Vol. III Ch.9 Hematology Key Terms
advertisement

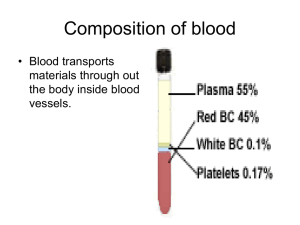
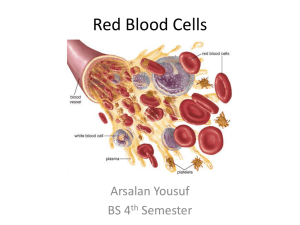
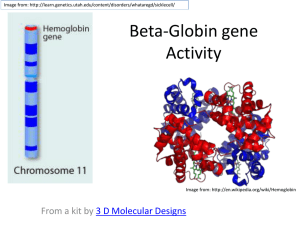
VIII Ch. 9 Hematology anemia-479-an inadequate number of red blood cells or inadequate hemoglobin within the red blood cells. antigen-471-protein on the surface of a donor’s red blood cells that the patient’s body recognizes as “not self.” autoimmune disease-467-condition in which the body makes antibodies against its own tissues. Bohr effect-463-phenomenon in which a decrease in PCO2 acidity causes in increase in the quantity of oxygen that binds with the hemoglobin and, conversely, and increase in PCO2 acidty causes the hemoglobin to give up a greater quantity of oxygen. chemotaxis-464-the movement of white blood cells in response to chemical signals. disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)-485-a disorder of coagulation caused by systemic activation of the coagulation cascade. erythrocyte-462-red blood cell. erythropoiesis-464-the process of producing red blood cells. erythropoietin-461-the hormone responsible for red blood cell production. fibrinolysis-470-the process through which plasmin dismantles a blood clot. hematocrit-464-the packed cell volume of red blood cells per unit of blood. hematology-460-the study of blood and the blood-forming organs. hematopoiesis-461-the process throught which pluripotent stem cells differentiate into various types of blood cells. hemoglobin-462-oxygen-bearing molecule in the red blood cells. It is made up of iron-rich red pigment calles heme and a protein called globin. hemolysis-464-destruction of red blood cells. hemophilia-484-a blood disorder in which one of the proteins necessary for blood clotting is missing or defective. hemostasis-469-the combined three mechanisms that work to prevent or control blood loss. inflammatory process-468-a nonspecific defense mechanism that wards off damage from microorganisms or trauma. leukemia-482-a cancer of the hematopoietic cells. leukocyte-464-white blood cell. leukocytosis-482-too many white blood cells. leukopoiesis-465-the process through which stem cells differentiate into the white blood cells’ immature forms. lymphoma-483-a cancer of the lymphatic system. major basic protein (MBP)-466-a larvacidal peptide. multiple myeloma-486-a cancerous disorder of plasma cells. neutropenia-467-a reduced number of neutrophils. phagocytosis-464-process in which white blood cells engulf and destroy an invader. plasma-461-thick, pale yellow fluid that makes up the liquid part of the blood. pluripotent stem cell-461-a cell from which the various types of blood cells can form. polysythemia-479-an excess of red blood cells. sequestration-464-destruction of red blood cells. sickle cell anemia-480-an inherited disorder of red blood cell production, so named because the red blood cells become sickle shaped when oxygen levels are low. thrombocyte-468-blood platelet. thrombocytopenia-484-an abnormal decrease in the number of platelets. thrombocytosis-484-an abnormal increase in the number of platelets. thrombosis-470-clot formation, which is extremely dangerous when it occurs in coronary arteries or cerebral vasculature. 2,3-diphosphoglycerate (2,3-DPG)-463-chemical in the red blood cells that affects hemoglobin’s affinity for oxygen. von Willebrand’s disease-485-condition in which the vWF component of factor VIII is deficient.