Chapter 22: Helminth Parasites of Laboratory Mice
advertisement

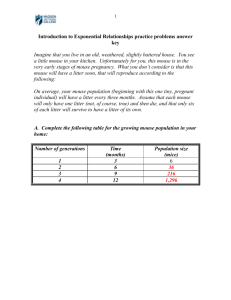
Fox J, Barthold S, Davisson M, Newcomer C, Quimby F, Smith A, eds. 2006. The Mouse in Biomedical Research, 2nd edition Elsevier Academic Press, San Diego, CA Volume 2 - Diseases Chapter 22 Helminth Parasites of Laboratory Mice. pp. 551-564 QUESTION:S 1. To which family do pinworms belong? Name 2 common pinworms in mice. 2. T/F: Syphacia and Aspiculuris inhabit the same section of the GI tract and therefore have to directly compete for resources, making concurrent infections in mice extremely unlikely. 3. T/F: In concurrent infections, A. tetraptera may have higher worm numbers because its longer lifespan may allow it to accumulate in the host. 4. Male/Female mice tend to have higher pinworm burdens. 5. Younger/Older mice tend to have higher pinworm burdens. 6. T/F: Rodent pinworms are a significant zoonotic hazard. 7. Match the following as characteristics of S. obvelata (So) or A. tetraptera (At): a. ova with one flattened side b. symmetrical ova c. presence of spicules and mamelons in males d. prominent cervical alae e. ova located in the fecal pellet f. ova located on the perianal skin g. 5-20 hours until ova is infective h. 5-8 days until ova is infective i. 21-15 day prepatent period j. 11-15 day prepatent period 8. Which oxyurid has the largest ova? a. Syphacia muris b. Syphacia obvelata c. Aspiculuris tetraptera 9. Syphacia spp. reside in the a. esophagus b. stomach c. small intestine d. cecum 10. S. obvelata has a direct/indirect life cycle. 11. What is the most common method of diagnosing S. obvelata infection? 12. T/F: Pinworm infections are considered to be clinically silent in mice with normal immune systems. 13. Pinworms may interfere with research by a. modification of the immune system b. inhibition of diabetes in NOD mice c. acceleration of the development of the hepatic monooxygenase system d. all of the above 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. e. none of the above T/F: S. obvelata eggs seem to be more fastidious than both S. muris and A. tetraptera ova. Ivermectin treatment a. is effective in controlling pinworms b. has no toxic side effects c. is ineffective against pinworm infections d. is ineffective if used in conjunction with piperazine Which class of anthelminthics binds to nematode beta-tubulin and inhibits microtubule formation? Avermectins/Benzimidazoles Which of the following is the rat pinworm? a. Syphacia muris b. Syphacia obvelata c. Aspiculuris tetraptera Give the scientific name of the mouse whipworm. Mouse whipworms a. have no known effect on research b. are relatively small worms c. have no known treatment d. have infective eggs 30 days after they are laid _______ is a trichostrongyloid nematode of mice with a strictly enteric life cycle. a. Trichuris muris b. Heligmosomoides polygyrus c. Rodentolepis nana d. Hymenolepis diminuta T/F: Mice are the definitive host of Rodentolepis nana, also known as the “dwarf tapeworm” and the most common cestode parasite of mice. Which of the following mouse tapeworms has the largest ova? a. Rodentolepis nana b. Rodentolepis microstoma c. Hymenolepis diminuta Which of the following tapeworms does NOT require an intermediate host? a. Rodentolepis nana b. Rodentolepis microstoma c. Hymenolepis diminuta Which of the following mouse tapeworms resides primarily in the bile duct rather than in the small intestine? a. Rodentolepis nana b. Rodentolepis microstoma c. Hymenolepis diminuta T/F: Alone among cestodes, R. nana can reproduce in immunocompetant hosts using either a direct or indirect life cycle. T/F: R. nana, R. microstoma, and H. diminuta are all potentially zoonotic. Taenia taeniaeformis (previously Cysticercus fasciolaris) a. uses the mouse as an intermediate host. b. c. d. e. develops into strobilocerci in an infected mouse’s muscle tissue or liver 30 days after eggs were ingested. infection indicates a breakdown in sanitation procedures within a facility. all of the above. none of the above. ANSWERS: 1. Oxyurid; Syphacia obvelata, Aspiculuris tetraptera 2. F – inhabit different sections of the GI tract; concurrent infections possible 3. T 4. male 5. younger 6. F – although S. obvelata is reported to rarely infect humans 7. a-So, b-At, c-So, d-At, e-At, f-So, g-So, h-At, i-At, j-So 8. b 9. d 10. direct 11. cellophane tape test 12. T 13. d. 14. T 15. a 16. Benzimidazoles 17. a 18. Trichuris muris 19. d 20. b 21. T 22. b 23. a 24. b 25. T 26. T 27. d