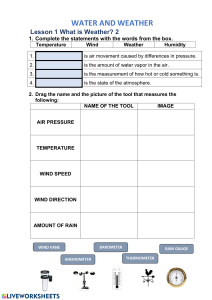
Name Class Date Weather Test Interpreting a Weather Map Use the map below to complete the following. 1. What are the heavy lines on the map called? __________________________________________________ 2. Is the air pressure in the areas that are receiving precipitation low or high? How do you know? __________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. What does the symbol mean? _______________________________________________________ 4. What symbol on the map indicates that snow is falling? _______________________________________ 5. What is the condition of the sky in the areas that have high air pressure? ________________________ 6. What kind of front is over the northeastern states? ____________________________________________ 7. What is the sky condition in the southern part of Florida? ______________________________________ 8. Name two forms of precipitation shown on the map. __________________________________________ 9. What symbol on this map means the same thing as the symbol • ?____________________________ 10. What kind of front is over the northern part of Florida? ________________________________________ Multiple Choice Write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement. __________ 1. The process by which plants give off water vapor into the air is a. evaporation. b. condensation. c. respiration. d. transpiration. __________ 2. Water vapor is water in the form of a. a gas. b. a solid. c. a liquid. d. oceans. Concepts and Challenges in Earth Science, Teacher’s Resources CD-ROM (c) by Pearson Education, Inc./Globe Fearon/Pearson Learning Group. All rights reserved. Weather Name Class Date Weather Test (continued) __________ 3. The amount of water vapor in the air is called a. capacity. b. saturation. c. humidity. d. air pressure. __________ 4. Air has more capacity to hold water at a. 4°C. b. 10°C. c. 20°C. d. 25°C. __________ 5. Relative humidity is measured with an instrument called a. a thermometer. b. a psychrometer. c. an anemometer. d. a calculator. __________ 6. The temperature at which air must be cooled to reach saturation is the a. frost point. b. specific humidity. c. dew point. d. condensation point. __________ 7. Clouds are formed by the process of a. evaporation. b. sublimation. c. transpiration. d. condensation. __________ 8. Light, feathery clouds made up of ice crystals are a. cumulus. b. cirrus. c. stratus. d. nimbus. __________ 9. Air masses that form over water are a. moist. b. dry. c. hot. d. cold. __________ 10. The forward edge of a warm air mass is a a. cold front. b. stationary front. c. warm front. d. tropical front. __________ 11. When giant storm clouds give off electricity, a. lightning forms. b. thunder forms. c. wind forms. __________ 12. A funnel-shaped storm that spins is a a. hurricane. b. tornado. c. thunderstorm. __________ 13. Weather scientists are a. petrologists. b. hurricanologists. __________ 14. Air pressure is measured in a. millibars. b. g/kg of air. c. mph. d. rain forms. d. tropical storm. c. meteorologists. d. station models. d. km/hr. __________ 15. The two main forms of precipitation are a. rain and ice. b. snow and hail. c. hail and sleet. d. rain and snow. __________ 16. A device used to measure precipitation is a. a rain gauge. b. a psychrometer. c. a station model. d. an air mass. __________ 17. A warm, dry air mass forms over a. polar ocean areas. b. polar land areas. c. tropical ocean areas. d. tropical land areas. __________ 18. Air with a relative humidity of 100 percent is a. occluded. b. saturated. c. condensed. d. evaporated. __________ 19. A cloud that forms near the ground is a. dew. b. frost. c. stratus. d. fog. Concepts and Challenges in Earth Science, Teacher’s Resources CD-ROM (c) by Pearson Education, Inc./Globe Fearon/Pearson Learning Group. All rights reserved. Weather Name Class Date Weather Test (continued) __________ 20. The weather in the eye of a hurricane is a. calm. b. rainy. c. windy. d. cool. Written Response Answer the following questions in complete sentences. 21. CONTRAST: What is the difference between the weather that occurs at a warm front and the weather that occurs at a cold front? ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 22. EXPLAIN: Why does high humidity make warm weather more uncomfortable? ___________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ Concepts and Challenges in Earth Science, Teacher’s Resources CD-ROM (c) by Pearson Education, Inc./Globe Fearon/Pearson Learning Group. All rights reserved. Weather Answer Key Weather Test Interpreting a Weather Map 1. fronts 2. low; the areas are designated by the letter L. 3. partly cloudy skies 4. small x’s or crosses 5. sunny 6. a cold front 7. partly cloudy 8. rain and snow 9. cloudy 10. stationary front Multiple Choice l. d 2. a 3. c 4. d 5. b 6. c 7. d 8. b 9. a 10. c 11. a 12. b 13. c 14. a l5. d 16. a 17. d 18. b 19. d 20. a Written Response 21. At a warm front, cirrus clouds form as a warm air mass gently rises over a cold air mass and cools. At a cold front, a cold air mass pushes underneath a warm air mass. Differences in pressure cause gusty winds and rain. 22. Evaporation of perspiration on the skin cools the body. High humidity slows the rate of evaporation, so perspiration does not evaporate and cool the skin as effectively when the humidity is high. Concepts and Challenges in Earth Science, Teacher’s Resources CD-ROM (c) by Pearson Education, Inc./Globe Fearon/Pearson Learning Group. All rights reserved. Weather