midazolam, intranasal delivery
advertisement
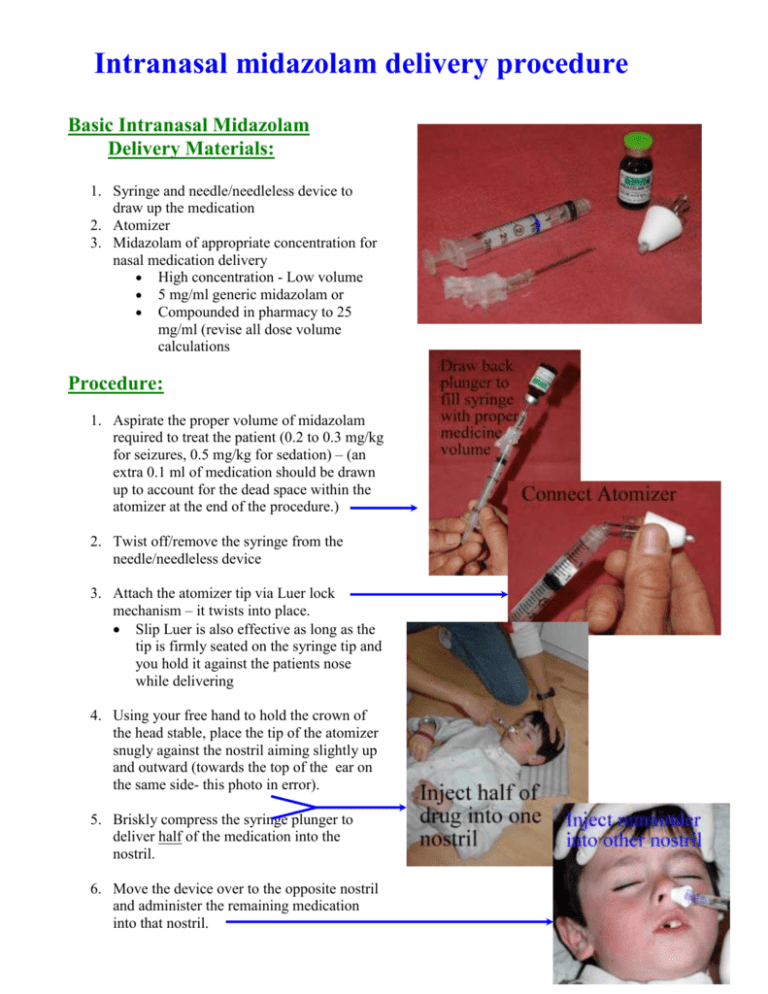
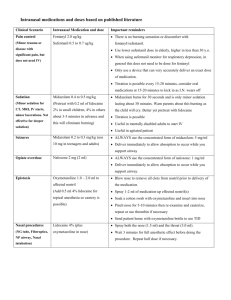
Intranasal midazolam delivery procedure Basic Intranasal Midazolam Delivery Materials: 1. Syringe and needle/needleless device to draw up the medication 2. Atomizer 3. Midazolam of appropriate concentration for nasal medication delivery High concentration - Low volume 5 mg/ml generic midazolam or Compounded in pharmacy to 25 mg/ml (revise all dose volume calculations Procedure: 1. Aspirate the proper volume of midazolam required to treat the patient (0.2 to 0.3 mg/kg for seizures, 0.5 mg/kg for sedation) – (an extra 0.1 ml of medication should be drawn up to account for the dead space within the atomizer at the end of the procedure.) 2. Twist off/remove the syringe from the needle/needleless device 3. Attach the atomizer tip via Luer lock mechanism – it twists into place. Slip Luer is also effective as long as the tip is firmly seated on the syringe tip and you hold it against the patients nose while delivering 4. Using your free hand to hold the crown of the head stable, place the tip of the atomizer snugly against the nostril aiming slightly up and outward (towards the top of the ear on the same side- this photo in error). 5. Briskly compress the syringe plunger to deliver half of the medication into the nostril. 6. Move the device over to the opposite nostril and administer the remaining medication into that nostril. Intranasal medications and doses based on published literature Clinical Scenario Intranasal Medication and Important reminders dose Pain control Sufentanil 0.5 to 0.7 ug/kg Always monitor for respiratory depression Fentanyl 2.0 ug/kg Use lower sufentanil dose in elderly Only use a device that can very accurately deliver an exact Diamorphine 0.1 mg/kg (in U.K.) Ketamine 0.5 to 1 mg/kg Sedation dose of medication. Titration is possible every 15 minutes, consider oral medications at 15-20 minutes to kick in as I.N. wears off Midazolam 0.5 mg/kg Always monitor for respiratory depression Sufentanil 1.0 to 1.5 ug/kg Combination therapy probably more effective than single drug therapy but greater respiratory risk so use less of each. Seizures Fentanyl 1.5 to 3.0 ug/kg Titration is possible Ketamine 10 mg/kg Midazolam burns for 30 seconds and is only minor sedation Dexmedetomidine 2-3 ug/kg Dexmed does not burn, onset is 20 min, lasts > 1 hour Midazolam 0.2 to 0.3 mg/kg ALWAYS use the concentrated form of midazolam: 5 mg/ml (use 10 mg in teenagers and Deliver immediately to allow absorption to occur while you adults) Opiate overdose Naloxone 2 mg (2 ml) support airway ALWAYS use the concentrated form of naloxone: 1 mg/ml Deliver immediately to allow absorption to occur while you support airway. Epistaxis Oxymetazoline 1.0 – 2.0 ml to affected nostril Blow nose to remove all clots from nostril prior to delivery of the medication. (Add lidocaine 4% if Spray 1-2 ml of medication up effected nostril(s) cautery to be done) Soak a cotton swab with oxymetazoline and insert into nose Pinch nose for 5-10 minutes then re-examine and cauterize, repeat or use thrombin if necessary Send patient home with oxymetazoline bottle to use TID Nasal procedures Lidocaine 4% (plus Spray both the nose (1.5 ml) and the throat (3.0 ml). (NG tube, Fiberoptics, oxymetazoline in nose) Wait 3 minutes for full anesthetic effect before doing the NP airway, Nasal intubation) procedure. Repeat half dose if necessary. General Comments: Prior to using a nasal medication, inspect the nostril for significant amounts of blood or mucous discharge. Presence of these will limit medication absorption. Suctioning the nasal passage prior to delivery and/or alternated delivery options should be considered. Always deliver half the medication dose up each nostril. This doubles the available mucosal surface area (over a single nostril) for drug absorption and increases rate and amount of absorption. Always use the MOST concentrated form of the medication available – dilute forms are less effective (example – use midazolam 5 mg per ml, not 1 mg per ml). If you have a compounding pharmacy and can get the concentrations such that the nasal volumes are 0.2 to 0.3 ml per nostril this would be ideal and may require slightly lower dosing. Do not use more than ½ to 1 ml of medication per nostril (0.2 to 0.3 is the ideal volume). If a higher volume is required, apply it in two separate doses allowing a few minutes for the former dose to absorb. For small volume doses of medication, be aware that most delivery devices have a “dead space” in the applicator tip where some of the medication will remain. Be sure to take that dead space into account when calculating the volume of medication to be administered. Titration to effect is probably possible for selected situations where time is not critical. If inadequate clinical effect is present after 5 to 15 minutes, re-administering a second dose may be effective. Midazolam burns for 30-45 seconds – forewarn the parents that the child will initially cry (but nothing like they will cry with a shot). It also only causes mild sedation/anxiolysis and lasts about 30 minutes Dexmedetomidine sedation is deeper than midazolam, has slower onset (20 min) and longer sedation Sufentanil is extremely potent. Monitoring with pulse oximetry is imperative. Both fentanyl and sufentanil pain control effects begin wear off at about 45 minutes to an hour. It is nice to the patient to give them an oral drug at about 15-20 minutes since this will then kick in about the time the nasal drug is wearing off. Another option is simply repeating the nasal drug. Therapeutic Intranasal Drug Delivery Needleless treatment options for medical problems Intranasal sedation protocol: General points: Midazolam, ketamine, dexmedetomidine and sufentanil are the most commonly used sedative medications for IN delivery. o Midazolam results in mild somnolence with resultant reduction in anxiety and probably amnesia. It will not make the patient unconscious. o Be aware that midazolam causes some nasal burning for 30-45 seconds when administered. o In small children you should administer lidocaine 2% or 4% - 0.2 ml per nostril 5 minutes prior to the midazolam to stop the burning. o Sufentanil will also cause deeper sedation and in doses over 1.5 mcg/kg has been noted to cause respiratory depression. o Dexmedetomidine takes longer to take effect (20 minutes) and lasts longest of all (over 1 hour). Combination therapy with midazolam plus either sufentanil or ketamine may work better than any of the medications alone Newer data discussed above suggests that IN dexmedetomidine may be the best option for sedation if more than just mild sedation is needed and prolonged affect is required (also slower onset of action). Reasonable IN starting dose: o Midazolam 0.4 to 0.5 mg/kg Use the lower dose for minor, non-painful procedures such as radiographic imaging Use the higher dose for better sedation prior to procedures such as laceration repair o Ketamine 10 mg/kg o Sufentanil 1 to 1.5 mcg/kg (this is a higher dose than required for pain control and increases the risk for respiratory depression) o Dexmedetomidine 2-3 mcg/kg o Combined dosing: Midazolam plus sufentanil: 0.2 to 0.3 mg/kg of midazolam plus 0.75 to 1 mcg/kg of sufentanil Midazolam plus ketamine: 0.2 to 0.3 mg/kg of midazolam plus 5 mg/kg of ketamine Use only concentrated midazolam (5 mg/ml) and ketamine formulations Be sure to monitor oxygen saturation in all patients Ideal volume is 0.3 to 0.5 ml per nostril, maximum is 1 ml per nostril, more will just run out nose. Nasal naloxone and flumazenil can be used as reversal agents Home | Overview | Off-label | Anatomy | Delivery | Protocols | Teaching | Bibliography | Links