10/14/13 Unit 4: Periodic Table Trends
advertisement

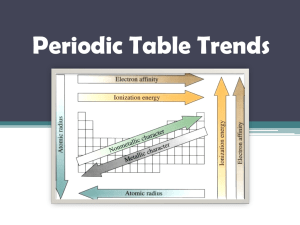
Periodic Table Trends Atomic Radius • Half the distance between the nuclei of two identical atoms bonded together Atomic Radius Atomic Radius • Across a Period= DECREASES ▫ As you add more protons, the attractive force of the nucleus increases, pulling electrons in more closely • Down a Group=INCREASES ▫ As you add more energy levels, the size of the electron cloud increases Which of the elements would have the largest radius? 84% 11% ne s ag 12 -M fu r iu m e or in 17 -C hl co n 0% 14 -S ili m in um 0% 5% 16 -S ul 13-Aluminum 14-Silicon 17-Chlorine 12- Magnesium 16-Sulfur 13 -A lu 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Ionization Energy • The energy required to remove one electron from a neutral atom. ▫ High I.E. – Harder to lose electrons ▫ Low I.E. –Easier to lose electrons Ionization Energy Ionization Energy • Across a Period=INCREASES ▫ Electrons are closer to nucleus, therefore harder to remove • Down a Group=DECREASES ▫ Electrons are farther from the nucleus, therefore easier to remove Which element would have the lowest ionization energy? 0% 68% 26% 5% 0% 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 20- Calcium 56- Barium 4- Beryllium 38- Strontium 12-Magnesium Electron Affinity • The energy released when a neutral atom acquires an electron. • Elements that really want another electron tend to release more energy (higher E.A.) Across a period= INCREASES Down a group= DECREASES Electronegativity • The ability of an atom to attract electrons • The most electronegative element is fluorine Across a Period= INCREASES Down a Group= DECREASES Which of the elements would have the highest electronegativity? 84% 13-Aluminum 14-Silicon 17-Chlorine 12- Magnesium 16-Sulfur 11% 12 -M fu r 5% 16 -S ul ag ne s or in iu m e 0% 17 -C hl co n 14 -S ili m in um 0% 13 -A lu 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. METALS vs NONMETALS • • • • • • METALLIC CHARACTER Lower I.E. (tend to lose e-) Lower E.N. (don’t want e-) High Luster (shiny!) Good Conductors Malleable and Ductile • MOST METALLIC ELEMENT: • NONMETALLIC CHARACTER • High I.E. (don’t want to lose e-) • High E.N. (tend to gain e-) • Dull (no luster) • Poor Conductors • Brittle as solids • MOST NONMETALLIC ELEMENT: Which of the elements would be the least reactive metal? 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 fu r 0% 16 -S ul ne s or in iu m e 0% ag 4 0% 12 -M 3 14 -S ili m 2 13 -A lu 1 0% co n 0% 17 -C hl 13-Aluminum 14-Silicon 17-Chlorine 12- Magnesium 16-Sulfur in um 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 19 20 Which of the elements would be the most reactive nonmetal? 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 fu r 0% 16 -S ul ne s or in iu m e 0% ag 4 0% 12 -M 3 14 -S ili m 2 13 -A lu 1 0% co n 0% 17 -C hl 13-Aluminum 14-Silicon 17-Chlorine 12- Magnesium 16-Sulfur in um 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 19 20 37-Rubidium would have all of the following characteristics except? 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 17 ro n al 1V om Ro 16 0% Ele ct pe r Te m Br Hi gh 15 ur e at ne it t le le ab al M 14 at 5 id 4 So l 3 0% en ce y ilit ity uc tiv 2 Hi gh Co nd Hi gh 1 ss 1. High Conductivity 2. High Malleability 3. High Brittleness 4. Solid at Room Temperature 0% 0% 0% 5. 1 Valence Electron 18 19 20 35-Bromine would have which one of the following characteristics? 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 17 s ro n ct en ce al om Ro 16 0% Ele pe r Te m Br Hi gh 15 ur e at ne it t le le ab al M 14 at 5 id 4 So l 3 0% 7V y ilit ity uc tiv 2 Hi gh Co nd Hi gh 1 ss 1. High Conductivity 2. High Malleability 3. High Brittleness 4. Solid at Room Temperature 0% 0% 0% 5. 7 Valence Electrons 18 19 20
![The electronic configuration of phosphorus is [Ne] 3s2 3p3](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/008974852_1-8381577ce936fbfa611892c1a5f109cd-300x300.png)




