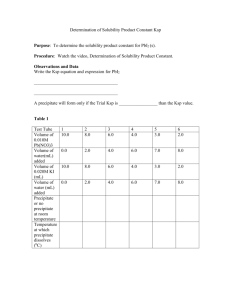
Solubility Product Constant:
advertisement

AP Chemistry Notes: Solubility Product (15.5-15.8) Solubility Product Constant: A special case of equilibrium involving dissolving. Solid Positive Ion + Negative Ion Mg(NO3)2(s) Mg2+(aq) + 2NO3-(aq) Keq = Ksp = Because the constant is a product of solubility, we call it the solubility product constant, Ksp Types • • • • of solubility product problems: Given Ksp, find solubility Given solubility, find Ksp Find solubility in a solution with a common ion Predicting precipitation Example: BaF2(S) Ba+2(aq) + 2F-(aq) Write out the equilibrium law expression… Some solubility generalizations: All ____________________________ are soluble All compounds of the ___________________________ are soluble (Li, Na, K, etc.) All compounds of the ammonium (__________) are soluble Example: Given Ksp, Find Solubility - What is the solubility of Silver Bromide (Ksp = 5.2 x 10-13) Example: Given Ksp, Find Solubility - What is the solubility of PbI2 (Ksp = 7.1 x 10-9) Example: Find Ksp Given Solubility - What is the Ksp of Boric Acid, given its solubility of 2.15 x 10-3 Moles/liter? AP Chemistry Notes: Solubility Product (15.5-15.8) Example: Solubility with a Common Ion - What is the solubility of lead iodide (PbI2) in a .15M solution of KI ? Example: Predicting Precipitation - A student mixes 0.010 mole Ca(NO3)2 in 2 liters of 0.10M Na2C03 solution. Will a precipitate form? Step 1: Write out the dissolving equations Step 2: Determine the most likely precipitate & write out it’s equation. Step 3: Determine the molar concentrations & calculate the reaction quotient (Q). In this case, reaction quotient (Q) is the product of the Ksp equation using the ion concentration before any reaction interaction. If Q > Ksp Then a precipitate will form. Example: Predicting Precipitation -.015 moles of AgNO3 is mixed with 5 liters of .02M NaCl solution. What is the most likely precipitate and will it form?