Click here for details of programme
advertisement

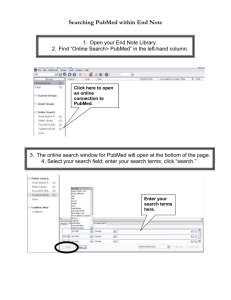
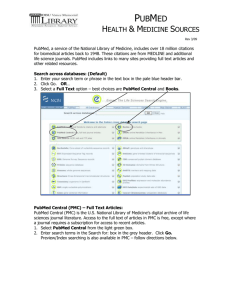
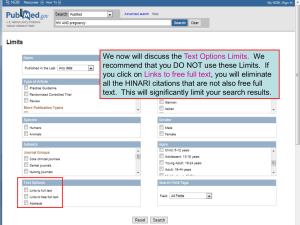
Workshop on NCBI, Pubmed & other open source software 11 – 13 April 2016 Draft vs 160104 Introduction The National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) is used daily by most life scientists, to search for literature, align nucleotides or proteins sequences, or obtain detailed information on specific nucleotides and proteins. This short course will cover these better-known-uses of NCBI with additional attention given to exploring other tools and databases aggregated at NCBI, as well as maximising the potential of the free-to-access Pubmed. The last day will be a bioinformatics course specifically aimed at bench scientists with little Bioinformatics experience. This part will focus on 'hacking' excel, which together with other free, easyto-use tools can be used to quickly interrogate 'omics' results across virtually any publicly accessible database. This course is organized by the Bioinformatics Dept. of the Erasmus MC and the Postgraduate School Molecular Medicine. Program The program features several short, concentrated presentations on various aspects of the data analysis, followed by interactive practical sessions behind the computers. Location: Duration: Participants: Dept. of Bioinformatics, computer room, Ee 15.28 (15th floor), Erasmus MC 9.30 – 16.30 (including lunch break and coffee breaks) Max. 18 participants Summary Day 1 and 2: NCBI: a bag of mixed lollies for life scientists. This part will start with an overview of NCBI and will cover as well: 1. GEO (Gene Expression Omnibus) - uploading data - downloading data (via GUI and BioConductor's geo2r() function) - NCBI analysis of GEO stored data 2. Sequence alignment (nucleotide and peptide) 3. Annotation (genes and proteins) Day 1 and 2: Systematic Literature Retrieval (in PubMed) The focus of these workshops will be on the systematicity of creating a search strategy, and not too much on PubMed. How do you know you did not miss important papers. PubMed is the most used database for medical literature searching, but many people use it suboptimal. PubMed is not a medical Google. We can teach you how to make PubMed a more valuable tool for day-to-day searches and the important searches for systematic reviews and theses, and while doing so can warn you about some hidden pitfalls of PubMed. 1 Day 3: Search and Integration strategies for gene and drug target information This workshop will detail how to select good keywords for searching gene and drug target information, and how to generate with minimum effort a simple data file to gain direct access to many gene information web sites for many genes. Detailed program Monday, 11 April 2016 NCBI, Pubmed Time Speakers Title Keywords 09.30–10.45 Andrew Stubbs NCBI: a bag of mixed lollies for life scientists 11.00–12.30 Andrew Stubbs Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO ) GEO; Sequence alignment; Annotation (genes and proteins), clinical variation, genome browser GEO practical 12.30–13.15 13.15–16.15 Lunch Wichor Bramer Systematic Literature Retrieval Pubmed Tuesday, 12 April 2016 NCBI, Pubmed Time Speakers Title Keywords 09.30–12.30 Wichor Bramer Systematic Literature Retrieval (cont.’d) NCBI: a bag of mixed lollies for life scientists (cont.’d) Pubmed Clinical variation resources Clinical variation resources Clinvar, dbSNP, dbGap, Genome view Practical: Clinvar, dbSNP, dbGap, Genome view Karl Brand, Justine Peeters, and Mario Pescatori 12.30–13.15 13.15–14.15 Lunch Andrew Stubbs 14.15–16.15 Andrew Stubbs, David van Zessen GEO; Sequence alignment; Annotation (genes and proteins) Wednesday, 13 April 2016 NCBI blast and other public domain software and applications Time Speakers Title Keywords 09.30–10.45 Jean-Marc Neefs 11.00–12.30 Blast (SRA blast), BLAT, others? Practical: Blast (SRA blast), BLAT, others? 12.30–13.15 13.15–14.15 14.15–16.15 Jean-Marc Neefs and Andrew Stubbs Lunch Jean-Marc Neefs Jean-Marc Neefs Sequence analysis strategies Sequence analysis strategies 16.15–16.30 Andrew Stubbs Information retrieval Integrative analysis and reporting – A programming free environment Course Summary Sources and pitfalls Practical: Integrative analysis No programming required Take home message 2 Attendance fees The subscription fee of non-commercial participants for the Course is € 500. Discounts are handled as followed: - PhD students get a discount of 50% and pay €250. - Only participants from the postgraduate school MolMed and members of the Bio Informatics Dept. get a discount of 100% and pay €0. - MGC members and master students from elsewhere get a discount of 50% and pay €250. Master students from elsewhere who pay the fee from their personal budget get a discount of 75% and pay €125. Invoices Fees can be paid upon an INVOICE. Shortly after your registration you will receive the INVOICE per mail. Payment per bank can be done on account: 43.47.01.408 / Erasmus MC, (IBAN code bank: NL86ANBA0434701408; SWIFT code bank: ABNANL2A), together with the number on your INVOICE. Late participants can also pay in cash upon signing in for the Course. Cancellations Our cancellation policy is that cancellation is possible up to one week before the start of the Course. Later cancellation will not be accepted, but you are allowed to send a substitute. 3