REFERENCE MODELS FOR COMPUTER NETWORKS
advertisement

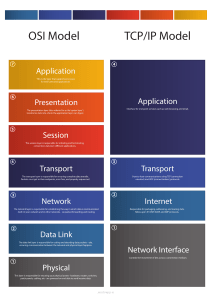
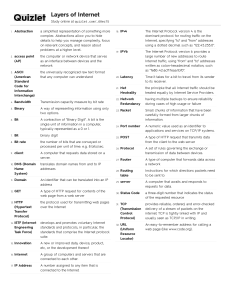
REFERENCE MODELS FOR COMPUTER NETWORKS Much of this material is taken from some developed by Ron Wyllys. Two major approaches: 1. The seven-layer OSI/ISO model – Open Systems Interconnection, currently maintained by the International Organization for Standards. 2. The five-layer TCP/IP model – Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol. OSI/ISO 1. Physical layer – controls electrical and mechanical aspects of data transmission, e.g., voltage levels, cable lengths, and so on. 2. Data-link layer – addresses the transmission of data frames (or packets) over a physical link between network entities, includes error correction. 3. Network layer – establishes paths for data between computers and determines switching among routes between computers, determines how to disaggregate messages into individual packets. 4. Transport layer – deals with data transfer between end systems and determines flow control. 5. Session layer – creates and manages sessions when one application process requests access to another applications process, e.g., MSWord importing a spread sheet from Excel. 6. Presentation layer – determines syntactic representation of data, e.g., agreement on character code like ASCII/Unicode. 7. Application layer – establishes interface between a user and a host computer, e.g., searching in a database application. TCP/IP 1. Physical layer – not really part of this model, since TCP and IP deal with software; usually thought to refer to all hardware beneath the network layer. 2. Network or data link layer – defined by whatever the Internet Protocol will run over, e.g., a token-ring network. 3. Internet or network layer – provides network addressing and routing, providing a common address space and connecting heterogeneous networks. IP runs here. 4. Transport layer – manages data-consistency by providing a reliable [two meanings!!] byte stream between nodes on a network. TCP and User Datagram Protocol (UDP) run here. 5. Process and applications layer – provides application services to users and programs.