Problem Solving
advertisement

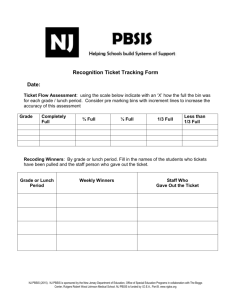
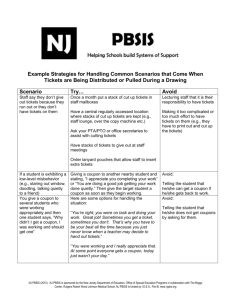
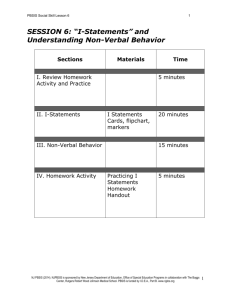
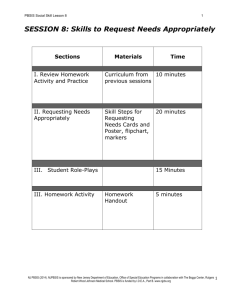
PBSIS Social Skill Lesson 7 1 SESSION 7: Problem-Solving Process Sections Materials I. Review Homework Activity and Practice Skills Time 10 minutes II. Problem-Solving Process Problem-Solving Poster, ProblemSolving Cards for each student 15 minutes III. Practice ProblemSolving Process Flip chart and markers 15 minutes IV. Homework Activity Homework Handout 5 minutes NJ PBSIS (2014). NJPBSIS is sponsored by New Jersey Department of Education, Office of Special Education Programs in collaboration with The Boggs Center, Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School. PBSIS is funded by I.D.E.A., Part B. www.njpbs.org 1 PBSIS Social Skill Lesson 7 2 SESSION 7: PROBLEM-SOLVING PROCESS I. Review Homework Activity and Practice Skills (10 minutes) Purpose: Reflect on students’ experience and comfort level with skills from last session. Go over Homework Handout. Skill instructor should provide additional instruction and practice of skills from previous sessions as needed. II. Problem-Solving Process (15 minutes) Purpose: To teach students how to engage in effective problem-solving and decision-making. Provide overview of problem-solving skills: In any situation, regardless of how you are feeling, you can make a good choice. There is a process you can use to help you make the best choice possible called the problem-solving process. We are going to go through the steps of the problem-solving process and then talk about different examples of how to use the process. Cut up and hand out Problem-Solving Process Cards to each student. Skill instructor goes through the problem-solving steps: Step 1: What is the problem? First, it is important to determine the problem. A helpful way to figure out the problem is to think about how you are feeling and determine what triggered the feeling. So two important questions to ask yourself are, “How do I feel?” and “Why do I feel this way?” Step 2: What are the choices? After you figure out what the problem is, it is important to come up with different possible choices. So in the second step of the problem-solving process it is important to brainstorm different solutions or choices for the problem. When you brainstorm you should list out all possible choices, even if they do not seem perfect at the time. Do not judge the ideas at this point, just list out all possible choices. Step 3: Select the best choice. After you brainstorm ideas and have a lot of possible solutions, the next step is to decide which idea is the best choice. To decide the best choice you need to consider the advantages, or what is good about the solution NJ PBSIS (2014). NJPBSIS is sponsored by New Jersey Department of Education, Office of Special Education Programs in collaboration with The Boggs Center, Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School. PBSIS is funded by I.D.E.A., Part B. www.njpbs.org 2 PBSIS Social Skill Lesson 7 3 idea, and the disadvantages, or what is not good about the solution. Once you have figured out the advantages and disadvantages of each solution you can then see which solution has more advantages and will result in a successful outcome. To help you think about the advantages and disadvantages of each solution there are questions you need to ask yourself about each solution. Let’s brainstorm some questions that you think would be helpful in figuring out the advantages and disadvantages of solutions. Skill instructor should write questions on flip chart and list the following questions if students do not identify them. For each solution, ask yourself: Is the solution acceptable here in this situation or is it against the rules? Is the solution safe or is it dangerous? How will I feel afterwards? Will I feel good about the solution afterwards or will I feel sorry afterwards? How would I feel if someone did this to me? Is this going to make the problem better for a long time or just right away? Explain to students that a problem may need an immediate action or solution but that the student may need to consider long-term solutions to address a reoccurring problem. Once you’ve determined the advantages and disadvantages of each solution, determine which solution has more advantages than disadvantages and which solution has the most important advantages. Step 4: Do it. Once you have looked over your decisions, the next step in the problemsolving process is to choose the best solution and do it. Put the solution in place. Step 5: Did it work? The last step in the problem-solving process is to ask yourself whether the choice you made worked. It is important to ask yourself this question so you can decide if you should use this choice the next time you are in the situation or if you need to try something else. How do you know if the choice worked? Instructor should guide students to consider the following: - Did I get the results that I wanted? If no, why did it not work? What went wrong? How can I improve the situation next time? Do I need to change this solution or do I need to use an entirely different solution? If the solution you chose did not work, go back to your list of possible solutions and try another one. NJ PBSIS (2014). NJPBSIS is sponsored by New Jersey Department of Education, Office of Special Education Programs in collaboration with The Boggs Center, Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School. PBSIS is funded by I.D.E.A., Part B. www.njpbs.org 3 PBSIS Social Skill Lesson 7 4 Read scenario to group. Choose the most appropriate scenario based on function of student behavior. If applicable read both scenarios separately. Attention-motivated scenario: Terrence’s class is having recess. There are some boys playing together and Terrence wants to join in but he doesn’t know how to. He feels sad because he wants to play with the other boys. Escape-motivated scenario: Julia’s teacher assigns the students to read in small groups. Julia doesn’t like to work in groups because she has a hard time reading and other kids laugh when reads. When it’s Julia’s turn to read, just like they always do, the other group members start looking at each other laughing. Julia feels herself getting very embarrassed and angry. Her body starts to feel really hot and she starts to sweat. After reading the scenario, prompt students through the problem-solving process. Step 1: What is (Terrence/Julia) problem? Instructor should have students consider how (Terrence/Julia) is feeling. Prompt students to think about physical clues and triggers. Guide students to identify the problem as (Terrence wanting to play with others/Julia being made fun of). Step 2: What are (Terrence’s/Julia’s) choices? Encourage students to brainstorm a list of choices and not evaluate them. Don’t worry about whether this is a good or bad choice, just think about all the things that (Terrence/Julia) could do. We’ll talk later about which ones are good and bad choices. Possible choices for Terrence’s: asking the boys if he can play, join in the game without asking the other boys, ask the teacher for help, stand by the boys and wait to see if they will ask him if he wants to play, play another game. Possible choices for Julia: walking away, telling the other students how she feels, asking them to stop, yelling at them, telling on them to the teacher, asking another student for help, telling the teacher ahead of time how she feels, asking the teacher for help. Step 3: Select the best choice. . For the choices brainstormed, discuss the following questions with students: Does the choice follow the rules or go against the rules? Is the choice safe or is it dangerous? NJ PBSIS (2014). NJPBSIS is sponsored by New Jersey Department of Education, Office of Special Education Programs in collaboration with The Boggs Center, Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School. PBSIS is funded by I.D.E.A., Part B. www.njpbs.org 4 PBSIS Social Skill Lesson 7 5 How will (Terrence/Julia) feel afterwards? Will (Terrence/Julia) feel good about the solution afterwards or will (he/she) feel sorry afterwards? How will the others in the situation feel? FOR OLDER STUDENTS ALSO DISCUSS: Is this a short-term or long-term solution? Explain to students that a problem may need an immediate action or solution but that the student may need to consider long-term solutions to address a reoccurring problem. Discuss evaluating the choices: - Which solution has the most advantages? - Which solution will result in the best outcome? - Do you think the solution will work? - Which solution has too many disadvantages? (Skill instructor should tell students not to use this solution) Step 4: Do it! Step 5: Did it work? Let’s pretend that (Terrence/Julia) picked the choice that we came up with and it worked. (He/she) felt really good about the situation and so did the people around (him/her). But what if the choice didn’t work, what would (Terrance/Julia) have to do? Discuss with students how sometimes the solution chosen may not work, and when that happens we may have to try something else. III. Practice Problem-Solving Process (15 minutes) Purpose: Provide students with an opportunity to practice the problem-solving process and learn from group members. As a group, go through the Problem-Solving Process: Have students identify problems they have encountered (can refer them to their trigger maps). List problems out on a flip chart. You can also choose examples listed below that are most appropriate based on the function of group member’s behavior. Possible example scenarios to discuss (or can use scenarios group members have identified): - A student comes up to you and says to you, “You are an idiot.” - You are in class and are bored with the assignment. - At lunch, you ask to sit with some students and they say no. - You are walking in the hallway and someone pushes you. NJ PBSIS (2014). NJPBSIS is sponsored by New Jersey Department of Education, Office of Special Education Programs in collaboration with The Boggs Center, Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School. PBSIS is funded by I.D.E.A., Part B. www.njpbs.org 5 PBSIS Social Skill Lesson 7 - You - You - You - You are are are are 6 in class and feel lonely. playing basketball and someone elbows you. in gym class and do not want to participate in the activity. in class and don’t know how to do the assignment. Write the Problem-Solving Process Steps on flip chart and record all responses. You will now take turns practicing using the problem-solving steps. You should go through each of the steps listed and think aloud so we all know what you are thinking at each step. Don’t worry if you get stuck, we’ll help you out! Questions/prompts to facilitate student role-plays Step 1: What is the problem? - How do you know this is a problem? - How do you feel? What cues are signaling to you that you feel a certain way? Why do you feel this way trigger? What was the trigger? Step 2: What are the choices? - How can you calm down in that situation? - Are there relaxation strategies you could use? - Who are people that could help you (friends, peers, adults)? - What are strategies you have seen work for other people in a similar situation? Step 3: Select the best choice (on flip chart have a pro and con column to help students decide which solution is the best) - Is the solution acceptable in this situation or is it against the rules? - Is the solution safe or is it dangerous? - How will you feel afterwards? Will you feel good about the solution afterwards or will you feel sorry afterwards? - How would you feel if someone did this to you? - How will others in the situation feel? - Will this solution keep the problem from happening again in the future? - Which solution has the most advantages? - Which solution will result in the best outcome? - Do you think the solution will work? - Which solution has too many disadvantages? (Skill instructor should tell students not to use this solution) Step 4: Do It Step 5: Did it work? - How will you know if the solution worked or did not work? NJ PBSIS (2014). NJPBSIS is sponsored by New Jersey Department of Education, Office of Special Education Programs in collaboration with The Boggs Center, Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School. PBSIS is funded by I.D.E.A., Part B. www.njpbs.org 6 PBSIS Social Skill Lesson 7 7 - If the solution did not work, what questions should we ask? (e.g. what prevented the solution from working? What can I do differently next time?) - If the solution does not work what else could you try? Direct students to go back to the list of solutions. IV. Assign Homework Activity and Departure (5 minutes) Before the next session, ask students to practice using the problem-solving process. Handout Homework Sheet. Students should come to the next session prepared to discuss their experience using problem-solving in a challenging situation. NJ PBSIS (2014). NJPBSIS is sponsored by New Jersey Department of Education, Office of Special Education Programs in collaboration with The Boggs Center, Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School. PBSIS is funded by I.D.E.A., Part B. www.njpbs.org 7 PBSIS Social Skill Lesson 7 8 Session 7 Homework Problem Solving State the The problem is: problem Think of possible solution Solution Option 1 Evaluate Pro: pros/cons of each solution Con: Solution Option 2 Solution Option 3 Pro: Pro: Con: Con: Choose the best option The best option for me is: Try out the solution Do I need help from anyone? Evaluate how it worked What went well: What should I do differently next time: NJ PBSIS (2014). NJPBSIS is sponsored by New Jersey Department of Education, Office of Special Education Programs in collaboration with The Boggs Center, Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School. PBSIS is funded by I.D.E.A., Part B. www.njpbs.org 8 PBSIS Social Skill Lesson 7 9 Problem Solving Prompt Card State the Problem State the Problem Two Solutions are.. Two Solutions are.. Think about the pros/cons of the options Think about the pros/cons of the options Choose the best option for me Choose the best option for me Try out the option Try out the option Evaluate how it worked Evaluate how it worked State the Problem State the Problem Two Solutions are.. Two Solutions are.. Think about the pros/cons of the options Think about the pros/cons of the options Choose the best option for me Choose the best option for me Try out the option Try out the option Evaluate how it worked Evaluate how it worked NJ PBSIS (2014). NJPBSIS is sponsored by New Jersey Department of Education, Office of Special Education Programs in collaboration with The Boggs Center, Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School. PBSIS is funded by I.D.E.A., Part B. www.njpbs.org 9