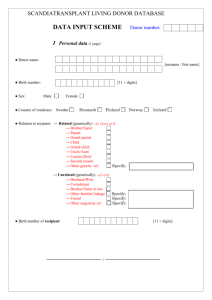
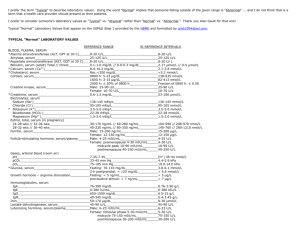
Dosud zdravý 28letý knihovník požil v sebevražedném úmyslu 30
advertisement

Course 6 Case 1 Kas 6-1E: Acute liver failure Hitherto healthy 28-year-old librarian ingested 30 tablets of paracetamol 500 mg each in a suicide attempt. He was found by relatives on the following day and immediately transferred to an intensive metabolic care unit. On admission the patient was mildly icteric, in deep coma without reaction to painful stimuli. He breathed irregularly at the rate of about 18 per minute, the heart rate fluctuated at about 120 per minute, his blood pressure was 105/70 mmHg and temperature 38,6 stC. The abdomen and extremities were normal on physical examination. Initial laboratory values: red blood count normal, leukocytes 28x109/l, thrombocytes 33x109/l, HBsAg negative, anti-HCV negative, creatinin 120 μmol/l, total bilirubin 87 μmol/l, conjugated 32 μmol/l, ALT higher than 40 μkat/l, AST 27,6 μkat/l, ALP 5,8 μkat/l, GMT 4,9 μkat/l, blood glucose level 2,8 mmol/l, serum minerals normal, amnonia 156 μmol/l, arterial blood pH 7,512, Pa02 10,6 kPa, PaCO2 4,84 kPa, HCO3- 27,5 mmol/l, base excess 4,5 mmol/l. Ethanol-gelification test positive, D-dimers markedly increased, prothrombin time 16,7 s (control 11,5 s), INR 2,23. In urine urobilinogen and bilirubin were found. Questions: 1. Why is the patient comatose? 2. Why is the patient hypoglycemic? 3. Why are breathing and heart action irregular? 4. Analyze the hemocoagulation disturbance 5. What is the mechanism of paracetamol toxicity? 6. Analyze blood pH abnormality 7. What treatment would you recommend? 8. What is the prognosis of the patient? 9. Morphology of toxic liver lesions 10. Liver necrosis