Human Heredity and Evolution
advertisement

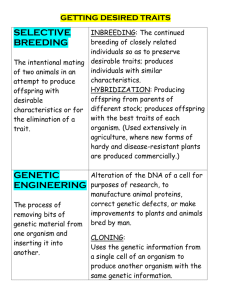
Human Heredity and Genetic Engineering Advances Farmington Public Schools Grade Level 8 Science Author(s) REVISION: 6/2007 Wenzel, Mirecki, Buckley, Wilbur Farmington Public Schools 1 Table of Contents Unit Summary ………………….….…………..page3 Stage One: Standards Stage One identifies the desired results of the unit including the broad understandings, the unit outcome statement and essential questions that focus the unit, and the necessary knowledge and skills. The Understanding by Design Handbook, 1999 …………………………….... pages 4 Stage Two: Assessment Package Stage Two determines the acceptable evidence that students have acquired the understandings, knowledge and skills identified in Stage One. ……………………………… page 9 Stage Three: Curriculum and Instruction Stage Three helps teachers plan learning experiences and instruction that aligns with Stage One and enables students to be successful in Stage two. Planning and lesson options are given, however teachers are encouraged to customize this stage to their own students, maintaining alignment with Stages One and Two. ………………..……………… page 11 Appendices ….....………………………. page 14 Author(s) REVISION: 6/2007 Wenzel, Mirecki, Buckley, Wilbur Farmington Public Schools 2 Unit Summary This 8-week unit for a heterogeneous class of eighth graders is part of a year-long life science course. It follows a unit on human body systems and precedes a unit on evolution and ecology. Chromosome theory, principles of genetics, patterns of inheritance and advances in genetic engineering are studied. The unit links back to cell division and lays groundwork for understanding the connection between genetics and natural selection of traits. The unit will include a three day review of CMT labs and practice constructed response questions just prior to the Science CMT. The unit also includes a grade 9-10 CAPT task concerning GM foods. Author(s) REVISION: 6/2007 Wenzel, Mirecki, Buckley, Wilbur Farmington Public Schools 3 Stage One: Standards Stage One identifies the desired results of the unit including the broad understandings, the unit outcome statement and essential questions that focus the unit, and the necessary knowledge and skills. The Understanding by Design Handbook, 1999 Science Essential Understandings and Content Standards #1-Scientific inquiry is an ongoing process building knowledge about events and phenomena The students will: 1.15-explain that scientists believe that the basic rules governing nature have been and are discovered by careful, systematic investigation 1.22-select appropriate format to communicate findings* #2-Science is a human endeavor which has lasting impact on civilization The students will: 2.14-describe the contributions made by various people and cultures to the advancement of science and technology, and explain their impact on civilization 2.16-recognize that scientists help people understand the likely causes and possible effects of matters of public concern 2.17-recongize the influence of societal factors (such as cultural values, human needs, resources) on the development of science and technology 2.18-identify current ethical issues involving the use of humans and other animals in scientific investigations Author(s) REVISION: 6/2007 Wenzel, Mirecki, Buckley, Wilbur Farmington Public Schools 4 #7-There is unity among the diverse types of life on Earth The student will: 7.15-describe … meiosis and [its] importance to organism growth and development 7.18-explain how diseases and other factors affect the health of life forms 7.19-apply the principles of genetics #9-Constancy, patterns, change and evolution permeate all systems The student will: 9.10-use patterns of change to make predictions and to solve practical problems State Frameworks Expected Performances: 8.2 - Reproduction is a characteristic of living systems and it is essential for the continuation of every species. The student will: C25 Explain the similarities and differences in cell division in somatic and germ cells. C27 Describe how genetic information is organized in genes on chromosomes, and explain sex determination in humans. 10.4. - In sexually reproducing organisms, each offspring contains a mix of characteristics inherited from both parents. The student will: D36 Explain how meiosis contributes to the genetic variability of organisms. D37 Use the Punnet Square technique to predict the distribution of traits in mono- and dihybrid crossings. D38 Deduce the probable mode of inheritance of traits (e.g., recessive/dominant, sex-linked) from pedigree diagrams showing phenotypes. D39 Describe the difference between genetic disorders and infectious diseases. Author(s) REVISION: 6/2007 Wenzel, Mirecki, Buckley, Wilbur Farmington Public Schools 5 Technology Standards #1 Information Accessing Standards – Information skill and strategies are necessary to effectively locate and use resources for solving problems, conducting research and pursuing personal interests. Students will demonstrate ability to extract and record information collected to meet their information needs.* Students will demonstrate ability to summarize and paraphrase important facts and details.* Student will recognize the need to analyze information based on timeliness, authority, reliability and relevance #4 Responsible Information Use – The responsibility student will demonstrate legal use of information resources, computers or other technologies, recognizing the attendant social, economic and ethical issues. Students will apply established MLA bibliographic standards for giving credit for information used. Author(s) REVISION: 6/2007 Wenzel, Mirecki, Buckley, Wilbur Farmington Public Schools 6 Unit Outcome Statement As a result of the unit on human heredity and genetic engineering, student will understand that traits are passed from parents to offspring in a predictable way. These traits are carried on genes, which make up chromosomes. Students will explore the current uses and potential future implication of genetic engineering. Essential Questions How is the scientific method used to gain knowledge about heredity? Why do I have the traits that I have? Does genetic engineering have more advantages or disadvantages? Author(s) REVISION: 6/2007 Wenzel, Mirecki, Buckley, Wilbur Farmington Public Schools 7 Knowledge and Skills The Knowledge and Skills section includes the key facts, concepts, principles, skills, and processes called for by the content standards and needed by students to reach desired understandings. The Understanding by Design Handbook, 1999 Knowledge Role of meiosis in chromosome segregation Chromosome Theory Development of the principles of modern genetics Patterns of inheritance in humans (including multiple alleles for blood types) Advances in genetic engineering such as GM foods, DNA fingerprinting, therapy, and selective breeding Skills/Processes Create and analyze a Punnett square for single alleles Create and analyze a Punnett square for multiple alleles Create and analyze a pedigree chart/case studies Evaluate the credibility of web based information Use web-based information to develop a web-based opinion(GM Foods labeling) Thinking Skills Sequencing events (meiosis) Making inferences (inheritance patterns) Identify pros and cons of GM foods Author(s) REVISION: 6/2007 Wenzel, Mirecki, Buckley, Wilbur Farmington Public Schools 8 Stage Two: Assessment Package Stage Two determines the acceptable evidence that students have acquired the understandings, knowledge and skills identified in Stage One. *Authentic Performance Task :Creature Feature Genetics Task (standards 1.22, 7.19, D37) Goal: Create a paper pet family with 2 parents and six offspring with five genetic traits to demonstrate the principles of genetics. Write an analysis of your findings. Role: You are tutoring a fellow eighth grade student in genetics. Audience: Eighth grade science student Situation: Review Punnett Squares You will be given traits for your P generation which you will copy onto your paper parents Use Punnett squares to determine possible outcomes for the offspring, the F1 generation Toss pennies to determine the actual genotypes of the six offspring of your parents Complete the related worksheets Create a poster or a 3-dimensional display showing the parents and six children Write a detailed analysis of your results Products and Performance Your Paper Pets Creature Feature Presentation should be complete and consist of a Family Portrait or 3-dimensional display showing the parents and six offspring along with their genotypes and phenotypes written out and the phenotypes drawn on one side of the pets. All of the traits should be neatly and correctly drawn and identified. The worksheets and Punnett squares have to be neatly and correctly completed. The word-processed analysis needs to: effectively explain the actual results compared to the expected results compare family members and explain their resemblance make connections among concepts and include sophisticated use of scientific terms Author(s) REVISION: 6/2007 Wenzel, Mirecki, Buckley, Wilbur Farmington Public Schools 9 Standards & Criteria for Success: WORKMANSHIP: 1. All required elements are complete plus additional student created items 2. The Family Portrait or other visual is exceptionally clear and relevant 3. The analysis is exceptionally clear and relevant ANALYSIS: 1. Completely accurate analysis and explanation of actual results from Punnett squares 2. Highly effective comparison and explanation of family resemblance 3. Ratios of genotypes and phenotypes of offspring have no errors (including sexlinked trait) CONTENT: 1. Parent phenotypes and genotypes of all traits are correctly identified and neatly drawn 2. Offspring phenotypes and genotypes of are complete and correct; including the sex-linked trait 3. Makes connections among concepts 4. Sophisticated use of science terms Tests, Quizzes, and Other Quick and Ongoing Checks for Understanding Principles of Genetics quiz (1.15, 2.14) Punnett Squares Quiz (7.19, 9.10, D37) Chromosome theory and DNA structure quiz (C27, D36) Meoisis quiz (7.15, C25) Unit test (7.18, 7.19, C25, D39) Projects, Prompts, etc. Penny for Your thoughts Lab(7.19, 9.10, D37) Pedigree case studies (1.22, 7.19, D38) GATTACA movie-ethical implication discussion questions (2.14, 2.17, 2.18) GM Foods internet research task-evidence-based opinion on mandatory labeling (2.14, 2.16, 2.18 and information literacy standards) *Bold face indicates required formative and summative assessments Author(s) REVISION: 6/2007 Wenzel, Mirecki, Buckley, Wilbur Farmington Public Schools 10 Stage Three: Learning Experiences and Instruction Stage Three helps teachers plan learning experiences and instruction that align with Stage One and enables students to be successful in Stage Two. Learning Experiences and Instruction Middle Grades : 8 The learning experiences and instruction described in this section provide teachers with one option for meeting the standards listed in Stage One. Teachers are encouraged to design their own learning experiences and instruction, tailored to the needs of their particular students. LEGEND: * = See APPENDIX for this document; RG = See Resource Guide Guiding Questions Lesson Topic: Instructional Strategies Check for Understanding Genetic Principles and Probability What are the key concepts in genetics? How can we predict the possible traits of offspring? Duration: 6 days HOOK: Lab Investigation: YOU ARE UNIQUE: Student pairs discover which traits are inherited (eye & hair color, tongue-rolling ability, colorblindness) and which are acquired. Punnett square exit card Prompt: How similar is Mendel’s work to the scientific method? Read 3-1 with organizer. Penny for Your Thoughts Lab Punnett square and principles quiz Notes: Mendel’s principles of Genetics (connect to prompt as the “findings” of his work) Read 3-2 and demonstrate punnett square construction and analysis statements Rehearsal: Punnett square practice problems, Sponge Bob Squarepants genetics, and Penny For Your Thoughts lab Author(s) REVISION: 6/2007 Wenzel, Mirecki, Buckley, Wilbur Farmington Public Schools 11 Guiding Questions Instructional Strategies Lesson Topic: The Cell and Inheritance What role do chromosomes play in inheritance? Why is DNA often called the “code of life”? How does DNA direct cells to make protein? Check for Understanding Duration: 7 days Students complete packet: Chromosomes and Inheritance (see Halina Mirecki) Alike and Different Chart Read 3.3 with organizer. Show online animations of meosis. Label meiosis diagram. DNA Model lab Cell Inheritance and DNA quiz Rehearsal: Alike and Different chart, Meiosis manipulatives, What are Chromosomes packet View Video: Assignment Discovery: Power of Genes (Library) Students brainstorm on what and why cells need to manufacture substances. Teacher delivers notes on protein synthesis. Show online animations. Students take notes on DNA structure and mutations, and complete related worksheets (Chapter 3.4 of textbook). DNA model lab Misconception Check: Baby Mice Probe [vol 2#17] Creature Feature Paper Pet Performance Assessment (show exemplar posters, review XX and XY for gender) Duration: 4 days Science CMT Preparation Duration: 3-4 days (use student work in CMT portfolios to review embedded tasks, complete and discuss practice constructed response questions) Author(s) REVISION: 6/2007 Wenzel, Mirecki, Buckley, Wilbur Farmington Public Schools 12 Lesson Topic: Human Heredity What is a multiple allele? What are sex-linked traits? Duration: 6 days Notes: Constructing and reading pedigree charts Case Studies: Pedigree Case Studies Read Section 4-1 Human Inheritance Notes- Sex linked traits Pedigree Case Studies of sex linked traits Lab : “Bloodless” Blood Type Lab Additional Punnett square problems with multiple alleles and sex-linked traits DI-challenge students with di-hybrid crosses Guiding Questions Instructional Strategies Check for Understanding Optional Lesson Topic: Genetic Diseases and Disorders Duration: 2 days (time permitting) How is an illness different from a genetic disorder? HOOK - Prompt: How is an illness different from a genetic disorder? Case Studies: Sickle Cell Anemia case study (RG) Case Studies: Sickle Cell Anemia case study (RG) Students take notes and complete related worksheets (Chapter 4.2 of textbook). Lesson Topic: Advances in Genetics What are three ways in which an organism’s traits be altered? What are the issues resulting from genetic engineering? Duration: 10 days Hook: What do you know about Dolly the cloned sheep? GM Food CAPT research Read 4.3 and take two-column notes Unit test View movie GATTACA with discussion question on ethics of genetic discrimination GM Foods magazine with note organizer Online DNA fingerprinting virtual lab and video clips from Secrets of the Sequence Give study guide for unit test GM Food CAPT research Author(s) REVISION: 6/2007 Wenzel, Mirecki, Buckley, Wilbur Farmington Public Schools 13 Appendices Resources Textbook: Prentice Hall: Science Explorer: Cells and Heredity Chapters 3 – 5 Resource Guide: Prentice Hall: Science Explorer: Cells and Heredity Video: Assignment Discovery: Power of Genes (part 1 & 2) Video: Assignment Discovery: Cloning Video: GATTACA www. Science-explorer.phschool.com This corresponds with the textbook. This website provides on-line review and extensions for topics covered. It also provides links for enrichment. See following pages for student work sheets Author(s) REVISION: 6/2007 Wenzel, Mirecki, Buckley, Wilbur Farmington Public Schools 14