Respiratory System Guided Notes
advertisement

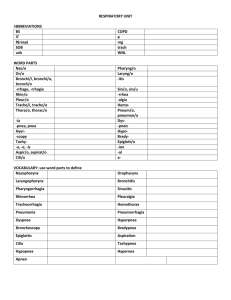
Notes Pt 2 - Respiratory Physiology Respiratory events I. Respiration consists of 4 distinct events. Describe each. A. pulmonary ventilation B. external respiration C. respiratory gas transport (discussed in blood chap) D. internal respiration II. define cellular respiration Pulmonary ventilation: event #1 I. pulmonary ventilation depends on ______________________________________. A. inspiration B. expiration II. Pressure relationships in the thoracic cavity A. intrapulmonary pressure - pressure within ____________ 1. changes with phases of breathing 2. always equalizes itself with ____________________________ B. intrapleural pressure - pressure within _____________________ 1. also fluctuates with breathing 2. always about _____________ less than intrapulmonary pressure 3. any condition that causes these 2 pressures to equalize causes immediate lung collapse a. atelectasis b. pneumothorax Why does breathing happen? The Rule: _____________________ lead to _____________________ which lead to _____________________ to equalize the pressure 5 When the diaphragm contracts, it flattens out and moves downward – see diagram on previous page. When the diaphragm relaxes, it moves up into the parachute shape. Understanding this is CRUCIAL to understanding how Boyle’s law explains this process. C. Boyle’s law : law: Pressure and Volume have an _____________ relationship Inspiration 1. main inspiratory muscles - ____________________________ 2. thoracic dimensions change during inspiration to increase volume of thoracic cavity by _______________ 3. intrapulmonary pressure drops and air rushes in for normal quiet inspiration 4. deep (forced) inspiration – requires activation of ________________________ Expiration 1. passive process dependent on ________________________ 2. lungs recoil when inspiration stops – so alveoli compress –which leads to a volume decreases -causing intrapulmonary pressure to rise - gas outflows to equalize 3. forced expiration - contraction of ___________________________ E. 6 D. What Doctors listen for and what the sounds mean: a. bronchial sounds vs. vesicular breathing sounds b. wheezing vs. rales E. Physical Factors influencing the process of Pulmonary Ventilation a. Respiratory passage diameter - (AKA: resistance due to increased friction of air on respiratory structures will diminish air flow) 1. smooth muscle __________constriction 2. local accumulations of mucus, infectious material, tumors b. Lung compliance - the ease with which lungs can readily _________________ 1. elasticity of lungs & thoracic cage can diminished by 2 factors: a. b. c. Lung elasticity – ability of lung tissue to _______________ after expansion 1. essential for normal expiration 2. Emphysema – loss of elasticity causes enormous effort to exhale – at end stages, alveoli rupture losing surface area for gas exchange d. Alveolar Surface Tension Forces 1. Surface tension is caused by the tendency of ___________ molecules such as water to stick to each other with hydrogen bonds – this can cause the walls of the alveoli to stick together like plastic wrap every time you exhale. a. Large amounts of energy /effort will be required to simply re-expand the lungs and allow you to inhale 2. surfactant - interferes with _______________ of water molecules so less energy needed to expand lungs – this is one of the things that keeps our lungs partially expanded at all times. (the other thing is the pressure difference previously discussed) 3. IRDS End of Quiz #2 Material Internal & External Respiration: Gas Exchanges in the Body: Event #2 & 4 I. Basic properties of gases A. Dalton’s law: 1. Dalton's law of partial pressures is used to determine the individual pressures of each gas in a mixture of gases. 2. Gas exchanges that occur between the blood and the alveoli AND between the blood and the tissue cells take place by simple ______________ and depend on partial pressure gradients of oxygen and carbon dioxide that exist on opposite sides of the exchange membrane. 3. Always moving from ___________________________ pressures 7 B. Henry's law: Deals with gases dissolving into liquids (works together with Dalton’s law of partial pressures) 1. states that the solubility of a gas in a liquid is directly proportional to the pressure of that gas above the surface of the solution (IOW: the higher the pressure of the gas, the more gas will be shoved into the liquid thus increasing solubility) 2. Solubility and partial pressure have a ______________ relationship 3. The solubility coefficient of the gas also affects this process – the higher the #, the more the gas “likes” to dissolve into a liquid (based on molecular structure, etc.) 4. Each gas will dissolve in a liquid in proportion to the ___________ between its partial pressure gradient and its solubility coefficient nd C.2 Law of Thermodynamics: solubility and temperature have an ________________ relationship. The reason for this gas solubility relationship: Increased temperature causes an increase in _______________ energy. The higher kinetic energy causes more motion in molecules which break intermolecular bonds and escape from solution and vice versa. II. Factors influencing external and internal respiration A. partial pressure gradients and gas solubilities a. oxygen - low solubility but steep partial pressure gradient (64mm Hg) b. carbon dioxide – higher solubility (20x that of oxygen) but partial pressure gradient only 5mm Hg c. due to the ratios of solubility coefficients and pressure gradients – _________ amounts of gases are exchanged B. thickness of respiratory membrane 1. Ideal thickness: 0.5 - 1 micrometer (0.000001 meter) 2. Edematous tissue can be caused by congestion and pneumonia – thick tissue hinders diffusion leading to _________________________________________ C. surface area 1. Ideal surface area: 50-70 square meters for gas exchange 2. Disorders such as emphysema or cancer can diminish _________ for gas exchange. Control of Respiration A. The two nerves that transmit to the respiratory muscles are the ______________ and __________________________ nerves. B. The neural centers that control respiration rate & depth are located in the ___________ & __________________________________. Some terms that deal with respiration rates are: 1. eupnea 2. hyperpnea 3. apnea 4. dyspnea 8 C. Physical factors, conscious control, emotional factors, and chemical factors all influence respiration rate & depth. 1. hyperventilation a. Define: b. Does this cause respiratory acidosis or respiratory alkalosis? c. Explain using the equation: CO2 + H20 H2CO3 (carbonic acid) d. What is the treatment for this? Explain why this works using the above equation. 2. hypoventilation a. Define: b. Does this cause respiratory acidosis or respiratory alkalosis? c. Explain using the equation: CO2 + H20 H2CO3 (carbonic acid) d. What usually causes hypoventilation? Respiratory Imbalances A. COPD: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disorder: a group of disorders that block airflow and make breathing difficult 1.chronic bronchitis 2. emphysema 3. features in common B. Lung cancer 1. info 2. 3 types: Be able to ID according to appearance & location a. b. c. 3. treatments C. Cystic Fibrosis 9 D. SIDS E. Asthma Hyperbaric conditions 1. Hyperbaric oxygen chambers - force greater amount of oxygen into patient's blood to treat ____________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ 2. How hyperbaric treatment works – explain using gas laws 3. Conditions that can be treated with hyperbaric medicine: Scuba Diving: 1. What happens in the body as you go down in depth? 2. What happens in the body as you come up at the correct rate? 3. What happens in the body if you come up too fast? 4. Discuss nitrogen narcosis and decompression sickness. High Altitudes: 1. Why is breathing difficult at high altitudes? 2. What kinds of problems can altitude sickness cause? 3. How does the body adjust given time? Developmental aspects A. _______ weeks gestation - resp. system sufficiently developed to allow baby to survive – surfactant production not up to speed yet B. lung development and alveoli formation are not completed until young adulthood smoking during early teens leads to permanent incomplete lung maturation and inadequate alveoli formation (Just another reason NOT to smoke!) C. 70 years of age - vital capacity decreases by 1/3 and can leads to sleep apnea and hypoxia protective mechanisms become less efficient 10