Nature20March2008Volume452Number7185pp253386 NMNAT_2
advertisement

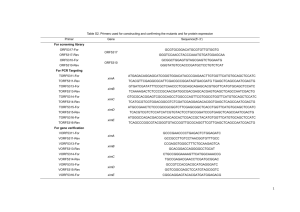
Nature20March2008Volume452Number7185pp253386 NMNAT_2 New Human Famsbase for New Human Famsbase for Nature 20 March 2008 Volume 452 Number 7185, pp253-386 NMNAT_2 wwwpdfamscomindexjahtml http://famshelp.gsc.riken.jp/famsbase/index.html http://www.pd-fams.com/index_ja.html Hideaki Umeyama, Ph.D., Professor School of Pharmacy, Kitasato University 5-9-1 Shirokane, Minato-ku, Tokyo 108-8641, Japan phone : +81-3-5791-6330 fax : +81-3-3446-9553 e-mail:umeyamah@pharm.kitasato-u.ac.jp 港区白金5-9-1 北里大学薬学部教授(理化学研究所客員主管研究員) 梅山秀明 http://famshelp.gsc.riken.jp/famsbase/index.html http://www.pd-fams.com/index_ja.html ENSEMBL Homo sapiens (human) hsap0 43797 - Metazoa Chordata ENSEMBL Homo sapiens (human) 137746 - Metazoa Chordata H-Invitational Homo sapiens (human) hsap1 hsap2 28983 - Metazoa Chordata NCBI Homo sapiens (cDNA) - Metazoa Chordata Kazusa huge0 2038 http://apr2007.archive.ensembl.org/Homo_sapiens/index.html http://www.h-invitational.jp/ http://hinv.ddbj.nig.ac.jp/index-j.html http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genome/guide/human/ http://www.kazusa.or.jp/huge/ New Human Famsbase for Nature 20 March 2008 Volume 452 Number 7185, pp253-386 NMNAT Nature 20 March 2008 Volume 452 Number 7185, pp253-386 NMNAT Translational control of the innate immune response through IRF-7 p323 Production of type-I interferon is regulated by the transcription factor IRF-7. This paper shows that IRF 7 is negatively regulated by translational repressor proteins 4E BP1 and 4E BP2. Viral infection promotes mTOR-mediated phosphorylation of the repressor proteins and allows type I interferon production to proceed. Rodney Colina et al. doi:10.1038/nature06730 First paragraph | Full Text | PDF See also: Editor's summary Abstract Article Nature 452, 323-328 (20 March 2008) | doi:10.1038/nature06730; Received 28 November 2007; Accepted 25 January 2008; Published online 13 February 2008 IRF-7 を介した自然免疫応答の翻訳による制御 . (Title in English; ).Rodney Colina1,4, Mauro Costa-Mattioli1,4, Ryan J. O. Dowling1, Maritza Jaramillo1, Lee-Hwa Tai2, Caroline J. Breitbach3, Yvan Martineau1, Ola Larsson1, Liwei Rong1, Yuri V. Svitkin1, Andrew P. Makrigiannis2, John C. Bell3 & Nahum Sonenberg1 Department of Biochemistry and McGill Cancer Center, McGill University, Montreal, Quebec H3G 1Y6, Canada Institut de Recherches Cliniques de Montréal, Laboratory of Molecular Immunology, Université de Montréal, Montréal, Quebec H2W 1R7, Canada Ottawa Health Research Institute, Ottawa, Ontario K1H 8L6, Canada These authors contributed equally to this work. Correspondence to: Mauro Costa-Mattioli1,4Nahum Sonenberg1 Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to N.S. (Email: nahum.sonenberg@mcgill.ca) or M.C.-M. (Email: mauro.costamattioli@mail.mcgill.ca). Top of pageAbstractI 型インターフェロン(インターフェロン(IFN)-αおよび IFN-β)のようなサイトカインの転写活性化は、抗ウイルス防御の最前線となってい る。本論文では、I 型 IFN の産生誘導に翻訳制御が重要であることを示す。翻訳リプレ ッサー4E-BP1 および 4E-BP2 を欠損するマウス胚性繊維芽細胞では、I 型 IFN 産生を引 き起こす閾値が低くなる。その結果、脳心筋炎ウイルス、水疱性口内炎ウイルス、イ ンフルエンザウイルス、およびシンドビスウイルスの複製が大幅に抑制される。また 、 4E-BP1 および 4E-BP2 (別名はそれぞれ Eif4ebp1 と Eif4ebp2 )遺伝子の両 方がノックアウトされたマウスは、水疱性口内炎ウイルス感染に耐性があり、この耐 性は形質細胞様樹状細胞での I 型 IFN 産生の亢進および肺での IFN によって制御される 遺伝子発現と相関している。 4E-BP1−/−4E-BP2−/− ダブルノックアウトマウスの胚 性繊維芽細胞での I 型 IFN 応答の亢進は、インターフェロン制御因子 7( Irf7 )メッ センジャーRNA 翻訳の上方制御によって引き起こされる。これらの知見は、4E-BP 群が I 型 IFN 産生の負の調節因子の役割をもち、 Irf7 mRNA の翻訳抑制を介して働くこと を明らかにしている。 Top of page 4E-BP1−/−4E-BP2−/− ダブルノックアウトマウスの胚性繊維芽細胞での I 型 IFN 応答の 亢進は、インターフェロン制御因子 7( Irf7 )メッセンジャーRNA 翻訳の上方制御 によって引き起こされる。これらの知見は、4E-BP 群が I 型 IFN 産生の負の調節因子の 役割をもち、 Irf7 mRNA の翻訳抑制を介して働くことを明らかにしている。 インターフェロン制御因子 7( Irf7 ) 4E-BP1 および 4E-BP2 (別名はそれぞれ Eif4ebp1 と Eif4ebp2 )遺伝子 4E-BP1 Eif4ebp1 3: Q13541 Reports BLink, Conserved Domains, Links Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E-binding protein 1 (4E-BP1) (eIF4E-binding protein 1) (Phosphorylated heat- and acid-stable protein regulated by insulin 1) (PHAS-I) gi|34921508|sp|Q13541.3|4EBP1_HUMAN[34921508] LOCUS Q13541 118 aa linear PRI 15-JAN-2008 DEFINITION Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E-binding protein 1 (4E-BP1) (eIF4E-binding protein 1) (Phosphorylated heat- and acid-stable protein regulated by insulin 1) (PHAS-I). ACCESSION Q13541 VERSION DBSOURCE Q13541.3 GI:34921508 swissprot: locus 4EBP1_HUMAN, accession Q13541; class: standard. extra accessions:Q6IBN3 created: Sep 19, 2003. sequence updated: Jan 23, 2007. annotation updated: Jan 15, 2008. COMMENT On or before Jan 24, 2006 this sequence version replaced gi:74721972, gi:1079483. [FUNCTION] Regulates eIF4E activity by preventing its assembly into the eIF4F complex. Mediates the regulation of protein translation by hormones, growth factors and other stimuli that signal through the MAP kinase pathway. [SUBUNIT] Nonphosphorylated EIF4EBP1 competes with EIF4G1/EIF4G3 to interact with EIF4E; insulin stimulated MAP-kinase (MAPK1 and MAPK3) phosphorylation of EIF4EBP1 causes dissociation of the complex allowing EIF4G1/EIF4G3 to bind and consequent initiation of translation. Rapamycin can attenuate insulin stimulation, mediated by FKBPs. [INTERACTION] P06730:EIF4E; NbExp=4; IntAct=EBI-74090, EBI-73440; O60573:EIF4E2; NbExp=1; IntAct=EBI-74090, EBI-398610; Q80ZJ3:Eif4e2 (xeno); NbExp=1; IntAct=EBI-74090, EBI-934970; Q9BSL1:UBADC1; NbExp=1; IntAct=EBI-74090, EBI-749370. [PTM] Phosphorylated on serine and threonine residues in response to insulin, EGF and PDGF. Phosphorylated upon DNA damage, probably by ATM or ATR. [SIMILARITY] Belongs to the eIF4E-binding protein family. FEATURES Location/Qualifiers source 1..118 /organism="Homo sapiens" /db_xref="taxon:9606" gene 1..118 /gene="EIF4EBP1" Protein 1..118 /gene="EIF4EBP1" /product="Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E-binding protein 1" >gi|34921508|sp|Q13541.3|4EBP1_HUMAN Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E-binding protein 1 (4E-BP1) (eIF4E-binding protein 1) (Phosphorylated heat- and acid-stable protein regulated by insulin 1) (PHAS-I) MSGGSSCSQTPSRAIPATRRVVLGDGVQLPPGDYSTTPGGTLFSTTPGGTRIIYDRKFLMECRNSPVTKT PPRDLPTIPGVTSPSSDEPPMEASQSHLRNSPEDKRAGGEESQFEMDI 4E-BP2 Eif4ebp2 Items 1 - 2 of 2 One page. 1: Q13542 Reports BLink, Conserved Domains, Links Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E-binding protein 2 (4E-BP2) (eIF4E-binding protein 2) gi|34921510|sp|Q13542.1|4EBP2_HUMAN[34921510] LOCUS Q13542 120 aa linear PRI 13-NOV-2007 DEFINITION Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E-binding protein 2 (4E-BP2) (eIF4E-binding protein 2). ACCESSION Q13542 VERSION Q13542.1 GI:34921510 DBSOURCE swissprot: locus 4EBP2_HUMAN, accession Q13542; COMMENT class: standard. created: Sep 19, 2003. sequence updated: Nov 1, 1996. annotation updated: Nov 13, 2007. On Mar 15, 2005 this sequence version replaced gi:2134670. [FUNCTION] Regulates eIF4E activity by preventing its assembly into the eIF4F complex. Mediates the regulation of protein translation by hormones, growth factors and other stimuli that signal through the MAP kinase pathway. [SUBUNIT] Nonphosphorylated EIF4EBP2 interacts with EIF4E. [INTERACTION] P06730:EIF4E; NbExp=1; IntAct=EBI-935137, EBI-73440; Q80ZJ3:Eif4e2 (xeno); NbExp=1; IntAct=EBI-935137, EBI-934970. [PTM] Phosphorylated on serine and threonine residues in response to insulin, EGF and PDGF. [SIMILARITY] Belongs to the eIF4E-binding protein family. FEATURES Location/Qualifiers source 1..120 /organism="Homo sapiens" /db_xref="taxon:9606" gene 1..120 /gene="EIF4EBP2" Protein 1..120 /gene="EIF4EBP2" /product="Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E-binding protein 2" >gi|34921510|sp|Q13542.1|4EBP2_HUMAN Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E-binding protein 2 (4E-BP2) (eIF4E-binding protein 2) MSSSAGSGHQPSQSRAIPTRTVAISDAAQLPHDYCTTPGGTLFSTTPGGTRIIYDRKFLLDRRNSPMAQT PPCHLPNIPGVTSPGTLIEDSKVEVNNLNNLNNHDRKHAVGDDAQFEMDI