File
advertisement
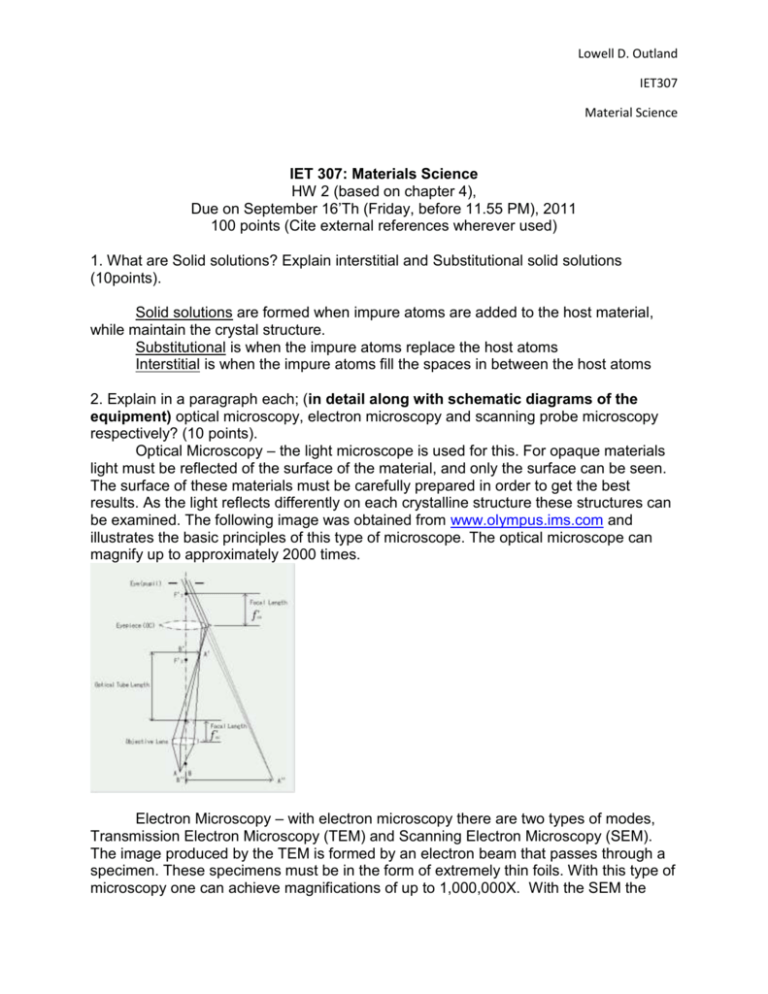
Lowell D. Outland IET307 Material Science IET 307: Materials Science HW 2 (based on chapter 4), Due on September 16’Th (Friday, before 11.55 PM), 2011 100 points (Cite external references wherever used) 1. What are Solid solutions? Explain interstitial and Substitutional solid solutions (10points). Solid solutions are formed when impure atoms are added to the host material, while maintain the crystal structure. Substitutional is when the impure atoms replace the host atoms Interstitial is when the impure atoms fill the spaces in between the host atoms 2. Explain in a paragraph each; (in detail along with schematic diagrams of the equipment) optical microscopy, electron microscopy and scanning probe microscopy respectively? (10 points). Optical Microscopy – the light microscope is used for this. For opaque materials light must be reflected of the surface of the material, and only the surface can be seen. The surface of these materials must be carefully prepared in order to get the best results. As the light reflects differently on each crystalline structure these structures can be examined. The following image was obtained from www.olympus.ims.com and illustrates the basic principles of this type of microscope. The optical microscope can magnify up to approximately 2000 times. Electron Microscopy – with electron microscopy there are two types of modes, Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) and Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM). The image produced by the TEM is formed by an electron beam that passes through a specimen. These specimens must be in the form of extremely thin foils. With this type of microscopy one can achieve magnifications of up to 1,000,000X. With the SEM the Lowell D. Outland IET307 Material Science surface of a specimen to be examined need not be polished, etched or made into thin foils. It must however be electrically conductive. Therefore on nonconductive materials a thin metallic coating needs to be applied. This type of microscopy has a magnification range from 10 to in excess of 50,000. Scanning Probe Microscopy- This is a relatively new concept. There are several different varieties of this microscope. This differs from optical and electron microscopy in the terms that it does not use reflected light or electrons to produce an image, instead this microscope generates a topographical map on an atomic scale. Some of the features of this microscope are,1) magnification of up to 10 9X with greater resolutions, 2) three dimensional images are provided, and 3) some SPM’s can operate in a variety of environments(such as in a vacuum or under water). 3. What makes plain carbon steel harder than pure iron? (5 points) Carbon steel is harder because the carbon steel alloy is a more dense material giving it a greater bonding strength. 4. An ASTM grain size determination is being made from a photomicrograph of a metal at a magnification of 100X. What is the ASTM grain-size number of the metal if there are 64 grains per square inch? (10 points). Using the formula: n = log N / log 2 (log64/log2)+1 = 7 The ASTM grain size is 7. 5. Calculate the energy for vacancy formation in silver, given that the equilibrium number of vacancies at 8000C (1073 K) is 3.6 * 1023 m-3. The atomic weight and density (at 8000 C) for silver are, respectively, 107.9 g/mol and 9.5 g/cm3. (10 points) = 1.10 eV/atom 6. What is the composition, in weight %, of an alloy that consists of 15 atomic % Au and 85 atomic % Pb? (10 points) C1 = M1/M1+M2 x100 C1 = (107.87/(107.87+207.19))x100 C2 = (207.19/(107.87+207.19))x100 C1 = 34.23 Au C2 = 65.76 Pb Lowell D. Outland IET307 Material Science 7. In structural applications, why do we use alloys rather than pure metals? (5 points) As a general rule alloys are normally stronger than pure metals. 8. Pure copper is strengthened by addition of small concentration of Be. What mechanism of strengthening is this related to? (5 points). Precipitation hardening. 9. A slab of steel is transformed into a car chassis. Does this process involve plastic or elastic deformation? (5 points) In order for the chassis to maintain its shape plastic deformation would have to be used. 10. Why would metals behave as brittle materials without dislocations? (5 points) Without dislocations the crystals are aligned is a row making the metal more brittle than if they were not aligned. 11. What is added to an alumina crystal to turn it into a ruby crystal? (5 points) To turn an alumina crystal into a ruby crystal you need to add a small amount of chromium, this gives it the red coloring. 12. Sterling silver consists of approximately 93 wt% silver and 7 wt% copper. Discuss all the ways by which the addition of 7 wt% copper is beneficial. (5 points) The copper enhances the strength of the silver while keeping its natural resistance to corrosion. 13. Describe the structure of a grain boundary. Why are grain boundaries favorable sites for the nucleation and growth of precipitates? (5 points) The grain boundary is a boundary separating two small grains and having different crystallographic orientations. Lowell D. Outland IET307 Material Science 14. What are edge and screw dislocations? (5 points) An edge dislocation is a linear defect associated with the lattice distortion close to the end of an extra half plane of atoms within a crystal. A screw dislocation is a linear defect created when normally parallel planes are joined together to form a helical ramp. 15. What are a solute and a solvent? Give 5 examples of a solute and a solvent from our daily lives? (5 points) A salute is the component that makes up the smallest portion of a solution. A solvent is the component that makes up the largest portion of a solution, and dissolves the solute. Examples include: Salute Solvent Kool Aid Water Paint Thinner Laundry detergent Water Sodium Bicarbonate Water Cocoa Milk








