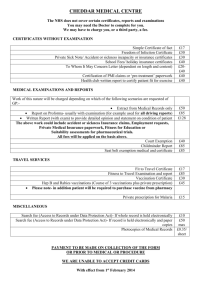
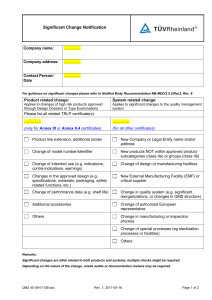
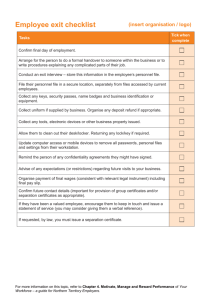
National Savings Organization
advertisement

1 Table Of Contents Chapter # Topic 1: Executive summary 2: Introduction & History 3: Current status of Organization 4: Organizational Setup 5: Hierarchy chart 6: Objectives & Scope 7: Primary & Ancillary services 8: Primary Services Defence saving certificates Special savings certificates Regular Income Certificates Savings Account Special Savings Account Pensioners Benefit Accounts Bahbood Savings Certificates Prize Bonds Features common to all schemes 9: Ancillary Services (Departments) Administration OR HRM Treasury Section Drawing and Disbursement Section Publicity Section Scheme Section 10: Independent Department Regional Account Office 11: NSC center in Bahawalpur 12: Intermediaries 13: External Analysis Customer Analysis Competitive Analysis Strategic Groups Market Analysis Size & Growth Cost Structure Environmental Analysis Economic analysis Technological Government Sociocultural 14: Internal Analysis Tangible Resources Intangible Resources Human Resources 15: SWOT Analysis 2 16: Suggestions & Recommendations 17: References 18: Appendices 19: Annexure 3 Executive Summary Mobilization of idle savings is necessary for the economic development of any country. Pakistan is trying to do so through national savings, as said earlier, and to reinvest them in the required or desired segment/ sector of economy.. The objective of national savings was to create motivations towards savings among people of Pakistan . Now it is trying well for this objective. People are concentrating toward the schemes of national savings. National savings also, launched many schemes for the attainment of this purpose like prize bonds, certificates etc. The other objective of NSO was to provide assistance to SBP in controlling the quantity of money in the country. Because suppose in inflationary conditions SBP has to launch securities and it feels difficulties to do soo in the absence of National Savings. My objective of internship was to work in the practical environment of NSO for six weeks to learn its functioning and analyze its performance. competitiveness, contribution in economy & Structure. This report include all these concerned areas of study 4 National Savings Organization Introduction And History The history of National Savings Organization dates back to the year 1873 when the Government Savings Bank Act, 1873 was promulgated. During the First World War, the British Government introduced several Schemes for collection of funds to meet the expenditure. It was in this context that the Post Office Cash Certificates and, during the Second World War, post Office Defense Savings Certificated were floated. The need to setup a separate agency was felt and a national savings Bureau was established in 1943-44 as a attached department of Ministry of Finance of the undivided Government of India. The department was headed by National Savings Commissioner with the status of a Joint Secretary. At that time the main functions of Savings Department were to initiated all policy matters and issue directives for the execution of policy matters and issue directives for execution of policy decisions of the Central Government, and to review the Savings Schemes for time to time. Gradually, Savings Organization were established in almost all the Provinces of the sub-continent with the objectives of popularizing the Savings Schemes among the masses as well as to supervise, guide and control the working of authorized agents under their jurisdiction. The local authorities appointed the agents. They were paid commission @ 2 ½ on the investment secured by them. These authorized agents were in those days the only agency for securing investment in terms of Saving Certificates from the general public. In nutshell the central agency via, National Savings Bureau, Simla, was mainly concerned with the policy and planning matters of the Saving Schemes whereas the responsibilities of execution of various savings schemes vested with provincial authorities. At the time of independence there was no time for any sort of innovations in the field of administration. Thus an organization with the name of “Pakistan Savings Central Bureau” was created and the Government of Pakistan entrusted the Savings work to it, but this Bureau had its own peculiarities. The Pakistan Savings Central Bureau had no independent entity and was not given the same status as enjoyed bye Savings Bureau, Simla. The head of Pakistan Savings Central Bureau was then called Central National Savings Officer, a junior Officer of the Ministry of Finance with the status of as Under Secretary having some auxiliary staff. In 1953, the Pakistan Savings Control Bureau was re-named as Central Directorate of National Savings and it carried out the functions on the liens of National Savings Bureau Simla but as a part of parcel of the Finance Division, Central Directorate of National Savings was only responsible for publicity, and the operative agents were the provincial Governments as well as Pakistan Post Offices. However, the entire expenditure in this regard was borne by the Central Government. Such an arrangement created a large number of administrative difficulties and stunted the growth of savings. In view of these difficulties the Central Directorate of National Savings was given the status of an Attached Department in September 1960, and was made responsible for all policy matters and execution of various National Savings Schemes. Subsequently, it was also declared a Technical Department by the Government. The Director General, National Savings (BPS-20) now enjoys full powers of a Head of the Department. Till December, 1971, the National Savings Organization functioned as a publicity Organization and its activities were merely promotional in nature, but in early 1972, the scope of its activates was enlarged as the Central Directorate 5 started selling II-Rupee Prize Bonds, and subsequently engaged in the operations of other savings schemes. This resulted in considerable expansion of the National Savings Organization. Current Status Of Organization These are 367 National Savings Canters all over Pakistan which are controlled by 12 Regional Directorate of National Savings (RDNS). Peshawar Abbottabad Lahore Bahawalpur Multan Faisalabad Quetta Gujranwala Islamabad Hyderabad Sukkur Karachi At present, this organization has a total sanctioned strength of 3365 employees in various grades and its main units are as under: a) Central directorate of national savings, Islamabad. b) Directorate of inspection and accounts, Islamabad. c) Training institutes of national savings, Islamabad along with the sub-training institutes at Karachi. d) 12 Regional Directorates Organizational Setup: 6 Hierarchy Chart Objectives and Scope of Organization Following are the purposes of the national savings. Now, it is trying hard for accomplishment of these objectives for which it was formed. Core Objectives o Generation of pool of funds for country o Provide secure system of Borrowing o Promotion of savings o Mobilization of idle savings o Motivation towards savings o Provide assistance to SBP o Establishment of a savings Banks Generation of pool of funds for country: The basic function of this organization is to generate the pool of funds from the nation by a trusted and ensured govt. body. Promotion of savings: The main and basic purpose of national savings was to collect the small amounts of savings from lower class & middle class of the society of Pakistan. Because the amounts of savings in this segment of people are very low so they often try to avoid the investment of this amount. National saving’s prime purpose was to create confidence among these people and collect their small savings through its savings schemes. Mobilization of idle savings: Mobilization of idle savings is necessary for the economic development of any country. So 7 Pakistan is trying to do so through national savings, as said earlier, and to reinvest them in the required or desired segment/sector of economy. Motivation towards savings: The objective of national savings was to create motivations towards savings among people of Pakistan. Now it is trying well for this objective. People are concentrating toward the schemes of national savings. National savings also, launched many schemes for the attainment of this purpose like prize bonds, certificates etc. Provide assistance to SBP: The other objective was to provide assistance to stat bank of Pakistan in controlling the quantity of money in the country. Because suppose in inflationary Conditions. SBP has to launch securities and it feels difficulties to do so in the absence of national savings. Establishment of a savings Banks: The last objective was to establish the savings bank in the country, which has performed all saving function. No doubt other commercial banks were doing and trying their best to act as savings bank but the speed of advancement was not satisfactory and people were not considering them. Primary and Ancillary Services It is important to distinguish between primary and ancillary services. The term "primary" is used to describe the business activity that provides the chief source of revenue for a business. The term "ancillary" is used to describe the secondary business activities conducted by an organization. The definition of check cashing restricts the focus to the population of businesses that provide this service as a primary activity. This definition filters out the nearly uncountable number of businesses that this organization is carrying its customers as an ancillary activity. Primary Services National Savings Schemes 1. Defence saving certificates. 2. Regular income certificates. 3. Special saving certificates /accounts. 4. Savings Accounts. 5. Prize Bonds. 6. Bahbood Savings Certificates. 7. Pensioners Benefit Accounts. 8. Special Savings Accounts 1 Defence Saving Certificates: The Government of Pakistan introduced Defence Savings Certificate scheme in the year 1966. This is the most popular scheme among investors. This scheme has Specifically been designed to meet the future requirements of the depositors. This is the only scheme with 10 years maturity with built in feature of automatic reinvestment after the maturity i.e. in case any certificate is not encashed on maturity, the balance at Credit (principal + profit) without any deduction, shall be deemed to have been reinvested for another period of 10 years on filling in a new application form. these Certificates are available in the following denominations S.No. Rupees 1. 500 2. 1000 3. 5,000 4. 10,000 5. 50,000 6. 100,000 7. 500,000 8. 1,000,000 8 SALIENT FEATURES: 1. Eligibility for Purchase: These certificates can be purchased by a single adult, a minor, two adults in their joint names with the options of payable to the holders jointly (Joint/A ) or payable to either (Joint/B). An adult can also purchase these certificates on behalf of a single minor, two minors jointly or himself (herself) and a minor jointly. 2. Procedure for Purchase: These certificates can be purchased by filling in a prescribed form (SC/I), obtainable from any National Savings Centre (NSC), Pakistan Post Office (PPO), State Bank of Pakistan, SBP BSC (Bank).A copy of the Computerized National Identity Card (CNIC) or in case of a foreign national, a copy of the Passport may be attached with the application form (SC/I). 3. Investment Limit: There is no maximum limit of investment in this scheme. 4. Encashability: Certificates can be encashed any time after one month from the date of purchase. 5. Mode of Deposit: These certificates can be purchased by depositing cash at the issuing offices or by presenting a cheque. The certificates shall immediately be issued on receipts of cash. However, in case of deposit through cheque the certificates shall be issued from the date of realization of the cheque after receipt of the clearance advice. 6. Profit Payable on Defence Savings Certificates: The Finance Division, Govt. of Pakistan, according to the notification dated 19-07-2005 has reviewed the rate of return on National Savings schemes. The return on Defence Savings Certificates has been fixed as given in table below, for the certificates issued With effect from 0107-2005. The Defence Savings Certificates purchased prior to the above said notification shall earn profit at the rate prevailing on the date of purchase. The year wise payable amount on initial investment of Rs.100 is given as under: After completion of year 1 Rupees 105 2 112 3 119 4 128 5 138 6 150 7 163 8 183 9 211 10 247 D.S.Cs Purchased from 01-07-2005 (Current) @ 9.46% Value on completion of period Rs. 500 1 Year 525 2 Years 560 3 Years 595 4 Years 640 5 Years 690 6 Years 750 7 Years 815 8 Years 915 9 Years 1,055 10 Years 1,235 1000 1,050 1,120 1,190 1,280 1,380 1,500 1,630 1,830 2,110 2,470 5000 5,250 5,600 5,950 6,400 6,900 7,500 8,150 9,150 10,550 12,350 10,000 50,000 10,500 52,500 11,200 56,000 11,900 59,500 12,800 64,000 13,800 69,000 15,000 75,000 16,300 81,500 18,300 91,500 21,100 105,500 24,700 123,500 100,000 500,000 105,000 525,000 112,000 560,000 119,000 595,000 128,000 640,000 138,000 690,000 150,000 750,000 163,000 815,000 183,000 915,000 211,000 1,055,000 247,000 1,235,000 1,000,000 1,050,000 1,120,000 1,190,000 1,280,000 1,380,000 1,500,000 1,630,000 1,830,000 2,110,000 2,470,000 PREVIOUS YEAR’s RATES D.S.Cs Purchased from 01-07-2004 to 30-06-2005 (Issue VIII & IX) @ 8.15% D.S.Cs Purchased from 01-07-2005 to onward @ 10% Note: Zakat shall be deducted only once at the time of actual encashment on the value fallen due on the relevant valuation date i.e. (1st Ramadhan) and not on the continuous reinvestment after the maturity. A Zakat collection receipt duly signed by the two officers is issued in token of the deduction of the amount. Value on of period 1 Year 2 Years 3 Years 4 Years 5 Years Rs 500 520 545 575 610 650 1,000 1,040 1,090 1,150 1,220 1,300 5000 10,000 50,000 100,000 5200 10400 52,000 104,000 5450 10900 54,500 109,000 5,750 11,500 57,500 115,000 6,100 12,200 61,000 122,000 6,500 13,000 65,000 130,000 500,000 520,000 545,000 575,000 610,000 650,000 1,000,000 1,040,000 1,090,000 1,150,000 1,220,000 1,300,000 9 6 Years 7 Years 8 Years 9 Years 10 Years 695 1,390 6,950 750 1,500 7,500 830 1,660 8,300 945 1,890 9,450 1,095 2,190 10,950 13,900 69,500 139,000 15,000 75,000 150,000 16,600 83,000 166,000 18,900 94,500 189,000 21,900 109,500 219,000 695,000 750,000 830,000 945,000 1,095,000 1,390,000 1,500,000 1,660,000 1,890,000 2,190,000 With Holding Tax As per directions of the Federal Government, the tax on profit from investment made on or after the 1st July,2002, shall be deducted at source at the rate of Ten Percent (10%) of such profit if such deposit exceeds Hundred and fifty Thousand Rupees (150,000) . 7. Transfer of Certificates: From one Centre to another Certificates are transferable from one city to another by applying on the prescribed form (SC/6) obtainable from any NSC/ SBP BSC (BANK)office and also available at the website of National Savings under the option of "Forms". The application duly filled in along with two copies of NIC may be presented at the office of issue or at the office where the transfer is desired. However, the certificates purchased from scheduled banks, State Bank of Pakistan, SBPBSC (Bank), PPO and NSC can be transferred to and from the respective branches of the issuing office / agencies only. (b) From one person to another: Certificates are transferable from one person to another on the expiry of non/encashability period, by applying on the prescribed form (SC/4). In case of death of the purchaser, certificates can be transferred in the name of nominee(s) without any fee/charges or to the legal heir(s) on furnishing among others, a succession certificate issued by the competent court of law, along with the following: 1. 2. 3. 4. Application on the prescribed form (SC/4); Death certificate of the purchase; Attested photocopies of CNIC of the deceased and the nominee (s); Specimen signatures of nominee (s) attested by a gazetted officer. 8. Pledging of Certificates: Certificates can be pledged in favor of a gazetted government officer, Officers of the State Bank of Pakistan, Officer of a Local Authority, or an Officer of a Government Sponsored Corporation or an officer of a scheduled bank, in his official capacity, for the purpose of being treated as security. The value of security shall be the payable value of the certificates including the amount of profit. 9. Replacement of Lost/Destroyed Or Damaged Certificates: If a certificate is lost, or destroyed, the purchaser or his nominee(s) or heir(s), as the case may be, entitled to have duplicate certificates issued from the issuing office on completion of certain requirements which, among others, include the following:i) A copy of First Information Report (FIR) or "Roznamcha" in case the value exceeds Rs.10,000. ii) Application for the issuance of certificates clearly mentioning the circumstances leading to the loss. iii) Photocopies of CNIC of the purchaser(s). iv) Deposit of prescribed fee with the issuing office. v) Indemnity Bond on Rs.50 stamp paper (specimen obtainable from any NS Centre). 10. Investment from Abroad: Investors from abroad may send applications along with remittance of the desired amounts either directly to the Director General or concerned Director/Joint Director or to the National Savings Centers, where investment is desired to be made. The remittance of the amount may be made either through a cheque or bank draft in the official designation of the concerned payee. The certificate shall be issued/account opened after the remittance accompanying the application is enclosed and credited to Government Account. The Principal and profit accrued on a certificate issued/account opened, against foreign exchange received through remittance or transfer from foreign currency account or surrendering foreign exchange bearer certificates/dollar bearer certificates shall be payable abroad to the purchaser in foreign currency, if so desired by the investor. The amount received in foreign currency shall be converted into Pakistani rupees, in accordance with the exchange rates prevailing on the date of clearance of the bank draft. The amount of principal or profit will be converted into foreign currency in accordance with the exchange rates prevailing on the date of remittance. 11. Sale Of Defence Savings And Special Savings Certificates Abroad Through Overseas Branches of Scheduled Banks of Pakistan. All branches of Pakistani Scheduled Banks Operating Abroad are allowed, in principle, to sell Defence Savings Certificates (DSCs)/Special Savings Certificates (SSCs) to Overseas Pakistanis against foreign currency on repatriable basis provided regulatory sanction/permission of the concerned country is available. The payment of principal and or profit of certificates, so issued is also payable abroad in local currency from the same branch of the bank. These certificates are 10 transferable from one person to another and also to Pakistan in any branch of the same bank from where the certificate purchased. 2. At the time of purchase, the face value of the certificates in Pak. Rupees is converted in local foreign currency at the prevailing rate for Pak. Rupees so as to generate Pak. Rupee equivalent to the face value of the certificate required. Similarly, at the time of encashment of profit and principal, the payable rupees amount is converted into foreign currency at the T.T. spot buying rate for Pak. Rupees on the date of payment. 3. In case of death of the purchaser, the amount of principal and or profit accrued on these certificates is payable to nominee(s) or legal heirs, if so desired? 4. Recently, the sales of Defence Savings Certificates and Special Savings Certificates have been started by the branches of HBL and UBL Operating in UAE after the grant of regulatory permission by the Central Bank UAE for sale of these securities of Government of Pakistan. The sale of these certificates would also be started in other countries as and when necessary regulatory permission is accorded by the Central Bank of the respective countries. 2 SPECIAL SAVINGS CERTIFICATES This scheme being of three years maturity was introduced in February, 1990 keeping in view the periodic needs of depositors. These certificates are available in the denomination of Rs.500, 1000, 5000, 10000, 50000, 100000, 500000 and Rs.1,000,000/ Profit is paid on the completion of each period of six months.. In case, the profit earned on these certificates is not drawn on due date, the undrawn profit will automatically stand reinvested from date of its accrual as per following tables: S.S.Cs purchased from 01-07-2005 (Current) @ 8.60% After Completion Of period 1st six Months 2nd six Months 3rd six Months 4th six Months 5th six Months 6th six Months Rs. 500 1000 5000 10,000 50,000 100,000 500,000 1,000,000 21 42 210 420 21,00 4,200 21,000 42,000 21 42 210 420 21,00 4,200 21,000 42,000 21 42 210 420 21,00 4,200 21,000 42,000 21 42 210 420 21,00 4,200 21 42 210 420 21,00 4,200 21,000 42,000 24 48 240 480 24,00 4,800 24,000 48,000 21,000 42,000 Compound Rate of Interest on SSCs Certificates purchased from 01-07-2005 (Current) Profit (in Rs.) On completion payable on a registration of each Rs100.00 of period 6 months 1 Year 1 ½ Year 2 Years 2 ½ years Nil 4.200 8.576 13.133 17.884 1st six months 4.200 8.576 13.133 17.884 2nd six months 4.200 8.576 13.133 18.481 3rd six months 4.200 8.576 13.733 4th six months 4.200 9.176 5th six months 4.800 3 Years 22.831 23.431 PREVIOUS YEAR’S RATES: S.S.Cs purchased from 01-07-2004 to 30-06-2005 (Issue VII & VIII) @ 6.95% After Completion Of period 1st six Months 2nd six Months 3rd six Months 4th six Months 5th six Rs. 500 1000 5000 17 34 170 17 34 17 17 10,000 50,000 100,000 340 1,700 3,400 17,000 34,000 170 340 1,700 3,400 17,000 34,000 34 170 340 1,700 3,400 17,000 34 170 340 1,700 3,400 500,000 17,000 1,000,000 34,000 34,000 11 Months 6th six Months 17 19.25 34 170 38.50 192.50 340 385 1,700 3,400 17,000 34,000 1,925 3,850 19,250 38,500 Compound Rate of Interest on SSCs: On certificates purchased from 01-07-2004 to 30-06-2005 (Issue VII & VIII) Note: (i) Zakat is deducted at the time of actual encashment @ 2.5% on the principal amount (Face Value) where applicable. (ii) With Holding Tax : As per directions of the Federal Government, the tax on profit from Investment made on or after , the 1st july,2002, shall be deducted at source at the rate of ten percent (10%) of such profit if such deposit exceeds Hundred and fifty Thousand Rupees (150,000). 3 Regular Income Certificates Keeping in view the monthly requirements of the general public, this five years' maturity scheme was launched on 2nd February, 1993. These certificates are available in the denomination of Rs.50,000, Rs.100,000, Rs.500,000, Rs.1,000,000, Rs.5,000,000 & Rs.10,000,000/=. Profit is paid on monthly basis reckoned from the date of issue of certificates. Who Can Invest? These certificates can be purchased by a single adult, a minor or two adults in their joint names with the options of payable to the holders jointly (Joint-A ) or payable to either (JointB). An adult can also purchase these certificates on behalf of a single minor, two minors jointly or himself/herself and a minor jointly. In addition to above individual investors, the following institutions are also allowed to invest in the scheme: a. Registered Charities (Non-profit bodies). b. Public Sector Enterprises excluding Banks. c. Private Educational & Health Institutions. d. Employees Old Age Benefit Institutions (EOBIs). e. Private Corporate Sector registered with the SECP excluding Banks. f. Non-Bank Financial Institutions (NBFIs) excluding Insurance Companies. How to Purchase? These certificates can be purchased from any National Savings Centre (NSCs) or from Pakistan Post Office (PPO) by filling in a prescribed form called SC-1, which is available at all, the above offices of issue free of cost. A copy of the National Identity Card or in case of a foreign national, a copy of the Passport may be attached with the application form (SC-I). Mode of Deposit. These certificates can be purchased by depositing cash at the issuing office or by presenting a Cheque. The certificates shall immediately be issued on receipt of cash. However, in case of deposit through Cheque the certificates shall be issued from the date of realization of the Cheque after receipt of the clearance advice. What Is The Investment Limit. The minimum investment limit is Rs.50, 000/-, however, there is no maximum limit of investment in this scheme. What about Redemption. These certificates are encashable any time subject to deduction of service charges at the following rates: 12 If encashed before completion of one year from the of issue. date @ 2.00% of the face value If encashed after one year but before completion of 02 @ 1.50% of the face value years from the date of issue. If encashed after two years but before completion of 03 @ 1.00% of the face value years from the date of issue. If encashed after three years but before completion of 04 @ 0.50%of the face value years from the date of issue. What is the return? At the prevailing rates monthly profit of Rs.795/- is paid on investment of each Rs.100,000/-. This way the profit rate works to 9.54% p.a. However, the facility of automatic reinvestment of profit to earn further profit is not available in this scheme. Tax & Zakat Status. The profit earned on these certificates is subject of deduction of 10% withholding tax at source. However, the investment made in this scheme is exempt from collection of Zakat. 4 Savings Account This is the oldest scheme among the National Savings instruments. The scheme has been designed to encourage the small savers and to meet their day to day needs. This is an ordinary account and frequent withdrawals (twice a week) can be made through this account. . Who Can Invest? The account can be opened by a single adult, a minor, two adults in their joint names with the options of payable to the holders jointly (Joint-A ) or payable to either (Joint-B). An adult can also invest in these account on behalf of a single minor, two minors jointly or himself/herself and a minor jointly. In addition to above individual investors, the following institutions are also allowed to invest in the scheme: a. Registered Charities (Non-profit bodies). b. Public Sector Enterprises excluding Banks. c. Private Educational & Health Institutions. d. Employees Old Age Benefit Institutions (EOBIs). e. Private Corporate Sector registered with the SECP excluding Banks. f. Non-Bank Financial Institutions (NBFIs) excluding Insurance Companies. How to Invest? These accounts can be opened at any National Savings Centre (NSCs) and Pakistan Post Office (PPO) by filling in a prescribed form called DA-1, which is available at all, the above offices of issue free of cost. A copy of the National Identity Card or in case of a foreign national, a copy of the Passport may be attached with the application form Mode of Deposit. The accounts can be opened by depositing cash at the issuing office or by presenting a cheque. The passbook and withdrawal slip shall immediately be issued on receipts of cash. However, in case of deposit through Cheque the account shall be opened from the date of realization of the Cheque after receipt of the clearance advice. 13 What Is The Investment Limit. The minimum investment limit is Rs.100/- in the scheme besides no maximum limit. However, only one account can be opened by person at an office of issue. What about Encashment. The deposits can be withdrawn any time from the date of deposit. However, there is a limit of two withdrawals within a week's time. What is the Return? Profit in this account is credited on 30th June every year and is worked out on the lowest balance of an account between the close of the sixth day and end of the month. The current rate of profit is 6.50% p.a. Tax & Zakat Status. At present the profit earned on the accounts, wherein the average balances within a month do not exceed the limit of Rs.150, 000/- are exempt from levy of withholding tax. However, withholding tax @10% is deductible at source on the profits earned on the accounts, wherein the balances exceed the aforesaid limit. Zakat is also applicable as per rules. 5 Special Savings Account A three years maturity scheme introduced in February, 1990. The deposits are maintained in form of an account. Profit is paid on the completion of each period of six months. Who Can Invest?. The account can be opened by a single adult, a minor, two adults in their joint names with the options of payable to the holders jointly (Joint-A ) or payable to either (Joint-B). An adult can also invest in these account on behalf of a single minor, two minors jointly or himself/herself and a minor jointly. In addition to above individual investors, the following institutions are also allowed to invest in the scheme: a. Registered Charities (Non-profit bodies). b. Public Sector Enterprises excluding Banks. c. Private Educational & Health Institutions. d. Employees Old Age Benefit Institutions (EOBIs). e. Private Corporate Sector registered with the SECP excluding Banks. f. Non-Bank Financial Institutions (NBFIs) excluding Insurance Companies. How to Invest. These accounts can be opened at any National Savings Centre (NSCs) and Pakistan Post Office (PPO) by filling in a prescribed form called DA-1, which is available at all, the above offices of issue free of cost. A copy of the National Identity Card or in case of a foreign national, a copy of the Passport may be attached with the application form. Mode of Deposit. The accounts can be opened by depositing cash at the issuing office or by presenting a cheque. The passbook and withdrawal slip shall immediately be issued on receipts of cash. However, in case of deposit through cheque the account shall be opened from the date of realization of the cheque after receipt of the clearance advice. 14 What Is The Investment Limit? The minimum investment limit in this scheme is Rs.500/-. There is not maximum limit, however, the deposits are required to be made in multiple of Rs.500/-. When Can I Encash My Certificates? The deposits can be withdrawn at par any time after one month from the date of purchase. However, no profit is payable in case the withdrawals are made before completion of 6 months. What Will I Get As Profit? At the prevailing rates the profit is paid @ 9.00% p.a. for 1st five profits and the last profit @ 10.50% p.a. However, if the profit is not withdrawn on due date, it will automatically stand reinvested and would be calculated for further profit on completion of the next 06 months period. Tax & Zakat Status. At present, the profit earned is exempt from withholding tax, if the total investment in the scheme by the investor(s) does not exceed Rs.150, 000/-. However, withholding tax @ 10% is deductible at source on the profit(s) earned if the total investment exceeds Rs.150,000/- by the investor(s). The Zakat is collected at source as per rules at the time of encashment. However, no Zakat is not collected in case of reinvestment. 5 Pensioner's Benefit Account Keeping in view the hardships faced by the pensioners and to guard them against the declining rate of return on National Savings Schemes, this ten years' maturity scheme was launched by the Government on 19th January, 2003. The deposits are maintained in the form of accounts and the profit is paid on monthly basis reckoned from the date of opening of the account. Who Can Invest?. The pensioners of Federal Government, Provincial Governments, Government of Azad Jammu & Kashmir, Armed Forces, Semi Government and Autonomous bodies are allowed to invest. How To Purchase? These accounts can only be opened at the National Savings Centre (NSCs) by filling in a prescribed form called DA-1, which is available at the offices of issue free of cost. A copy of the National Identity Card and the copy of Pension Payment Order may be attached with the application form. Mode of Deposit. The account can be opened by depositing cash at the issuing office or by presenting a cheque. The account shall immediately be opened on receipt of cash. However, in case of deposit through cheque the account shall be opened with effect from the date of realization of the cheque after receipt of the clearance advice. What Is The Investment Limit? The minimum investment limit is Rs.10, 000/-, whereas, the maximum limit is Rs.3, 000,000/-. If an investor has already opened an account, he is eligible to invest only two subsequent deposits in that account. What About Encashment? The deposits can be withdrawn any time after date of deposit subject to deduction of service charges at the following rates: 15 if withdrawn before completion of one year from the date of deposit. @ of the face value if withdrawn after one year but before completion of 02 years from the date of deposit. 1.00% @ 0.75% of the face value if withdrawn after two years but before completion of 03 years from the date of deposit. @ 0.50% of the face value if withdrawn after three years but before completion of 04 years from the date of deposit. @ of the face 0.25% value What Will I Get As Profit? At the prevailing rates monthly profit of Rs.970/- is paid on investment of each Rs.100,000/-. This way the profit rate works to 11.64% p.a. Automatic reinvestment of profit facility to earn further profit at the scheme's rate is not admissible in this scheme; however, further profit is paid on undrawn profit at the rate applicable on Savings Account. Tax & Zakat Status. The withholding tax is not collected on the profit earned on the deposits made in this scheme. The investment made in the scheme is also exempt from Zakat. 6 Bahbood Savings Certificates Keeping in view the hardships faced by the widows and senior citizens and to guard them against the declining rate of return on National Savings Schemes, this ten years' maturity scheme was launched by the Government on 1st July, 2003. Initially the scheme was meant for widows only, however, the Govt. later decided to extended the facility for senior citizens aged 60 years and above with effect from 1st January, 2004. These certificates are available in the denominations of Rs.5,000/-, Rs.10,000/-, Rs.50,000/-, Rs.100,000/-, Rs.500,000 and Rs.1,000,000/-. Profit is paid on monthly basis reckoned from the date of purchase of the certificates. Who Can Invest ? Only widows and senior citizens aged 60 years and above are eligible to invest. How to Purchase? These certificates can only be purchased from the National Savings Centre (NSCs) by filling in a prescribed form called SC-1, which is available at the offices of issue free of cost. A copy of the National Identity Card and necessary evidence regarding eligibility is required to be attached with the application form. Mode of Deposit. The certificates can be purchased by depositing cash at the issuing office or by presenting a cheque. The certificates shall immediately be issued on receipt of cash. However, in case of deposit through cheque the certificates shall have the effect from the date of realization of the cheque after receipt of the clearance advice. What Is the Investment Limit? The minimum investment limit in this scheme is Rs.5, 000/-, whereas, the maximum limit is Rs.3, 000,000/-. Investment in allowed in multiple of Rs.1, 000/-. 16 What about Redemption? The certificates can be encashed any time after issuance subject to deduction of service charges at the following rates: If encashed before completion of one year from the date of purchase. If encashed after one year but before completion of 02 years from the date of purchase. If encashed after two years but before completion of 03 years from the date of purchase. If encashed after three years but before completion of 04 years from the date of purchase. If encashed after completion of 04 years @ 1.00% of the face value @ 0.75% of the face value @ 0.50% of the face value @ 0.25% of the face value No service charges What is the return? At the prevailing rates monthly profit of Rs.970/- is paid on investment of each Rs.100, 000/-. This way the profit rate works to 11.64% p.a. Automatic reinvestment of profit facility to earn further profit is not admissible in this scheme at the scheme's rate; however, further profit is paid on undrawn profit at the rate applicable on Savings Account. Tax & Zakat Status. The withholding tax is not collected on the profit earned on these certificates. The investment made in this scheme is also exempt from Zakat. 7 Prize Bonds Introduction Prize Bonds are bearer type of security available in the denominations of Rs.200, Rs.750, Rs.1, 500, Rs.7, 500, Rs.15, 000 and Rs.40, 000. These bonds are issued in series. Each series consist of one less than 1,000,000bonds. No fixed return is paid Prize draws are held on quarterly basis. These Bonds shall enchased at par any time after their issue These bonds can b purchased or sale at the following places, namely: 1. Office of the Stat Bank of Pakistan. 2. Banks authorized in this behalf by the State Bank of Pakistan. 3. National Saving Centers. 17 Denomination First Prize No. Amount 2nd Prize No. Amount 3rd Prize No. Amount Rs. 200/- 01 Rs. 500,000 03 Rs. 150,000 2,300 Rs. 1,000 Rs. 750/- 01 Rs. 1,000,000 03 Rs. 300,000 1,376 Rs. 7,500 Rs. 1,500/- 01 Rs. 2,000,000 03 Rs. 600,000 1,376 Rs. 15,000 Rs. 7,500/- 01 Rs. 10,000,000 03 Rs. 3,000,000 1,376 Rs. 75,000 Rs. 15,000/- 01 Rs. 20,000,000 03 Rs. 6,000,000 1,376 Rs. 150,000 Rs. 40,000/- 01 Rs. 50,000,000 03 Rs. 15,000,000 1,376 Rs. 400,000 Terms and Conditions 1. The Federal Government may withdraw any of the Bonds of circulation time by notification in the official Gazette. 2. No claim of a prize on the Bonds so withdrawn shall be admissible after the issue of the notification under sub-rule. 3. These Bonds may be purchased any time on payment in cash and no application form shall be necessary. 4. The sale of these Bonds shall be opened till such time as the Federal Government withdraws the Bonds. 5. The Bonds shall not bear interest but lots shall be drawn for each series quarterly for prizes on Such dates as specified below, namely:- Draw Schedule Rs. 200 15th day of March, June, September and December every year. Rs .750 15th day of January, April, July, and October every year. Rs .1500 15th day of February, May, August and November every year. Rs. 7500 1 st Rs .15000 1 days of January, April, July and October every year. Rs .40000 1st days of March, June, September and December every year. day of February, May, August and November every year st The draws are held under common draw method and the numbers of prizes are same for each series. It means that if 50 series of Rs.200 Prize Bond are in circulation. Then on each draw we have 50 winners of 1st prize and 150 winners of 2nd Prize and so on. The number and amount of prizes on various denomination of prize bonds for each series is shown in the following table: Feature Common to All Schemes: 1: Government of Pakistan guarantees the security of investment. 2: Certificates are transferable from one person to other expect Bahbood saving certificates. 3: Certificates /accounts are transferable from one city to another city’s centre. 4: Expect Bearer certificates, duplicate certificates can be issue only in case of lost, theft or waste. 5: Certificates can be pledge with Government officers, scheduled bank etc. As security. 6: Principal and profit of the investment made from the abroad can be got repatriated abroad in foreign exchange, provided investment has been made in foreign exchange. 7: Zakat is collected as per law/rules, except on regular income certificates, Pension benefit account and Behbood savings certificates, which are totally exempt from Zakat at source. 8: In case of Defence savings certificates is collected only once at the time of actual encashment on the payable value (principal plus profit) as on the valuation date immediately preceding such encashment. 18 9: In case of special saving certificates and accounts , Zakat is collected only once on principal amount on the date of actual encashment/withdrawal. 10: Non-resident Pakistan can also invest in these schemes. 11: The investors have the facility of making nomination. 12: Regular income certificates and Bonds are totally exempt from tax. 13: There is no tax on profit which is get from one lack and fifty thousand (150,000) rupees except regular income certificates and Bonds. 14: Yet in case of more then one lack fifty thousand (150,000) rupees, there is a deduction of Tax at the rate of 10% on profit more over the amount which is invested before 30 ,June 2001 is totally exemp from the tax. 15: According to the rules, the amount is considered reinvest from the date maturity. If and there is no encashment after completing maturity. 16: In case of indifferent time investment, according to rules and regulations and rate of profit, the investment will complete its maturity. The above facilities are provided subject to the completion of formalities laid down under these rules. Procedure of Transfer of Certificate from One Center to Another: Sc-6 from is used for transfer from one center to another. When an investment is desires to transfer his/her certificate(s) from one centre to another, the following requirement will be fulfilled by the investors. 1. Application for transfer: (a) He/She shall personally present a written application on the prescribed form SC-6 in duplicate at the centre where the investment is originally being maintained along with the certificate(s). (b) Application for transfer of certificates(s) may also be presented in duplicate along with the certificates(s), at the center where these are desired to be transferred, which shall be sent to the original center under registered post. (c) A stamp “Under Transfer” shall be affixed on the reverse of certificate(s) being transferred And on unused profit coupons of profit coupon book before sending to the center concerned. 2. Duplicate National Identity card copy for every registration (attested by incharge). 3. Original Certificate. 4. SC-6 in duplicate. 5. Profit coupon slip if issue. 6. For transfer of each registration of certificates, separate application shall be required to be presented. 7. In case of illiterate person: A person known to the officer concerned or to his/her satisfaction must attest his/her thumb impression on the application. 8. In case of Joint investment: ‘A’ or ‘B’, the application must be signed by both the investors. 9. In case of minor: The application should be signed by the person who has originally made the investment on minor’s behalf along with certificate that minor is alive are certificate are being transferred his /her behalf. The following steps be kept in view while examining the application for transfer of certificate(s) 1. The signature on SC-6 form should tally with those recorded on the originally application. 19 2. In case of illiterate person: A person other then the staff members Known to the centre incharge should be attested Thumb impression. 3. The certificate(s) desired to be transferred, are actually issued in the name of applicant(s) and not enchased, pledged, report lost, stolen, burnt or spoilt and that .no of applicant certificate(s) have been issued in view there of. 4. It shall be ensured that no audit observation in respect of the registration being transferred is Pending for rectification. 5. Serial Nos. of profit coupons book shall be cancelled and kept along with the paid profit coupons for the day. Transfer not allowed from one centers to another Transfer of certificate(s) shall be refused in the following cases: 1. within the city (local center). 2. Part of any one registration (local period). 3. Before the expiry of period of non-encashability. 4. within three moths of transfer from another centre. 5. Duplicate certificate(s) issued in? Of. 6. After the death of certificate holder. 7. In the absence of life certificate of minor fro his/her guardian. 8. The certificates of minor after he/she has attained majority until the operations are allowed to him. 9. Court restrictions. 10. Both the NSCs we located at the same station except with the prior permission of controlling officer. Note: All the transferred cases shall e attended on ‘Top Priority’ basis ensuring that no delay is occurred on the part of any one concerned with it and the whole processes shall be completed with in one month at the most. Transfer of certificate(s) from one person to another SC-4 is a form which is for transfer from one person to another 1: Subject to the fulfillment of provisions of rules both the transferred(s) and the transferee(s) Shall apply in person to the centre on form SC-4 dully filled in and complete along with certificate(s) and photo copies of NIC in his/her application. 2. After verifying by center in charge the application shall obtain the approval from, the Regional Directorate and otherwise the requested transfer. 3: The original certificate(s) shall be discharged under dated signatures of the transferee. 4. New certificate(s) issued in the name of transferee which shall bear the same date as of original certificate. 5. The un-used Profit Coupons of a Profit Coupon book issued, if any shall have to be Surrendered by original holder, cancelled & attached. 6. New Profit Coupon book issued to the transferee their serial numbers, and the office of issue of each. 7. Name and address of the applicant. 8. Face value of the certificates it is sought to transfer, their serial numbers, and the office of issue of each. 9. Name of person to whom transfer is proposed. 10. Relationship (if any with) the person to whom transfer is proposed. 11. The full circumstances, which necessitate the transfer 12. A fee of rupee one only will be payable on an application for transfer. Nomination In the case of purchase of certificate by individual or individual, whether adult or minor , holding 20 the certificate singly or jointly, nomination may be made by purchase(s) of certificate in the application form at the time of the purchase, specifying the amount, whether whole or in part receivable purchaser(s). A holder of a certificate may, at any make a nomination if he has not done so earlier or, by notice to the issuing Authority, varies or cancels his previous nomination. In case of more then one nomination they shall be presumed to hold equal shares if the same is not specified in the application for purchase of certificate(s). In case of more then one nomination, payment can be made to one of the nominees when the others have not lodged their claims. Certificate(s) purchase on behalf of minor Transactions there of on attaining maturity. When a minor holder of certificate attains maturity the person who purchased the certificate(s), on his/her behalf or the minor himself/herself attaining maturity shall be required to intimate the fact of his/her having attained maturity to the center on a plain paper along with following documents:1: An attested copy of NIC along with date of attain maturity. 2: Specimen signatures of minor duty attested certificate. 3: The original certificate. Ancillary Services Administration Section or Human Resource Management. Scheme Section. Treasury Section. Drawing and Disbursement Section. Publicity Section. The separate independent department of NATIONAL SAVINGS. Regional Accounts Office. 1 HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT/ ADMINISTRATION SECTION Human resource management is the great asset for any organization. This is off balance sheet precious asset. The personal of any organization are the pillars of the success of that organization. The importance of human resource management keeps important place in the financial institutions like banks and saving centers because these institutions requires great deal of expertise from its employees. National savings is the important financial institution under Govt. control. Due to its importance it requires high class personal. Under this topic. We will discuss the procedure of managing the Human Resources in National Savings. In details for the discussion of all aspect, we have classified this topic under following such headings: 1. EMPLOYEES STATUS. 2. EMPLOYEES DISCIPLINE. 3. PENALTIES. 4. EMPLOYEES LEAVES. 5. ALL FIELD EMPLOYEES SCALE. 6. DETAILS OF DIFFERENT CENTERS 21 7. RECRUITMENT. 8. RETIREMENT. 9. TRAINING. 10. INCENTIVES FOR MOTIVATION. Now all the topics will be discussed in brief but in comprehensive way. 1. Employee’s status. All these are civil servants. Civil servant act 1973, an Act to regulate the appointment of person do, and the terms and conditions of service of persons in the service of Pakistan. (All central Govt. employees) apply this act. 2. Employees Discipline. Conduct rules 1964, civil employees are bound to Govt. conduct rules. When any employ inefficient rule may be involve corruption. 3. Penalty. Two type of penalty: (1) Minor penalty. Censure mean, just tough warning With holding, for a specific period, promotion or increments otherwise ban for unfitness for promotion or financial advancement in accordance with rule or order training to a service or post. Stopped, for a specific period, at any efficiency bar in the time scale, otherwise than for unfitness, to cross such far. Recovery from pay of the whole or any part of any pecuniary loss cause to Govt. by negligence or break of orders. (2) Major penalty. Reduction to a lower post or time scale, or to a lower stage. Compulsory retirement Removal from service. (May be work other Govt. institutions). Dismissal from service. (Not work any Govt. institute). 4. Employee leaves. Calendar year 20 casually vacation every holiday can not be claimed as a matter of authority 7. Recruitment. Recruitment is very important step in the H.R management in the financial institutions like National saving. It requires a great deal of experience National saving was adopting two methods for recruitment of employees up to last year. How Recruitment Proceed. Gunman. Direct recruitment no promotion and qualification is primary pass. People who are related to retire Army, Police, and any security department prefer these persons. Driver Direct recruitment but driving license is necessary. Lower Division Clerk (L.D.C). Qualification is must be metric and typing speed is 25 per second. The maximum age of person 25 years .10% promotion quota for gunman and 90% direct recruitment. Upper Division Clerk (U.D.C). Qualification is must be necessary inter but typing is not necessary.50% promotion quota for 22 (L.D.C) and 50% direct recruitment. Deputy National savings officer. No recruitment, 100% promotion quota. National saving officer grade 16 50% quota of (D.N.S), and 50% direct recruitment, qualification is M.A Economics, statistics, commerce, (2nd division at least) through PSC (public service commission). 50% reserve for promotion and 50% direct recruitment through (PSC), the qualification is must be necessary M.A economics, statistics, commerce, (First division). Joint director 100% promotion quota. 8. Retirement When age of any of person is completed 60 years then this person is retire the job. But if any person wants a retirement before 60 years. If any person service is completed for 25 years they voluntarily retire they request the institution and easily get the retirement. During job a person may be serve ill/accident on the basis of medical ground they easily get the retirement (no age limit in this situation). If the Government service is completed for 10 years then the person avail all facilities .but if the Govt. service is not completed for 10 years than the person is not availing all facilities. We can calculate the pension by this formula. Pension = last pay down * length of the service *7/300 Length of service =date of joining years – date of retirement years. Then the answer is the gross profit. Pension =half the gross pension* 12* commutation factor. Suppose the gross pension is 9000 than we calculate the net pension Pension =4500* 12*18.3129 9. Training Training is the process of refinement of abilities of the employees. National savings uses two methods of training for its employees so that they can face the challenges of modern techniques. These methods are: (1) Initial training (2) Routine training (1) Initial Training This method of training is used for those employees who are directly recruited in the officer of national savings. So after selection, they are given training in the training center. National saving has training institute in Islamabad and a sub-training institute in Karachi. (2)Routine training This type of training is given to employed workers. Who are already working in national saving. National saving offers two kinds of this training: Training in Pakistan includes the training through regular courses, refresher courses that are of short term in nature in the training institute at Islamabad. The directorate of national savings also arranges training in aboard. It keeps membership of international savings operation of ISBI in Geneva. 10. Incentive for Motivation: No doubt, National Savings is the Govt. institution it has to adopt the financial rules and regulations of Govt. Regarding financial compensation But for the motivation of it employees, it is 23 giving following incentives to them along with the pay package. (1) Advance increments are given to the able workers. (2) Money rewards are also given due to the height of performance of worker. 2 TREASURY SECTION Function of National Savings, Treasury: To receive cash, Cheques and prize bonds from NSCs. To meet cash and prize bond requirement of NSCs. To collect private and Govt. Cheques from NSCs for clearance and deposit. To accept RAO Cheques for payment. To remit cash and Cheques for deposit /collection in to state bank of Pakistan To issue Govt. Cheques for drawing cash or for payment to third party. To keep stock of blank deposit/savings certificates. Safe custody of valuable documents or articles under the directions of joint director. 3 DRAWING & DISBURSEMENT SECTION DRAWING & DISBURSEMENT SECTION This section is working only in the Regional Directorate of National Savings, and is controlling all the centers of the concerned Regional as like in Bahawalpur region this section is controlling 22 centers and regional office. All payments, such as pay & allowances, T.A, etc. of the officers and staff in the National Savings Organization, including contingent expenditure are made by the Regional Accounts Officer through the respective Directorate in whose area the claim arises. This section sanctions the expanses of all the centers including regional offices. The ministry of finance gives funds to this section through “New Item Statement” on annual basis for the expenses of national savings , so this section distribute the funds to centers according to their performance. The expenses may be for the: Purchase of durable goods as like: Transport, Machinery and equipment Furniture and Fixtures and Others. Repairs and Maintenance of durable goods and work: Transport, Machinery and equipment Furniture and Fixtures and Others. Commodities and Services as like: Transport of goods (Freight cartage, coolly charges) P.O.L charges aero plane, Helicopter, staff cars, Motorcycle, etc.) Conveyance charges. Communication: Postage and Telegraph, Telephone and Trunk call, Telex and tele-printer Courier and pilot service. 24 Utilities: 1: Gas, Water, Electricity, Hot and- Cold water charges, Office Stationery, 2: Printing, Newspapers, Periodicals and books, Uniform and Liveries, Rent royalties, Rates and Taxes. 3: This section is also dealing with the pay bills of the employees of the national savings, various Allowance are calculated by this section for the employees of the national savings as like House Rent allowance, Conveyance allowance, Dearness allowance, washing allowance, Overtime allowance, Medical charges and Rest and Recreational allowance. In addition to these Allowance this section is also deducting various deductions as like Benevolent fund, General Provident Fund, Postal life insurance, income tax, Trade Tax, House building advance, Motor Cycle advance, House Rent etc 4: This section is dealing with expenses of the office and employees of this department. Now we are concerned with the proper way to give sanction for the bill of expenses to the employees and offices of this department. All this procedure is done through various sorts of forms as like T.R 30, T.R 16, T.R 31, T.R 22, T.R 25, T.R 20, and pension papers etc. Through these sorts of form this section is dealing with the expenses of the national savings. These forms have various heads of allowance and deductions of pay as like: T.R 20: This form is used to show the Traveling allowance of the Gazetted Officers. T.R 22: This is a pay bill for the Non-Gazetted employees; in this from the allowance and deductions are recorded. T.R 16: This is a pay boll of the Gazetted Officers, and shows all the allowance and deductions. T.R 31: In this form the expenses of the officers are recorded, the expenses are taken over by the form T.R 30. 4 PUBLICITY AND STOR SECTION PUBLICITY AND STORE SECTION: In the publicity of schemes agencies are involved, because national savings are not paying any reward to them. After the publicity schemes the paper owner send bill along with tear sheet to concerned advertising agency. The budget for advertisement is about 15 million, (Overall Publicity). Payment for publicity is made by cheque. Govt. Rate Govt. commercial Rates Govt. Rate for govt. institutions. for Banks. for private Banks. Electronic Media: PTV.PTV WORD, In NSC Govt. Rates are applicable. The add time in PTV is minimum 7 seconds. If in ordinary time (any time) the rate of the add (advertisement) of 7 second is approximately 45000. But in fixed time (prime time, or specific time) its rate is extra 200%. But in news time it is 400% extra. The rate of PTV World is comparatively less then PTV. 25 Procedure for Selection of Advertisement Agency: Procedures for selection of advertisement NSC do competition call. Than distribute the schemes to those agencies for preparing campaign. Then NSC has to select campaigns keeping in view various aspects. Short listing. Selection of advertising agency. Board of selecting agency. Fixing of date of final selection should call at least 10 agencies, than these campaigns will be exhibited, then director of each agency will explain its campaign for removing fraud, the title of the agency will be hidden on campaign. More than are agency can be selected. Transfer or sending to press paper. Minister (issue of appointment letter). APNS Budget verification (advertisement, printing charges, local publicity, press & media). Final approval from competent authority. Selection of newspaper. (Considering holidays). Issue of release order will send to press information department. Instructions, about the size of the add, wording page is also given. PID (press information department) will give a copy of its approval to NSC and other. PROCEDURE OF FOREIGN MEDIA: External publicity wing, we send our requirements, add, page. Size, color, length, impotence to external publicity wing (EPW). EPW observe and decide that either add should or not be placed in our media. (EPW) also check that weather we have NOC or not or weather we have bill or approval for pointing. 5 SCHEME SECTION National savings offers eight types of schemes. 1. Defence saving certificates. 2. Regular income certificate 3. Special saving certificates /accounts. 4. Savings Accounts. 5. Prize Bonds. 6. Bahbood Savings Certificates. 7. Pensioners Benefit Accounts. 8. Special Savings Accounts. The function of this department is to examine and audit the reports of the all stated schemes. It compiles the report of each scheme of every branch of the city. 26 1: Daily 2: Monthly 3: Annually Calculate and evaluate the incoming and outgoing cash of every scheme of every branch of the city. The separate independent department of NATIONAL SAVINGS. Regional Accounts Office Regional Accounts Office As the District accounts office of any district is performing its job for the passing of the bills of the Govt. offices, as like this the Ministry of Finance has decided to situate Accounts Offices in the National Savings for the convenient of the employees of this organization. So every bill or Cheque of this organization is send to Regional Accounts Office for Pre-audit. Drawing & Disbursement section send all types of bills as like employees pay, House Rent allowance, Medical allowance for pre-audit and clearance. So in short this office is performing the following functions. After departmentalization of accounts the claims of pay/allowance, payments of contingencies etc, are being honored/processed by Regional Accounts Offices attached with each Regional Directorate of National Savings in the manner: Main functions of RAO RAO’s established in 1978.and above separately submitted …RAO is just like cash. 1. All monthly expenditure statement is prepared by RAO. 2. All claims presented by Rdns (DDO) traveling allowance, contingencies. 3. All reconciliation with National Savings treasury. 4. Reimbursement of medical charges. 5. The RAO reconciles the amount authorized by him to be drawn from local National Savings Treasury on monthly basis 6. The remittances into and withdrawal from Government Accounts are consolidation by the National Savings Treasuries under the administrative control of each Directorate. 7. Every Treasury and every National Savings Center has to submit their accounts to the respective Regional Directorate of National Savings where the same are consolidated and Submitted to the respective regional accounts office, where the same are further consolidated by inserting the figures of expenditure and then submitted to the Accounts General concerned. 8. All service record of officers is maintained at Regional Accounts office and provident fund Accounts (except of Grade 1-2) are maintained and pension cases are processed by him in respect of all officers and staff. National Savings Centre In Bahawalpur Region. Administration section. NONE Scheme section. Mr. Iftakhar NAQVI Treasury section. Mrs. Ayesha Safdar Drawing and Disbursement. Mr. Muhammad Akram Publicity and store section. None Regional Account Officer Mr. Abdul Bari 27 Financial Intermediaries Financial intermediaries play vital role in the economy. They fall into three categories 1: Depository Institutions 2: Contractual saving Institutions 3: Investment Intermediaries. NSO fall into the third category of Investment Intermediaries.. Investment Intermediaries is further divided into 3 types 1: Finance companies 2: Mutual funds 3: Money market mutual funds NSO fall into (Money market mutual fund). These Investment intermediaries raise funds by selling financial instruments to individuals. These institutions acquire funds by selling deposit type accounts. The interest on these accounts is then paid to the account holders External Analysis The External Analysis examines opportunities and threats that exist in the environment. Both opportunities and threats exist independently of the organization. The way to differentiate between a strength or weakness from an opportunity or threat is to ask: Would this issue exist if the company did not exist? If the answer is yes, it should be considered external to the firm. Opportunities refer to favorable conditions in the environment that could produce rewards for the organization if acted upon properly. That is, opportunities are situations that exist but must be acted on if the firm is to benefit from them. Threats refer to conditions or barriers that may prevent the firms from reaching its objectives. The following area analyses are used to look at all external factors effecting the organization: Customer analysis Segments: There are two major segments of customers 1: Lenders(investors) 2: Borrowers(investors) National savings is a NON Banking Bank and it don’t facilitate the both categories of the customers its only concern lie in the Investors. Thus we will focus only on the investors. These customers are divided into 4 major segments 1. 2. 3. 4. Senior citizens Retired Employees Widows Other Investors All above mentioned segments of employees are focused by the NSO as well as by other financial institutions. Pensioners are supposed to hold large amount of money as compare to other investors and they need a constant income for their future life thus all financial institutions try to attract, facilitate and retain these potential customers. The senior citizens and widows are also supposed to be back upped by constant and reasonable amount of income thus they are also focused in the same manner as the pensioners. All other potential investors who don’t lie in the above discussed categories are the ones who want to deposit and grow their savings. They don’t need any constant income but, they expect return on their investments. They constitute a large number of investors. In the future these customers are supposed to convert in to the other 3 discussed categories. Competitive analysis Identification: The competitors of NSO are all those financial institutions that offer the investment schemes to the potential and current investors. These competitors include all the Banks in Pakistan. Money markets (e.g. Stock exchange). 28 strategic groups Image, objectives, Strategies, Culture, Cost structure, Strengths, Weakness There are basically three strategic groups that are effecting the potential investments of NSO. They are Stock exchanges Money Changers Banks Performance Evaluation 1: Stock Exchanges In stock exchanges the investors lend money to the different corporations and purchase the shares of the corporations. They earn profit in the form of 1: Dividends 2: Increased Market value of shares. But risk factor is also involved in this type of investment. As the market value of shares can be decreased due to certain reasons. And the company may or may not declare the dividends. Thus investments in this sector are highly risky. In addition to all these risks investors have to bear the service charges. 2: Money Changers: There is a group of investors who earns through the change in the currency exchange rates. These investors on their personal judgment predict the increase or decreased in the currency rates and invest to increase the amount of their investments. This type of investment is also risky because the situation can be reversed due to certain uncertain reasons. 3: Banks: These financial institutes offer the fixed return on the investments. The risk factor is low because the original investments are secure and additional markup is paid on the original invested amount. As compare to the above two financial strategic groups this group offers relatively low amount of return. The banks cannot offer the return rates on their own will. The rates offered by banks are regulated and fixed by the State Bank Of Pakistan. Market Analysis Important and potentially important markets: NSO is operating only within the country premises; If it broadens its operations overseas it would earn higher investments. So whole world is its potential market. Cost Structure What are the major cost and value-added components for various types of competitors? Competitors are regulated by State Bank Of Pakistan. Being a Govt. body it is supported by highest interest rates. Still a large number of customers believe in the superior value added services provided by competitors and they pay additional service charges for availing those services. These additional service charges are earnings of the competitors. One of the most important fact is that NSO don’t conduct service charges from its customers (e.g.: opening of new accounts, issuing check books, transfer of accounts) this is all because to invite more investments. But to provide these services in free NSO looses a large portion of its potential income. In other words it is the opportunity cost of the operations. Environmental Analysis An environmental analysis is the four dimension of the External Analysis. The interest is in environmental trends and events that have the potential to affect strategy. This analysis is divided into five areas: economic, technological, political-legal, sociocultural, and future. 29 1 Economic What economic trends might have an impact on business activity? (Interest rates, inflation, unemployment levels, energy availability, disposable income, etc) Analysis: The basic purpose of National Savings Organization is to motivate the Pakistanis towards savings. The profit rates are affected bcoz of inflation. The interest rates decrease due to inflation. When employment rate decreased interest rates are lowered to demotivate investments in banks. Intern investments in other businesses increases which decrease the unemployment. In recent years the interest rate is increased at a very less extent due to high inflation and unemployment. 2 Technological To what extent are existing technologies maturing? Analysis: Electronic Technologies: The existing technologies used by the NSO include Fax Telephone Computers Printers Infrared devices Security Alarm systems Among all above stated technologies Computers are currently (since 3 years) adopted. Well trained employees deal with computers. System is transforming from manual to computers. Different soft wares are been installed on hit and trial basis for experiment. A serious consideration is given to convert whole system on computers. Other technologies are well established and well adopted. What technological developments or trends are affecting or could affect our industry? ATM services adopted by competitors add an extraordinary utility for customers of savings account. NSO lacks this facility and in spite of its highest offered rates it faces turnover of customers (those customers who value ATM services). In the same manner Cr cards are also one of those technological facility that is responsible for turnover of customers. 3 Government What changes in regulation are possible? What will their impact be on our industry? Rules and regulations could be affected by incoming elections. The unstable political status plays a vital role in inflation. This would affect interest rates inversely. 30 Are there political or government stability risks? Yes definitely. There are 95% chances for elections. No one is sure about upcoming Governmental body 4 Sociocultural What are the current or emerging trends in lifestyle, fashions, and other components of culture? Life style is moving dynamically towards high technological adaptation. The one who adopt and upgrade its operating structure according to it would survive and the one who lack this adoption would definitely be a looser. demographic trends such as the market size of the population (growth rate, income, population shifts) are increasing tremendously this is a positive sign for potential investments and shows a great opportunity for the organization. What are there implications? NSO must adopt high technology in its operations like ATM, CR cards. It must broaden its operations and a special training must be given to employees to facilitate, motivate and retain its customers. Internal Analysis Understanding a business in depth is the goal of internal analysis. This analysis is based resources and capabilities of the organization. Resources A good starting point to identify company resources is to look at tangible, intangible and human resources. Tangible resources are the easiest to identify and evaluate: financial resources and physical assets are identifies and valued in the firm's financial statements. Intangible resources are largely invisible, but over time become more important to the firm than tangible assets because they can be a main source for a competitive advantage. Such intangible recourses include reputational assets (brands, image, etc.) and technological assets (proprietary technology and know-how). Human resources or human capital are the productive services human beings offer the firm in terms of their skills, knowledge, reasoning, and decision-making abilities. Tangible Resources 31 Findings: 1: Tangible Resources National Savings is a government's institution and it don’t conclude its financial statements by itself. It just maintain the General journals and ledgers to maintain the Dr & Cr ratings. Balance sheet, income statement are not provided to the functional units. The financial resources of the organization could'nt be measured because financial statements are not provided to non organizational members (internies). Intangible Resources Technological Findings: Simple manual data entry system exists currently. NSO has no technological edge over its competitors. Although different efforts are been made to transform the whole system on computer. Reputation Findings: 1: Product Reputation NSO is been working since 1873. Its current offered rates are higher than any other's. It is highly recognized throughout Pakistan. One of its reorganization is for the PENSIONERS BENEFITS ACCOUNT and BAHBOOD SAVINGS CERTIFICATES. Not much people know its schemes of RIC, SA, SSC. A very small number of people know that Prize bonds are NSO's financial products. They thought it as a product of State Bank Of Pakistan. 32 Once a customer invests with NSO; he develops a comprehensive understanding of its financial products and become its loyal customer. Because of its customer oriented investments. 2: Customers Reputation As compare to the other Financial Institutions (with low interest rates) employees are not provided with the entertainment allowances. So they cant entertain their customers. Most of potential customers rate this particular behavior with other financial institutions and prefer their dealings. Employees Reputation: Employees are very much concerned with their duties. They don’t give any particular attention for customer retention and customer loyalty. They show a good behavior generally but, don’t bother to maintain an excellent relationship with their customers. Human Resource Findings: Education: Senior employees are not highly educated. The senior employees are under Graduate. The currently employed employees are graduate and Masters. Professional Qualification and Training: The senior employees are well learned about the professional handling of the official matters. National savings uses two methods of training for its employees so that they can face the challenges of modern techniques. These methods are: (1) Initial training (2) Routine training (1) Initial Training This method of training is used for those employees who are directly recruited in the officer of national savings. So after selection, they are given training in the training center. National saving has training institute in Islamabad and a sub-training institute in Karachi. 33 (2)Routine training This type of training is given to employed workers. Who are already working in national saving. National saving offers two kinds of this training: Training in Pakistan includes the training through regular courses, refresher courses that are of short term in nature in the training institute at Islamabad. The directorate of national savings also arranges training in aboard. It keeps membership of international savings operation of ISBI in Geneva. Capabilities Resources are not productive on their own. The most productive tasks require that resources collaborate closely together within teams. The term organizational capabilities is used to refer to a firm's capacity for undertaking a particular productive activity. Our interest is not in capabilities per se, but in capabilities relative to other firms. To identify the firm's capabilities we will use the functional classification approach. A functional classification identifies organizational capabilities in relation to each of the principal functional areas. Findings: Strategic financial Control: The financial strategic control is maintained by the State Bank of Pakistan Through FISCAL POLICY AND Monitoring Policy. The profit rates are proficiently controlled and regulated by State Bank Of Pakistan. Financial Management: Inter Organizational financial management is controlled through Regional Accounts Office. the claims of pay/allowance, payments of contingencies etc, are being honored/processed by Regional Accounts Offices attached with each Regional Directorate of National Savings. Effectiveness in Motivating and Coordinating Business Units: The city centers are operated and coordinated by their respective Regional Directorates. Each regional directorate is controlled and coordinated by its respective zonal Directorate. All zonal directorates are managed and commanded by Central Directorate. 34 SOWT ANALYSIS Internship in a National Savings in quite different experience from my expectations. It is very difficult to analyze the performance or structure of National Savings or nay organization while worked in its small unit. Another problem is that information are not available, I can’t get the annual reports. In these circumstances it is very difficult to analyze but, I tried my best. STRENGTHS Security of Security of Investments National Savings organization is the Govt. owned organization that is why the Pakistan public trusts his organization and its schemes are secured. Due to this the deposits of the organization are in creasing day by day. Excellent Intra Organizational Employees relation The staff members are well equipped with the tool of personal relations Experienced And Energetic Employees Majority of the staff is experienced and energetic. Vast Network of Centers National Saving organization has the large network of centers. Schemes for All Income Levels National saving organization has so many schemes for the lower middle and higher Level income people of Pakistan. Highest Profits National Saving organization has paying more profit for different schemes as compare to its competitors. Favorable Working Environment The working environments of the branches are favorable for the working of staff. Friendly Attitude Generally the attitude of the employees is very good with the customers and with each other. WEAKNESSES lack new and modern technology The National Saving organization lack new and modern technology. The transactions in the regional offices as well as the branches are not computerized. Slow Development The organization is in high profits but it’s working in the manual form. Well the organization has admitted the need in this regard and has been developing computer department for this purpose. Poor Marketing There is no specific marketing department to develop general awareness about the schemes of organization. People invest in the other higher risked and low profitable schemes of other banks. If they are provided with proper guidance and awareness about the schemes of this Organization this organization would earn the highest investments. Unavailability of Financial Reports Financial Reports and magazines are not published for public and therefore its financial 35 analysis is not possible. OPPORTUNITIES Enhancement of NSC's In other countries There is need of rapid enhancement of NSC's branches especially in foreign countries. National saving centers do not exist out side the Country. So they are loosing market which will be effective source of revenue for government of Pakistan. Develop Efficient Computerized system The National Saving organization has the opportunity to computerize its branches and Regional offices. Thus all dealing of record would be more secure & efficient Create more customers and Employment Though National Savings organization has a vast network of branches all over the Pakistan but, Still there are a large number of cities that lack NSC's. Thus National Savings has an opportunity to introduce new and modern layout of branches and regional offices to attract the employees and Develop customers delight through ATM NSC should develop the ATM facility to enhance the customer's delight and feasibility THREATS World Bank pressure for cutting interest rates. Political changes and influences with the passage of time. Low salary officers are a threat for the organization, as they don’t give proper attention to their work. Illiterate customers don’t know how to deal with their certificates and accounts. Due to their unawareness they create great problems for org. and for themselves as well. Number of banks has enormously increased if proper attention would not be given the National savings would loose its unawared potential customers 36 SUGESTIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS Branch Environment In case of financial institution the branch environment plays a vital role. National savings center requires a lot of improvement in this respect. General cleanliness conditions are very bad. So there is need to take immediate action for the improvement of branch environment. Implementation of technology Now a day every organization has the opportunity to implement development in technology. So That to provide high quality products. It is a computer age. As all other financial institutions are computerized National savings centers must fill up this flaw. Training of the personnel Employees are most important asset of an organization. They must be provided with proper training to meet the changing needs of Business. National savings organization does not have such culture. An advertisement campaign must be run to educate the current and potential customers about the rates of its products and handling of accounts certificates Establishment in other countries There is need of rapid enhancement of NSCs branches especially in foreign countries. National saving centers do not exist out side the Country. So they are loosing market which will be effective source of revenue for government of Pakistan. Promotion of Schemes National saving centre is working in high competitive environment. So promotion of schemes can be a very important strategy to take competitive advantage. So a full fledged promotional program .should be launched to create awareness about the schemes of national savings organization. 37 REFERENCES: o www.savings.org.pk o www.nationalsavings.org.pk o www.mystrategicplan.com o Anwer Bhatti ( September 13, 2007) Assistant Director, Regional Office NSO, Bahawalpur o Tariq Mahmood (August'2007) Branch Manager, National Saving Center II Bahawalpur o Ghulam Murtaza Syal (August '2007) Cashier , National Savings Center II Bahawalpur o o o o Rana Sb (August '2007) Operational Manager, National Savings Center II Bahawalpur Usman Sb (August '2007) Account Officer, National Savings Center II Bahawalpur Noreen (August '2007) Account Officer, National Savings Center II Bahawalpur Fredric S. Mishkin (2006) Financial Markets + institutions 5th edition 38 APPENDIXES A: Detail of different centers of BWP region B: Restricted Account of NSO (Mahana Amdani Account) 39 Appendices: Details of Different Centers of Bahawalpur Region: Total centers =20 Nsc 1 Nsc 2 Nsc 3 Nsc 4 Nsc 5 Nsc 6 Nsc 7 Nsc 8 Nsc 9 Nsc 10 Nsc 11 Nsc 12 Nsc 13 Nsc 14 Nsc 15 Nsc 16 Nsc 17 Nsc 18 Nsc 19 Nsc 20 D I G chock Bahawalpur welcome gate railway road Bahawalpur model town Bahawalpur Commercial Area Bahawalpur Ahmed-pur(east) liquat pur. khanpur Rhaimyar-khan Sadiqabad. Yazman. lodhran kahroadpaka Malsee kharpur tamawali Hasil pur Chishtian Bahawalnagar Minchanabad Haroonabad Fortabas Restricted Scheme Of NSc Mahana Amdani Account: This Scheme is entertaining the existing account holders but is not opening new accounts. Monthly deposits from Rs. 500, to Rs. 5000, in this account for continuous 84 months entitle the investor to receive an amount which is equal to his monthly deposit every month , after the completion of 84 months, until the account is closed. A missing installment can be deposited within 6 months of the month to which the installment relates with a surcharge at the rate of two rupees per hundred per month. Only one account may be opened in the name of any one person either singly or jointly with another person. Every Rs.100 becomes Profit/return not exceeding Rs.1000 is exempt from deduction of tax at source. (2) Period of receiving deposits Monthly deposit in an account under these rules shall beas under: (a) on the accounts opened before 01-07-2000. (For period of five years). (b) on the accounts opened on or after 01-07-2000. (For a period of 6 years. (3) Operation account The account may be opened only in the National Savings Center. Eligibility. The account may be opened by 40 (i) a single adult ; or (ii) two adults in their joint name,--(a) Payable to the holders jointly or to either of them with the consent of the other, or (b) Payable to either; (III) father or mother or legal guardian on behalf of a minor or minors. One account only,-Only one account may be opened in the name of one person either singly or jointly with another person. Father or mother or legal guardian may, however, open an additional account on behalf of a minor. Deposit in multiple--1. The account may be opened with a minimum monthly installment of five hundred rupees. 2. The amount of monthly installment may be increased in multiples of one hundred rupees, but the installment less than last installment shall not be placed. 3. The monthly installment shall not exceed five thousand rupees whether held by one person or by two person jointly. And for the purpose of calculating the individual installments when two persons are joint account holders, one half of the joint installment shall be assumed to belong to each. 4. An account holder hall, under no circumstances, exceed the monthly maximum permissible limit of instalment Monthly installment:1. Only one installment may be received in an account for a month. 2. Any installment received in the first fortnight of the month may be reckoned to have been received on the 1st month and an installment received in he second fortnight of the month may be reckoned to have been received on the 16th of the month. (3). advance installments for any period may also be received provided the is talment for each month does not exceed five thousand rupees:Provided that such deposit shall be reckoned to have been received on the Its of the month to which it rates (4) Month to which the instalment related with a surcharge at the rate of two rupees per hundred per month, and such deposit shall be reckoned to have been made on the 16 the of the month to which the instalment related (5) The profit earned under these rules shall be subject to tax as per rules. (6)Closure of Account,(1) The account shall be considered as closed if . (i) withdrawal from the account is made within a period of six years; or (ii) monthly instalments are not deposited consecutively for six months ;or (iii) all the deposits are withdraw after 6 years of the 41 opening of an account, but the withdrawal of one or more deposits shall not close the account. (2) Omitted. (11) Automatic re-investment— 1. The monthly instalment in an account on completion of each 6 years shall be deemed to have been re-invest for another period of 6 years. 2. Disbursement of profit as monthly income shall commence on the completion of 6 years of each deposit and shall continue so long as account is not closed. (12) How to open an account.: 1. Any person wishing to open an account should apply to any National Savings Center, here in after to as the Center, in the Application form. 2. Application need not necessarily be made in person, but the applicant sign the application and stat his or her name, father’s or husband’s name, complete address and occupation. 3.The applicant shall also affix his or her signature on the specimensignature card. 4. If the account is desired to be opened through a bank, the Bank Manager would attest the signature of the depositor, or his or her Thumb-impression of the depositor is unable to write, or if the Accounts desire to be opened through an agent shall attest the Signature or thumbimpression of the applicant before the Center-in-Charge where the account is desired to be opened.