Questionnaire
advertisement

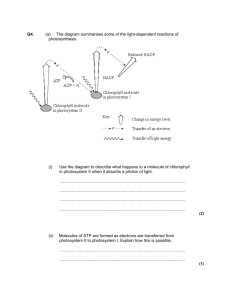
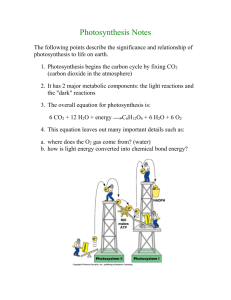
Photosynthesis Questionnaire The paragraph below describes the events of the light dependent reactions. Fill in the blanks in the paragraph. _______________________1 _______________________2 _______________________3 _______________________4 _______________________5 _______________________6 _______________________7 _______________________8 _______________________9 ______________________10 ______________________11 ______________________12 ______________________13 ______________________14 ______________________15 ______________________16 ______________________17 ______________________18 ______________________19 ______________________20 ______________________21 ______________________22 ______________________23 ______________________24 ______________________25 ______________________26 ______________________27 ______________________28 ______________________29 ______________________30 ______________________31 ______________________32 ______________________33 ______________________34 ______________________35 ______________________36 ______________________37 ______________________38 ______________________39 ______________________40 ______________________41 ______________________42 ______________________43 ______________________44 ______________________45 ______________________46 ______________________47 Photosynthesis occurs in the part of the cell called the ___1___. Inside this part of the cell are flattened sacs called ___2___. Within the membranes of these flattened sacs the ___3___ reactions will occur. Large stacks of these sacs are called ___4___. Surrounding these flattened sacs is a dense solution called the ___5___. In this solution, the ___6___reactions will occur. The purpose of photosynthesis is to take the reactants ___7___, ___8___, and ___9___ and produce the products of ___10___ and ___11___. A ___12___is a collection of chlorophyll molecules that serve as the light collecting unit of photosynthesis. These chlorophyll molecules are found embedded in the ___13___membranes . Let’s start with photosystem II. Chlorophyll molecules in photosystem II absorb the ___14___from the sun. The ___15___ of these chlorophyll molecules become very excited. The ___16___are boosted to a higher energy level and are passed to an ___17___. The electrons that were lost from these molecules of ___18___ must now be replaced. Molecules of ___19___ are split and the ___20___ from this are used to replaced the electrons that were lost. ___21___ from the water is considered a waste product and is ___22___. The high energy electrons now move down the ___23___ as they are passed from ___24___ to ___25___. As the electrons are passed down this electron transport chain, protein molecules use the energy from these electrons to create ___26___. The electrons from photosystem II arrive at ___27___. The ___28___ molecules of photosystem I absorb ___29___ from the sun and use it to reenergize the electrons. These electrons are passed down a second ___30___ to the electron acceptor called ___31___. NADP+ joins with these electrons and one H+ to form ___32___. ATP is actually formed when ___33___ ions flow through ___34___ from an area of ___35___ concentration inside the thylakoid to an area of ___36___ concentration outside the thylakoid. As hydrogen passes through the enzyme ___37___ the protein spins, creating energy. This energy is used to convert ___38___ to ___39___ Hydrogen ions must now be pumped back inside the ___40___ from the ___41___. These will be pumped against the concentration gradient and will require ___42___. The energy for this process comes from ___43___. Was any glucose produced in these light dependent reactions? ___44___. The purpose of the light dependent reactions is to produce ___45___ and ___46___so that they can be used in the ___47___. 1 48. What is the relationship between sunlight and chlorophyll? Why are both of these needed for photosynthesis? 49. What two substances are produced by the light dependent reactions that are required for the light independent reactions? 50. What is the role of plant pigments in the light dependent reactions? 51. What is the function of ATP synthase? How does it work? 52. How does light enter the light dependent reactions? 53. What happens to the electrons that are lost by photosystem II? What happens to the electrons that are lost by photosystem I? How are electrons that are lost by the chlorophyll molecules replaced? 54. Name three substances that are produced when water molecules are split during the light dependent reactions. 55. The air contains oxygen that we need to breathe. What is the source of this oxygen? 56. What is the relationship between these two terms: grana / stroma 57. What happens to the components of water molecules that are split during the light reactions of photosynthesis? 58. How is ATP actually produced in photosynthesis? 2 59. _____________________ This adds a phosphate group to ADP to form ATP. 60. _____________________ This is a cluster of pigment molecules embedded in the thylakoid membrane. 61. ______________________ This is produced in the light dependent reactions, but is released and does not participate any further in photosynthesis. 62. ______________________ Flattened sacs containing chlorophyll. 63. ______________________ The dense solution found inside the chloroplast. 64. 65. ______________________ The molecule that serves as the carrier of high energy electrons between the thylakoids and the stroma. ______________________ What substances are required for the light dependent reactions? 66. ______________________ What substances are required for the light independent reactions? _________67 Where would one find photosystems and electron transport chains? (1) along the cristae membrane (2) embedded in the outer membrane of the chloroplast (3) embedded in the inner membrane of the chloroplast (4) embedded in the thylakoid membranes (5) in the stroma of the chloroplast. _________68 What is produced in the light dependent reactions that is not needed for the light independent reactions? (1) water (2) carbon dioxide (3) NADPH (4) ATP (5) oxygen __________69 Which one of the following is true of both photosystem I and photosystem II? (1) They both absorb light energy which is used to energize electrons in chlorophyll-a molecules. (2) Each receives electrons from the other photosystem. (3) Both photosystems produce NADPH. (4) Both photosystems split molecules of water. (5) Both photosystems produce glucose molecules. __________70 Which of the following is the most immediate role of water in the light dependent reactions? (1) It is split so that it can donate electrons to NADP+ to form NADPH. (2) It is split and then can donate electrons to photosystem II. (3) Water accepts electrons from the electron transport chain. (4) The hydrogen from water is used to accept electrons from ADP. __________71 Which of the following is not produced during the light dependent reactions? (1) NADPH (2) oxygen (3) glucose molecules (4) ATP (5) hydrogen ions __________72 Which one of the following occurs at the end of the electron transport chain of photosystem I? (1) Electrons combine with NADP+ to form NADPH (2) ATP is produced (3) The electrons from photosystem II are replaced. (4) Water molecules are split. (5) Glucose is produced. 3 True/False _________73 High energy electrons move along the thylakoid membrane from photosystem I to photosystem II. _________74 The oxygen that is released into the atmosphere comes from the splitting of a carbon dioxide molecule. _________75 Photosynthesis is the process of converting light energy into the chemical energy of a molecule of glucose. _________76 ATP molecules are produced during the light independent reactions of photosynthesis. _________77 Carbon dioxide is produced during photosynthesis. _________78 The light dependent reactions takes place along the thylakoid membranes of the mitochondria. _________79 Chlorophyll molecules are found embedded along the thylakoid membrane. _________80 In the light dependent reactions, electrons pass from water to chlorophyll to electron transport chains, ultimately producing NADPH. _________81 There are two photosystems but only one electron transport chain. 4 Answers: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. chloroplast thylakoids light dependent reactions grana stroma light independent reactions carbon dioxide water light energy glucose oxygen photosystem thylakoid energy electrons electrons electron transport chain chlorophyll water electrons oxygen released to the atmosphere electron transport chain photosystem II photosystem I ATP photosystem I chlorophyll energy electron transport chain NADP+ NADPH H+ ATP synthase high low ATP synthase ADP ATP thylakoid stroma energy the electron transport chain no ATP NADPH light independent reactions 5 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. 60. 61. 62. 63. 64. 65. 66. 67. 68. 69. 70. 71. 72. 73. 74. 75. 76. 77. 78. 79. 80. 81. The chlorophyll is able to absorb all the wavelengths of light (except green) from the visible spectrum. This energizes the electrons of chlorophyll. The chlorophyll is needed to absorb the energy of the sun, and the sun is needed to energize the electrons found in chlorophyll molecules. ATP and NADPH Pigments absorb the visible spectrum of light causing electrons in pigments to become energized. ATP synthase is a protein embedded in the thylakoid membrane that converts ADP to ATP. Hydrogen ions flow through ATP synthase from an area of high concentration inside the thylakoid to an area of low concentration in the stroma. As the hydrogen ions flow through ATP synthase, it turns a rotor. This generates the energy used to bind the third phosphate onto ADP to form ATP. The light energy is absorbed by the molecules of chlorophyll. Electrons from photosystem II are passed down the electron transport chain to photosystem I. Electrons from photosystem I are passed down an electron transport chain and are accepted by NADP+ to form NADPH. The replacement electrons come from the splitting of water molecules. ATP, NADPH, oxygen The oxygen is released to the atmosphere when water molecules are split. Grana: the site of the light dependent reactions Stroma: the site of the light independent reactions The oxygen is released to the atmosphere. The hydrogen atoms are used to produce ATP and NADPH. ATP synthase is a protein embedded in the thylakoid membrane that converts ADP to ATP. Hydrogen ions flow through ATP synthase from an area of high concentration inside the thylakoid to an area of low concentration in the stroma. As the hydrogen ions flow through ATP synthase, it turns a rotor. This generates the energy used to bind the third phosphate onto ADP to form ATP. ATP synthase photosystem oxygen thylakoids stroma NADP+ water, sunlight, chlorophyll carbon dioxide, RuBP, ATP, NADPH 4 5 1 2 3 1 False False True False False False True True False 6