Advia - Red Blood Cell Laboratory
advertisement

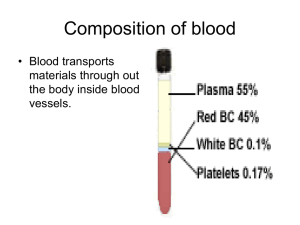
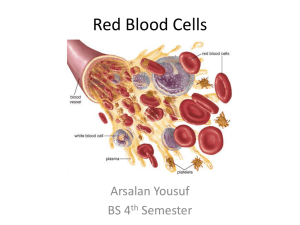
Hematology Analyzer Complete Blood Count (CBC) The Advia 120 Hematology Analyzer yields data related to the cell counts, cell size, cell type, and cell contents. A complete blood count (CBC/Diff/Retic) produces data in three main categories: CBC includes the hemoglobin, red blood cell, and platelet methods, the Diff includes the white blood cell differential, and the Retic includes the reticulocyte analysis. Figure 1. The Bayer/Siemens Advia 120 instrument. The hemoglobin reagent lyses the red blood cells to release hemoglobin. The heme iron in the hemoglobin is oxidized from the ferrous to the ferric state, and then it is combined with cyanide to form the reaction product. The RBC/platelet reagent causes isovolumetric sphering and fixation of the RBC and platelets. Laser light detects the cells: the low angle scatter is used to measure volume and the high angle scatter is used to detect the hemoglobin concentration. Parameters measured or calculated: Total Hemoglobin, Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin, Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration.RBC Count, Mean RBC Volume, Hematocrit, Platelet Count, Mean Platelet Volume. Figure 2 shows the RBC volume and hemoglobin concentration histograms as they relate to the dot plot of hemoglobin concentration versus volume. The 9 quadrants marked in the dot plot correspond to the macrocytic, microcytic, normocytic, hypochromic, hyperchromic, and normochromic cells. The values of the quadrant markers are shown in blue. Figure 3 shows the PLT scatter cytogram. This plot is the graphical representation of two light-scatter measurements; the low-angle and high-angle light scatter signals for each cell are transformed into volume and refractive index values. White Blood Cell (WBC) Differential (Diff) The perox reagents lyse the RBC, fix the WBC, and stain the granules within the WBC to complete the differentiation. The cells absorb light proportional to the amount of peroxidase stain present, and scatter light proportional to their size. The baso reagent lyses all cells except basophils. Cluster analysis of the cytograms identifies each population based on its position, area, and density, and then the number of cells/nuclei in each population is processed. The lines that separate the different cell populations are calculated by the software on a sample-by-sample basis. Parameters (# and % for each): total WBC, Neutrophils, Lymphocyte, Monocyte, Eosinophil, Basophil, Mononuclear Cells, and Polymorphnuclear Cells. Figure 4. The perox cytogram shows the amount of peroxidase stain represented on the x-axis and the light scatter represented on the y-axis. Figure 5. The baso cytogram shows the high-angle light scatter (nuclear configuration) on the x-axis, and the low-angle light scatter (cell size) on the yaxis. Reticulocyte Analysis (Retic) The Retic reagent contains a surfactant that isovolumetrically spheres the red cells, and a dye that stains the RNA contained in the reticulocytes. The events are plotted with maturation (RNA staining) along the x-axis and cell size (light scatter) along the y-axis. Gates are set within the software to differentiate mature RBC from the reticulocytes. Parameters: Retic Count (# and %), Retic Volume, Retic Hemoglobin Content and Concentration.