Water - Water occurs in 3 basic forms: 1. 2. 3.
advertisement

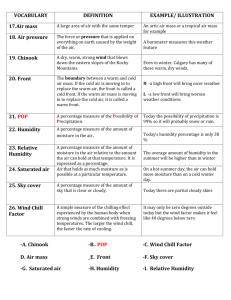
Water - Water occurs in 3 basic forms: 1. ___________________________________________________ 2. ___________________________________________________ 3. ___________________________________________________ - The distribution of Earth’s water can be studied using a world map. The Earth is made up of: - Salt water – oceans and seas = _______% - Land = _______% - Frozen land or ice = ________% -Fresh Water -lakes, ponds, swamps, streams, and rivers =_________________% - Therefore most of the water on the Earth is ___________ water and ______ is the second most abundant form of water. - Melting and expansion of the _______ ____________ and _____________ causes water levels in the ocean to rise and fall. - _______________ are underground layers of rock and soil that holds water. If we were to look at only the water on Earth, and take out the land, of that water: _____________% = Salt water _____________% = Ground water _____________% = Fresh water _____________% = Ice Water Cycle Evaporation - ____________________________________________________________ Condensation - ___________________________________________________________ Precipitation - ____________________________________________________________ Transpiration - ___________________________________________________________ Extensive _______________ in the warm tropical and subtropical seas add much of the atmospheric moisture to the water cycle. _______________ heats quicker than land, and this uneven heating and the Earth’s rotation causes _____________. _____________ helps evaporation and moves moist-rich air called _______________. Glacial ice forms in colder regions (polar regions and Mountain areas) as moisture is carried from the _____________ salt and freshwater sources and precipitated as ______________. Lakes and rivers are also formed by precipitation of ocean-derived moisture. _________________, ___________________, and _____________________ are the dominant processes that form the ________ _________ and determine the distribution of Earth’s water. _________ ___________ and cooling result in significant changes in water cycle processes and surface distribution of Earth’s water supply. A Mater of Change Humidity -___________________________________________________________ Relative Humidity - ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ Dew Point - __________________________________________________________ Most air contains water in _________ form. It is measured and described as relative __________ - ratio of the amount of water vapor present in the air relative to the total quantity that would make it saturated and cause precipitation. The amount of water that air can hold is largely determined by ______________ and __________________. Warmer air can hold _________ water vapor. Lower pressures also allow the amount of water to _______________. Temperature: warm = _____________ water cold = ______________ water Pressure: (think of a sponge) Low pressure = ____________ water High pressure = ____________ water ** The more water in the air = the more humidity. ** Rainy Days = __________ humidity Sunny Days = __________ humidity ** It will rain when relative humidity reaches 100%. Moisture is added to atmospheric air mostly by warm ________ that moves across the ocean and land surfaces. As the warm humid air cools, relative humidity increases causing cloud formation (_______________) and rain and snow (_______________). This process can be directly seen along mountain coastal areas where warm humid ocean breezes are moved upward as they encounter the mountains. As a result, __________ and then _________or snow form. Evaporation also ______________ water supplies by leaving salt, sediments and other contaminants behind as the lower density water vapor moves into the atmosphere. As a result, ________ water carry and deposit larger volumes of dissolved and suspended rock material in the ______________. The water cycle is an ongoing process that never stops. _______________ measure the pressure resulting from the air (atmospheric pressure). _______________ measures the airs temperature.