El Rancho Unified School District
advertisement

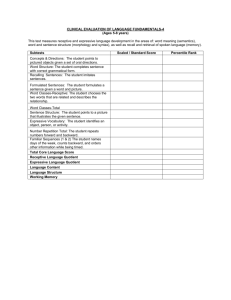
Name Date School District Address Multi- Disciplinary Report/ Speech and Language Report CONFIDENTIAL This report contains confidential information and is the property of School District. Name: Date of Birth: Chronological Age: Gender: Ethnicity: Grade: Parents: Address: Home Phone: Work Phone: Primary Language: EL: School: Date of Report: Assessor: CELDT Level: CONFIDENTIALITY: The following assessment report may contain sensitive information subject to misinterpretation by untrained individuals. Nonconsensual disclosure by unauthorized individuals is prohibited by both the California State Education Code and the Welfare and Institutions Code. REASON FOR REFERRAL: Include information about the source of referral, description of presenting behaviors, and major reason the student was referred. Include information provided by the parent, teacher and student, if applicable. List areas of suspected disability. Example: “STUDENT was referred for evaluation by X due to concerns in the areas of X. Parent expressed concerns with X. Teacher has observed difficulties with X. Based upon the referral information and review of school records, areas of suspected disability include X, X, and X”. EVALUATION PROCEDURES: The assessment included all the components of a comprehensive evaluation required by state regulations, including information provided by STUDENT’S parents or primary caregiver (if the student is younger than 18 years of age). Information regarding STUDENT’S current classroom - Page 1 of 9- Name Date performance (observations and assessments), and the observations of his/her teachers and other providers of instructional or educational services were also included. STUDENT’S primary language, racial, and ethnic background were considered prior to selection and interpretation of evaluation procedures and measures and were administered by qualified personnel. All assessment procedures measure a limited sample of a person’s total repertoire. The selected measures should only be interpreted within the limits of their measured validity. The following procedures were components of the evaluation: PROCEDURES/ASSESSMENTS DATE BACKGROUND INFORMATION: HEALTH AND DEVELOPMENTAL HISTORY: Provide detailed information about developmental milestones, including language and communication. Indicate how you obtained this information (was it through record review, developmental questionnaire, parent interview?) Include any health issues that might impact learning (i.e. frequent ear infections, seizures, cleft palate, oral motor issues, etc) Include information about past vision and hearing screenings, if remarkable, as well as current hearing and vision screening results. Example: “On DATE, STUDENT’S vision and hearing were screened by the district nurse. Vision screening results were/were not within normal limits. Hearing results were/we not within normal limits. (If applicable) STUDENT uses X for amplification and wore X during the assessments. (If applicable) STUDENT wears prescription glasses and wore them during the assessments. STUDENT has/does not have adequate vision and hearing for academic functioning. STUDENT does/does not require any accommodations be made for his/her vision or hearing.” FAMILY HISTORY: Include information about who the child lives with (biological parents, adoptive parents, foster parents, grandparents, relatives). If the child does not live with biological parents, indicate who holds educational rights. LANGUAGE: Indicate the primary language of the home. If the student is an English Learner, include the most recent CELDT scores. Best practice is to conduct a bilingual assessment for any student who is at Beginning, Early Intermediate or Intermediate level. You may also need to consider a - Page 2 of 9- Name Date bilingual assessment for students at Early Advanced level is you believe second language may still be an issue. EDUCATIONAL HISTORY: Include information about number of schools attended, daily school attendance, information from report cards, teacher comments, IEP records, and discipline records. Document student strengths and weaknesses, history of difficulties, and state test scores. PREVIOUS ASSESSMENTS: A thorough record review should be conducted prior to sending out an assessment plan. This will help you determine what areas need to be assessed. You must always assess in all areas of suspected disability for every assessment. If a parent or teacher continues to express concern about something, (i.e. dysfluency), you must assess in this area even if it was ruled out at the last assessment. Include name of assessment, date it was administered and scores. INTERVIEWS Include detailed interview information gathered from the parent(s) or caregivers if the student does not reside with his or her biological parents. Interview questions should focus on the student’s language and communication. See semi- structured interview questions. The interview process is also an opportunity to identify other possible areas of suspected disability. Example: “Parent was interviewed by the SLP on DATE. According to the parent, STUDENT is able to communicate needs by X. When he becomes frustrated, STUDENT has difficulty expressing his thoughts/emotions which results in X behavior. Student has difficulty following directions, for example X”. BEHAVIORAL OBSERVATIONS: Observations should be conducted in: Classroom Unstructured environments During Testing Example: “STUDENT was observed in the classroom on DATE during language arts time. He/she was observed to X. STUDENT was able to follow _ step directions. Student participated in classroom discussion and appeared X. Student was observed during recess on DATE. STUDENT’S interaction with peers was X. STUDENT conversed with peers in English/Spanish”. STUDENT was cooperative and compliant during testing. He/She conversed comfortably with the examiner and rapport was easily established. He/She put forth a good effort and remained attentive throughout the testing sessions. He/She appeared to - Page 3 of 9- Name Date enjoy the one to one nature of the assessment. His/her motivation during testing appeared to be consistent/inconsistent. STUDENT’S response time to verbal tasks was X. STUDENT’S language consisted of single words, phrases and complete sentences. He/she exhibited good attending skills and contributed good effort toward testing. For example STUDENT X. Other behaviors noted during testing include X. VALIDITY OF ASSESSMENTS: Your report must include a statement about the validity of the assessments conducted. If the results are not a valid estimate of student’s ability, indicate so here. Example “A credentialed speech language pathologist administered all speech and language testing. Test and assessment materials and procedures used for the purposes of assessment and placement of individuals with exceptional needs were selected and administered so as not to be racially, culturally, linguistically, or sexually discriminatory. Child’s dominant language was considered in selecting assessment instruments. Tests have been validated for the specific areas of educational need. The results that have been provided accurately reflect the child’s current abilities as measured by the assessment procedures. CURRENT ASSESSMENTS: Include a brief description of the tests used and a brief description of scores. Save your analysis for the eligibility section of the report. Clinical Evaluation of Language Fundamentals – Fourth Edition The Clinical Evaluation of Language Fundamentals-4th Edition, is an individually administered clinical for the identification, diagnosis, and follow-up evaluation of language and communication disorders for people for 5-21 years old. Subtest Scaled Score Core Language (13-21) Receptive Language (13-21) Recalling Sentences Formulated Sentences Word Classes – Receptive Word Classes – Expressive Word Classes – Total Word Definitions Understanding Spoken Paragraphs Sentence Assembly Semantic Relationships Sum of Subtest Scaled Scores - Page 4 of 9- Expressive Language (9-21) Language Content (13-21) Language Memory (13-21) Name Date Standard Score Confidence Interval (90% Level) Percentile Rank Percentile Rank Confidence Interval Descriptive Classification The Receptive One Word Picture Vocabulary Test - Fourth Edition (ROWPVT-4) The Receptive One Word Picture Vocabulary Test – Fourth Edition (ROWPVT-4) is an individually administered, norm-referenced assessment of an individual’s ability to match a spoken word with an image of an object, action, or concept. Appropriate for English – speaking individuals ages 2 through 80+ years. A word is spoken by the examiner and the examinee indicates (by pointing or verbal response) which of the four illustrations on a page matches the word. Standard Score Percentile Rank You may choose to summarize your assessment data after each assessment but leave your eligibility analysis for the Summary and Eligibility section. SUMMARY AND ELIGIBILITY: This is the section of your report where you interpret all the assessment data as it relates to eligibility criteria. ELIGIBLITY STATEMENT In order to qualify for special education services under the eligibility category of speech and language , the student must: 1) demonstrate difficulty understanding or using spoken language; 2) to such an extent that it adversely affects his or her educational performance; and 3) it cannot be corrected without special education and related services. In addition, the student must meet the definition of having at least one of five possible disorders in any of the following areas: 1) articulation; 2) abnormal voice; 3) fluency; 4) language disorder; or 5) hearing loss which results in a language or speech disorder. Student has a suspected speech and language disorder in (insert all areas tested) of spoken language. Each of these areas will be addressed in turn. - Page 5 of 9- Name Date Articulation Pursuant to 5 CCR section 3030(c)(1)(A) a student qualifies as having an articulation disorder if: 1) the pupil displays reduced intelligibility or an inability to use the speech mechanism; 2) which significantly interferes with communication; and 3) it attracts adverse attention. Significant interference in communication occurs when the pupil's production of single or multiple speech sounds on a developmental scale of articulation competency is below that expected for his or her chronological age or developmental level, and which adversely affects educational performance. Reduced intelligibility or an inability to us the speech mechanism Should address both and state whether either one is met. Significantly interferes with communication Remember the definition above. Attracts adverse attention Courts view this exactly as it sounds…are student’s peers looking at the student differently due to student’s speech. Adversely affects academic performance Grades, performance on benchmarks, state testing, classroom participation, teacher interview. Also consider behavior. PRESCHOOL: Look at the preschool learning foundations for expected age appropriate skills. Requires special education and related services Are there less restrictive interventions? The law prefers general education accommodations to special education services. Based on the foregoing, Student does/does not meet the eligibility requirements for an articulation disorder. Language Disorder Pursuant to 5 CCR section 3030(c)(1)(4) a student “has an expressive or receptive language disorder when he or she meets one of the following criteria: (A) The pupil scores at least 1.5 standard deviations below the mean, or below the 7th percentile, for his or her chronological age or developmental level on two or more standardized tests in one or more of the following areas of language development: morphology, syntax, semantics, or pragmatics. When standardized tests are considered to be invalid for the specific pupil, the expected language performance level shall be determined by alternative means as specified on the assessment plan, or (B) The pupil scores at least 1.5 standard deviations below the mean or the score is below the 7th - Page 6 of 9- Name Date percentile for his or her chronological age or developmental level on one or more standardized tests in one of the areas listed in subsection (A) and displays inappropriate or inadequate usage of expressive or receptive language as measured by a representative spontaneous or elicited language sample of a minimum of fifty utterances. The language sample must be recorded or transcribed and analyzed, and the results included in the assessment report. If the pupil is unable to produce this sample, the language, speech, and hearing specialist shall document why a fifty utterance sample was not obtainable and the contexts in which attempts were made to elicit the sample. When standardized tests are considered to be invalid for the specific pupil, the expected language performance level shall be determined by alternative means as specified in the assessment plan.” At Least Two Standardized Tests – Subsection A Expressive or receptive language deficits in morphology, syntax, semantics, or pragmatics on two standardized tests Must be 1.5 standard deviation below mean or below 7th percentile for age or developmental level. Adversely affects academic performance Grades, performance on benchmarks, state testing, classroom participation, teacher interview. Also consider behavior. PRESCHOOL: Look at the preschool learning foundations for expected age appropriate skills. Requires special education and related services Are there less restrictive interventions? The law prefers general education accommodations to special education services. Based on the foregoing, student does/does not meet the eligibility requirements for a language disorder due to expressive/receptive deficits in _____________________ areas. One Standardized Test and a Language Sample – Subsection B Expressive or receptive language deficits in morphology, syntax, semantics, or pragmatics on one standardized test Language sample Minimum is 50 utterances. Recorded or transcribed and analyzed. If not obtainable, state why including context. Adversely affects academic performance Grades, performance on benchmarks, state testing, classroom participation, teacher interview. Also consider behavior. PRESCHOOL: Look at the preschool learning foundations for expected age appropriate skills. - Page 7 of 9- Name Date Requires special education and related services Are there less restrictive interventions? The law prefers general education accommodations to special education services. Based on the foregoing, student does/does not meet the eligibility requirements for a language disorder due to expressive/receptive deficits in _____________________ areas. Abnormal Voice A pupil has an abnormal voice which is characterized by persistent, defective voice quality, pitch, or loudness. Persistent and defective voice quality, pitch or loudness Must be persistent, i.e., constant! Adversely affects academic performance Grades, performance on benchmarks, state testing, classroom participation, teacher interview. Also consider behavior. PRESCHOOL: Look at the preschool learning foundations for expected age appropriate skills. Requires special education and related services Are there less restrictive interventions? The law prefers general education accommodations to special education services. Based on the foregoing, student does/does not meet the eligibility requirements for abnormal voice. Fluency Disorder A pupil has a fluency disorder when the flow of verbal expression including rate and rhythm adversely affects communication between the pupil and listener. Deficit in the flow of verbal expression, including rate and rhythm That adversely affects communication between the pupil and listener Interviews with the teacher is key here. Adversely affects academic performance Grades, performance on benchmarks, state testing, classroom participation, teacher interview. Also consider behavior. PRESCHOOL: Look at the preschool learning foundations for expected age appropriate skills. Requires special education and related services - Page 8 of 9- Name Date Are there less restrictive interventions? The law prefers general education accommodations to special education services. Based on the foregoing, student does/does not meet the requirements for a fluency disorder. Hearing Loss A student qualifies for speech and language with a hearing loss which results in a language or speech disorder and significantly affects educational performance. Hearing loss Speech and language disorder Student must also meet the eligibility of one of the other speech and language eligibilities. Adversely affects academic performance Grades, performance on benchmarks, state testing, classroom participation, teacher interview. Also consider behavior. PRESCHOOL: Look at the preschool learning foundations for expected age appropriate skills. Requires special education and related services Are there less restrictive interventions? The law prefers general education accommodations to special education services. Based on the foregoing, student does/does not meet the requirements of a speech and language impairment due to hearing loss. Example: “STUDENT meets eligibility as a student with ________ disability. Final determination will be made by the IEP team.” Recommendations: If the student is eligible for services, provide a recommendation for services (including frequency and duration) Accommodations and modifications to support language and communication in the classroom. _______________________________________ Signature - Page 9 of 9-
![What Is Language? What Is Speech? [en Español] Kelly`s 4-year](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/007027130_1-6ae911bbc18a3f7f2409aa622adfa71a-300x300.png)