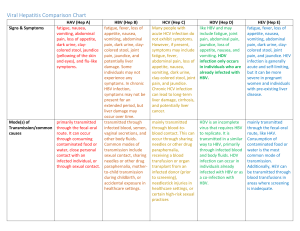
Hepatitis B • The Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a small (3200 base pair) DNA virus with a viral envelope. HBV replicates in the liver cells of humans and other higher primates, and produces an excess of the viral envelope protein (Hepatitis B surface antigen, HBsAg) that circulates in the blood. HBV is transmitted by percutaneous and permucosal exposure to infected blood or other body fluids, including semen and vaginal fluids. In highly endemic areas, HBV is most commonly spread from mother to child at birth, or from person to person in early childhood. It has a worldwide distribution and currently more than 2 billion persons have been infected, with approximately 360 million chronically infected. The outcomes of HBV infection are agedependent and persons with chronic HBV infection have a 15-25% risk of dying prematurely from HBV-related causes include hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, and hepatocellular cancer.