Supplementary Materials and Methods. (doc 36K)
advertisement

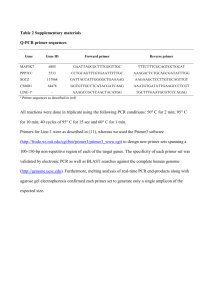
Wicke et al. Gene Therapy of Mpl deficiency Supplementary material and methods Murine bone marrow transplantation model Lin- cells were isolated from complete BM by magnetic cell sorting using MACS lineage cell depletion (Miltenyi Biotec GmbH, Bergisch Gladbach, Germany). The lineage negative cell population was then prestimulated for two days in StemSpan medium (Stem Cell Technologies, France), containing 50 ng/mL mSCF, 100 ng/mL hFlt-3 ligand, 100 ng/mL hIL11, 20 ng/mL mIL-3, penicillin/streptomycin and 2 mM glutamine. Lin- cells were transduced on two following days (day 3 and 4) using plates coated with Retronectin (TaKaRa, Otsu, Japan) and vector. For preparation of plates, the surface of the wells was coated with 10 ng/cm2 Retronectin and virus loaded by centrifugation of viral supernatants at 1000 g for 30 min at 4° C. Virus preloading was repeated up to two times. Transgene expression was measured on day five just prior to transplantation. 5 - 10 x 105 cells were transplanted into lethally (10 Gy) irradiated mice. Mouse analysis PB was collected periodically from the retro-orbital cavity using EDTA-coated glass capillary tubes and analyzed by automated complete differential blood cell counts (Scil ABC Vet Blood Counter, ABX Diagnostics, France). Mice were sacrificed when symptomatic and macroscopically examined for pathological abnormalities. Enlarged organs were weighed. A panel of tissues was collected, fixed in 4% formalin, and paraffin-embedded for histological examinations. Cells from BM, spleen and PB were subjected to flow cytometry (Becton Dickinson, Heidelberg, Germany) and analyzed with CellQuest, FlowJo and Diva software. After RBC lysis, cells were stained with lineage-specific antibodies against Gr1, CD11b, TER119, CD71, CD19, CD3, Sca1, ckit or HA-Tag (BD Bioscience, Heidelberg, Germany; eBioscience, San Diego, CA, USA; Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany). Antibodies were usually directly linked to FITC, PE, APC, PerCP-Cy5.5 or PE-Cy7 fluorochromes. Dead cells were excluded by propidium iodide (PI) or 4',6-Diamidino-2- phenylindoldihydrochlorid (DAPI) staining. Leukocyte morphology was evaluated in Giemsa stained PB smears and cytospins of BM and spleen cells. The LSK cell fraction was analysed in total BM cells that were flushed form both hind limbs. The lineage negative fraction was determined by staining for the lineage markers CD11b, Gr1, CD19, CD3 and Ter119 and the Sca1/ckit double positive cell fraction within the lineage marker negative cells was detected. Western Blot Analysis 1 Wicke et al. Gene Therapy of Mpl deficiency 2 32D cells were transduced with retroviral vectors and expanded to achieve suitable cell numbers. Cells were then starved overnight without IL-3 and 0.5% BSA and stimulated with different cytokines (w/o, IL-3, Thpo) for 10 min on the following day. Cells were collected directly after stimulation and lysed in lysis buffer containing phosphatase inhibitors (50 mM HEPES, 150 mM NaCl, 50 mM NaF, 10 mM Na4P2O7, 10% Glycerin, 1% NP-40). Protein concentration was measured by Bradford Assay (BioRad, Munich, Germany) and 10-20 µg of protein samples were separated by electrophoresis. Nitrocellulose membrane was blocked in 5% milk and incubated with one of the following antibodies: phos-ERK and phos-AKT. For loading controls, blots were stripped and reprobed using anti-ERK and anti-AKT antibodies (Cell Signaling Technologies, Boston, USA) as appropriate. Vector copy number and mRNA expression levels wPRE specific primers forward 5’-GAGGAGTTGTGGCCCGTTGT-3’ and reverse 5’TGACAGGTGGTGGCAATGCC-3’ and flk1 intron enhancer (AF061804, bases 352-459), forward 5'-GGTTTCAATGTCCCGTATCCTT-3' and reverse 5'-CTTTGCCCCAGTCCCAGT TA-3' were used. For the quantification of mRNA expression of the genes Sfpi-1 (Cat. No. QT00098077) and Fli-1 (Cat. No. QT00153559) mRNA was prepared from splenocytes and translated into cDNA which was used for quantitative analysis using primers of Qiagen (Hilden, Germany). LM-PCR LM-PCR was performed as described 1. DNA (100-500 ng) was digested with 2.5 U Tsp509I (New England BioLabs, UK). Primer extension was performed using 0.25 pmol biotinylated primer LTR-1 5’-TGCGGTGACCATCTGTTCTTGGCCCCG-3’. The first PCR (95°C for 5 min; 95°C for 1 min, 55°C for 30 sec, 68°C for 2 min for 30 cycles; 68°C for 10 min) was performed using Extensor Hi-Fidelity PCR Master Mix (ABgene, Hamburg, Germany) and primers: LTR-2 primer 5’-GACCTTGATCTGAACTTCTC-3’ and linker primer-1 5’- GACCCGGGAGATCTGAATTCG-3’. The nested PCR was performed under identical conditions: LTR-3 primer 5’-TCCATGCCTTGCAAAATGGCG-3’ and linker primer-2 5’AGTGGCACAGCAGTTAGGACG-3’. PCR products were isolated by gel electrophoresis, purified using QIA quick Gel Extraction Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) and sequenced after subcloning into TA cloning vector (Invitrogen, Karlsruhe, Germany). Recovered sequences were screened using the NCBI mouse genome database (NCBI37, accessed February 2009). Gene classification followed database records and PubMed literature. In vitro colony-forming assays (CFU) Wicke et al. Gene Therapy of Mpl deficiency Myeloid colony forming assays were performed in methylcellulose-based medium containing 3 U/mL erythropoietin, 10 ng/mL IL-3, 10 ng/mL IL-6, and 50 ng/mL SCF per manufacturer’s protocols (M3434, StemCell Technologies, France). BM cells from CMPD mice were plated at 2.5 x 105 cells per dish, in duplicates. Plates were incubated at 37 °C for seven days and colonies counted. Histopathological evaluation All necropsies were fixed in buffered methanol-formol (BM) or formalin solution (specimens from the other organs) for at least 24 hours and embedded in paraffin (WAX) after decalcification of the BM specimens by ethylene-diamine tetra-acetic acid. From all necropsies, 3 µm thick sections were cut and stained with Hematoxylin-Eosin (HE), Giemsa, PAS, Prussion blue and Gomori silver impregnation. Micrographs were taken with Olympus Microscope BX51TF (Olympus, Japan). Referrences 1. Schmidt, M., Hoffmann, G., Wissler, M., Lemke, N., Mussig, A., Glimm, H., et al. (2001). Detection and direct genomic sequencing of multiple rare unknown flanking DNA in highly complex samples. Hum Gene Ther 12: 743-749. 3