Properties and Applications of Hydrocarbons Chart
advertisement

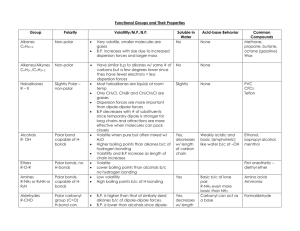
Properties and Applications of Hydrocarbons Recall: As molecular polarity increases, boiling point increases. As molecular polarity increases, solubility in water increases. Type Structure Polarity Solubility in Water Uses Alkanes non-polar -insolube in water -dissolve in organic solvents -commercial fuels, natural gas, Alkenes non-polar -insolube in water -dissolve in organic solvents -starting material (monomers) for polymers -addition reaction starting material Alkynes non-polar -insoluble in water -dissolve in organic solvents -used in welding Aromatics non-polar -insoluble in water -dissolve in organic solvents -foods, drugs, explosives, major source of coal tar Alcohols OH groups are polar -soluble in water -antifreeze, fuel (ethanol), beverages Aldehydes carbonyl groups are polar -soluble in water Ketones carbonyl groups are polar -soluble in water -cinnamaldehyde gives cinnamon its flavor and odour –also in perfumes -can produce carboxylic acids -solvent, paint remover, fingernail polish remover Carboxylic Acids carbonyl and OH groups are polar -smaller acids are soluble in water -in food, e.g. acetic acid is vinegar. –used in preparation of esters, drugs, soaps Ethers bent shape around oxygen so polar. C-O bond less polar than OH so less polar than alcohol -usually soluble -aerosol spray propellant, used in cosmetics and pharmaceuticals Esters C-O bonds and carbonyl groups are polar -usually soluble, less so with increasing chain length -artificial flavours, perfumes, taste of many fruits Amines C-N bonds and N-H bonds are polar -6 carbon amines or less are soluble -fabric softeners, parts of valuable pharmaceuticals like novocaine. Amides C-N bonds and carbonyl groups are polar -smaller amides are soluble -part of important polymers like nylon 1 2