CHNOPS
advertisement

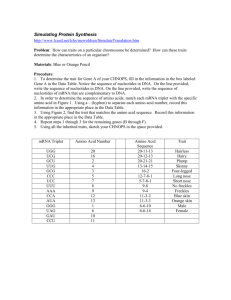
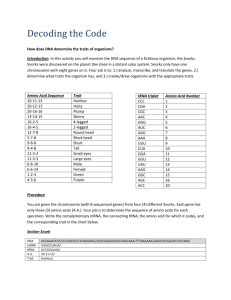
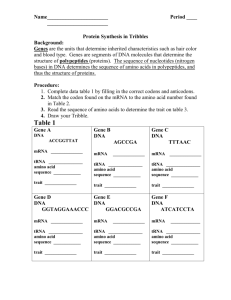
CHNOPS 1 Simulating Protein Synthesis A CHNOP is a fictitious organism that only has one chromosome. On this chromosomes are 8 different genes. Each box represents one gene. All the boxes represent one chromosome. For each gene transcribe the DNA into mRNA. Then translate the mRNA into a protein. For this activity each protein is being represented by a numeric sequence. Certain sequences tell you what trait to give your CHNOP (example—one box (gene) makes a protein that controls skin color) DNA ACC GGT TAT DNA AGC TTT DNA TTT AAC mRNA: _________________________ mRNA: _________________________ mRNA: ________________________ amino acid sequence: __________________________________ __________________________________ amino acid sequence: _______________________________ _______________________________ amino acid sequence: ______________________________ ______________________________ trait: _____________________________ trait: ___________________________ trait: ___________________________ DNA DNA DNA GGA CGC CGA GGG AGG AAA CCC ACC GAA GAA mRNA: _________________________ mRNA: _________________________ mRNA: ________________________ amino acid sequence: ________________________________ ________________________________ amino acid sequence: ________________________________ ________________________________ amino acid sequence: _______________________________ _______________________________ trait: _____________________________ trait: ___________________________ trait: ___________________________ DNA DNA GGG CGA ACC GGA CCC AGG AGC mRNA: _________________________ mRNA: ________________________ amino acid sequence: __________________________________ __________________________________ amino acid sequence: ______________________________ ______________________________ trait: ___________________________ trait: ___________________________ Draw your CHNOP on a sheet of white paper CHNOPS 1. Explain the difference between translation and transcription. 2. Where is the specific site for transcription? 3. Where is the specific site for translation? 4. Suppose you knew the order of amino acids in a protein. How would you determine the order of the DNA for that protein? 5. How could a change in one nitrogen base alter a protein? CLASS SET AMINO ACID CHART Amino Acid Sequence Tryptophan-ProlineIsoleucine Tryptophan-ProlineHistidine Tryptophan-LeucineLeucine Isoleucine-ArginineThreonine Serine-Lysine Aspartic Acid-Serine Proline-SerinePhenylalanine-Glycine Proline-Valine-TyrosineGylcine Lysine-Phenylalanine Lysine-Leucine Glycine-Phenylalanine Cytesine-Stop Proline-AlanineAlanine Proline-Serine-Serine Proline-Alanine-Lysine Proline-ArginineArginine Tyrosine-TyrosineAspartic Acid Tyrosine-TyrosineHistidine Proline-AlanineTryptophan-Proline Proline-Leucine-SerineProline Proline-AlanineLeucine-Proline Glycine-Serine-Serine Glycine-AlanineAspartic Acid Glycine-Serine-Alanine Trait Hairless Hairy Plump Skinny Four-legged Six-legged Long nose Short nose No freckles Freckles Dimples Birthmark Blue skin Orange skin Green skin Purple skin Male Female One tooth Three teeth Lots of teeth Bushy monobrow Thin eyebrow No eyebrows