HEPATITIS B - Paschal`s sports medicine
advertisement

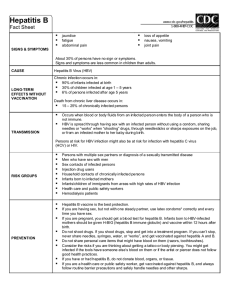
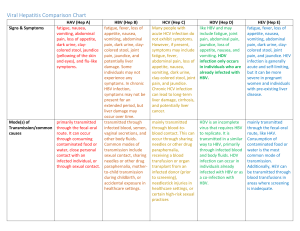
HEPATITIS A, B, C, D, E NOTES D 2 Hepatitis _________ (1st of 3 Main Types) - Abbreviated (_______) 1. Most common ____________________ disease in the US. 2. Signs and Symptoms a. __________________ b. Fatigue c. ________________________ ___________ d. Loss of appetite e. _________________ f. Diarrhea g. _________________ 3. Once you have had ______________________ ________ you cannot get it again 4. Transmission a. Found in __________________ of an infected person b. Usually spread to a person by putting something ________________________________ with the feces of an ________________________ person into the _____________________. 5. Prevention is ________________________________ Hepatitis ______ (2nd of Main Types) –Abbreviated (_______) 6. Most adults infected with the _________________ ________ virus fully recover and develop ________________________ immunity. Between _______% and ________% of individuals infected as adults will become _________________ carriers, which means they will be ________________________ to others and can develop chronic _______________ damage. Infected _____________________ , especially ________ - _______________, are much more likely to become chronic carriers. 7. S / S - Jaundice, ____________________, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, nausea, _________________________ , and __________________ pain. - About 30% of people have no s/s. s/s are even less common in children than adults 8. Transmission - ________________________ , sexual contact, and ____________________ to fetus 9. Complications of HBV (a positive blood test can show 1---PAST INFECTION- which means you have been in ____________________ with HBV and your body _____________________ it. You will now have a ______________________ _________________________ against the virus. 2---CARRIER- this means you carry HBV and can ______________ _____ ______ to others. You are at risk of ______________________ ____________________ ________________________.) - chronic hepatitis - liver ________________________ - liver ___________________ 10. Risk groups - _______ ________________ users - Sexually active ____________________________ - ________________________________ men - Infants and children of immigrants from _______________________ areas - Low socioeconomic level - Household contacts with infected persons - Infant born to positive mother - ________________________________ workers - _________________________________ patients 11. Hep. B is a disease mainly of _____________________ _______________. Most cases are reported by persons age ________ to ________. 12. Occurrence of chronic hepatitis B is largely dependent upon the ___________ at which the disease was acquired. ________ to ________% of infants infected in the first year will develop chronic hepatitis B. That level drops to _________ to ________% if infected between _____ and ______ and only ______ to ________% if infected as an adult. 13. Levels of HBV - High- ________________ , serum, wound exudates - Medium- _________________ , vaginal fluids and _____________________ - Low- _________________ , feces, ____________________ , breast milk and ______________ 14. Important stats - death occurs in ________ to ________% of chronically infected persons due to _____________________ or liver _____________________ - Vaccine licensed for use in US in ____________. Available since for use since ___________ - Estimated 300,000 new infections each year in the U S - ______ ______________!!!!! - Incubation period is __________ to ___________ days - If you get HBV you can also develop a satellite virus called _____________---- can only replicate in cells already infected with HBV - Causes an estimated __________________ to _______________ deaths in the U S each year 15. Treatment for chronic infections - _______________________ effective only 35 to 40% of the time - Adefovir dipivoxil, alpha interferon, and lamivudine Hepatitis C (3rd of Main Types) – Abbreviated (________) 16. A Bloodborne pathogen that is usually passed on by __________________________ use 17. Signs and Symtoms a. Jaundice b. Fatigue c. ____________________ ________________ d. abdominal pain e. loss of __________________________ f. nausea 18. Transmission is a _____________________________ ____________________________ 19. Prevention a. No ____________________ b. Not sharing _____________________ c. Carefully handling sharps d. Standard __________________________ Hepatitis D (abbreviated ________) 20. Occurs only in persons with ________________________________ infection. Virus cannot __________________________ by itself. Can only replicate in the presence of ___________ 21. Transmission is __________________________ 22. Can occur ____________________________________ with Hep. B infection (________-_____________________) or can develop ____________________ in chronic Hep. B patients (__________________ _______________________) 23. Signs and Symptoms are _____________________________, fatigue, ____________________________________ pain, loss of appetite, nausea, ______________________ pain and ____________________ _______________________ Hepatitis E 24. 25. 26. 27. Occurs in persons age __________ to __________ years __________________________ in developed countries like the US Signs and Symptoms are jaundice, fatigue, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, nausea and dark urine Transmission is usually contaminated _________________________ _____________________or _____________________. Found in __________________. 28. Prevention is _______________________________ vaccine and washing hands with soap and water after using the _____________________ or ___________________________ _____ ____________________________. ADDITIONAL NOTES: