not all organic and not all clastic are stratified. There is no relationship between formation and stratification of sedimentary rocks.__ 18. What are the 3 types of sedimentary rock? How is each formed? Word bank: clastic, chemical, organic a.___Clastic________bits of other rocks compressed and cemented together.(pebbles, mud, sand, clay). b.___Organic_______bits of organisms that were once alive glue together by minerals. c.___Chemical______formed by evaporation or precipitation of minerals out of a solution. 19. Why is coal organic sedimentary?___It is formed from the remains of plants______________ 20. Circle the stratified rock(s) pictured below. Label each as clastic (CL) , chemical (CH) or organic (O) Conglomerate Sandstone Coquina (made of shells) Coal (from plants) Geode __CLASTIC__ _CLASTIC__ __ORGANIC___ __ORGANIC___ __CHEMICAL__ Reread your sedimentary rock notes and the graphic organizers you completed. Metamorphic Rock dynamic 21. Complete the diagram with the following words: (one word is used 2 times) thermal contact local regional heat pressure foliated non foliated DYNAMIC Area size = ____Regional__________ ___THERMAL_____or _____CONTACT______ Area size=___Local_______ magma Mountain building & Tectonic Plates high__Heat________&___Pressure____ cause minerals to layer in the rocks. Layered rocks are called __Foliated____ Near magma chambers ____Heat____ causes minerals to chemically change These rocks do not have layers so they are ___Non-foliated_____ 22. The following image shows foliation. Which kind of metamorphism produces foliation?_Dynamic__ 23. Why does dynamic metamorphism produce foliation and thermal/contact doesn’t?_______________ _Dynamic metamorphism involves heat AND pressure and pressure is needed for foliation to occur. Thermal/Contact metamorphism only provides heat so foliation cannot occur._(this is known as a causative relationship. Dynamic metamorphism CAUSES foliation.___ 24. Why are metamorphic rocks called daughter rocks?__They come from other parent rocks.__________ 25. Which types of rocks can be parent rocks?__Any rock type of rock can be a parent rock.______ 26. Why would fossils be deformed if they were found in metamorphic rock?_The heat and pressure are great enough to deform rocks AND the fossils they contain._ 27. Look at the image of gneiss to the left, is gneiss foliated or non-foliated?__Foliated___ 28. Is gneiss formed by Dynamic or Thermal/Contact metamorphism?_ Dynamic because it is foliated._ Reread your metamorphic notes. Be able to identify a rock as foliated or non-foliated. 29. ALL ROCKS: Identify the following statements as Igenous ( I ), Sedimentary (S) or Metamorphic (M): _S__ stratified or unstratified __ M ___foliated or nonfoliated _ M _regional or local __ S ___most likely to have fossils _ I__magma & lava __ I ___intrusive & extrusive __ M ___heat & pressure __ I ___ felsic or mafic __ M ___deep in the earth __ I __surface/volcanoes __ M __changed by magma, mountains or tectonics __ S ___clastic, organic, chemical __ M___ deformed fossils __ S ____ lithification __ M ____parent and daughter __ S ____ layers over time __ I _____coarse, fine, or glassy texture