Important Things to Memorise for Higher Computing
advertisement
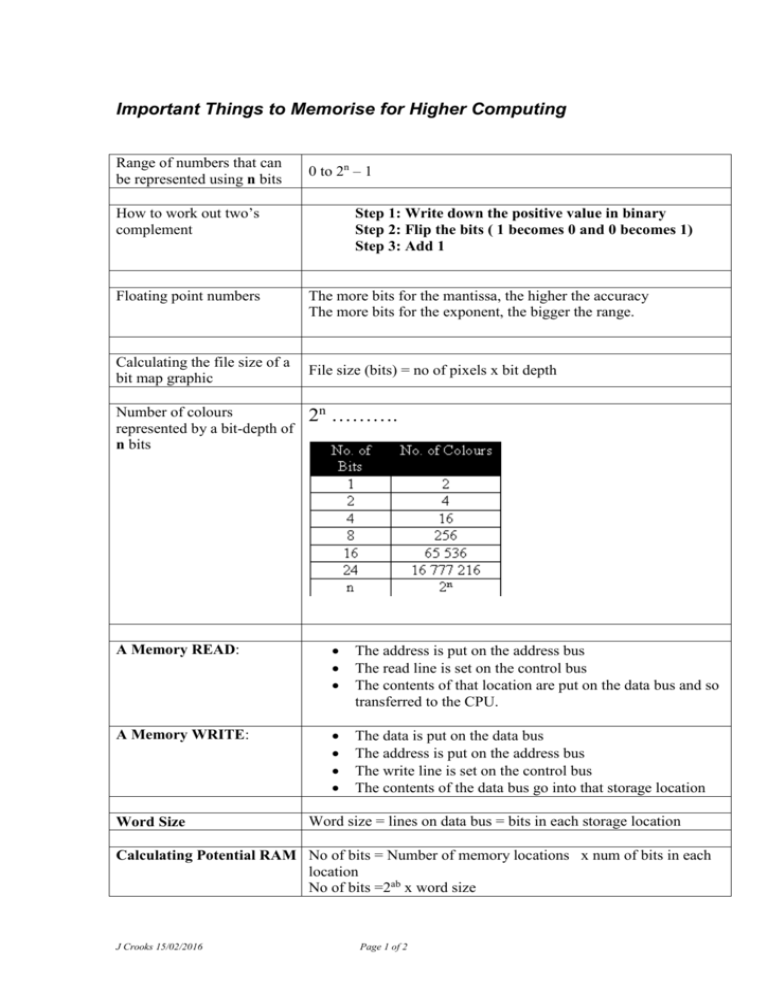
Important Things to Memorise for Higher Computing Range of numbers that can be represented using n bits 0 to 2n – 1 How to work out two’s complement Floating point numbers Calculating the file size of a bit map graphic Number of colours represented by a bit-depth of n bits Step 1: Write down the positive value in binary Step 2: Flip the bits ( 1 becomes 0 and 0 becomes 1) Step 3: Add 1 The more bits for the mantissa, the higher the accuracy The more bits for the exponent, the bigger the range. File size (bits) = no of pixels x bit depth 2n ………. A Memory READ: The address is put on the address bus The read line is set on the control bus The contents of that location are put on the data bus and so transferred to the CPU. A Memory WRITE: The data is put on the data bus The address is put on the address bus The write line is set on the control bus The contents of the data bus go into that storage location Word Size Word size = lines on data bus = bits in each storage location Calculating Potential RAM No of bits = Number of memory locations x num of bits in each location No of bits =2ab x word size J Crooks 15/02/2016 Page 1 of 2 Calculating the file size of a digitised audio file Calculating the file size of a digital video file J Crooks 15/02/2016 Filesize (bits) = sampling frequency(Hz) x sample depth(bits) x length(s) x no of channels Filesize (bits) = no of pixels x bit depth x frame rate(fps) x length(s) Page 2 of 2











