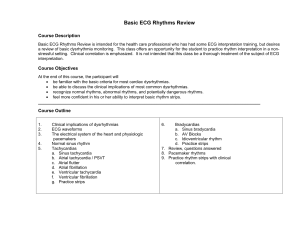
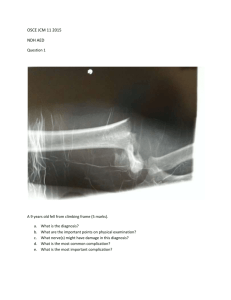
Cardiac arrhythmias
advertisement

Subject 9 - Cardiac arrhythmias (4 hours) Part I. Classification of cardiac rhythm and conduction. Mechanisms. Arrythmia. Paroxysmal tachycardia (atrial, nodal, ventricular ) (2 hours) Place Classroom , Department of Cardiology . Purpose Students must know: • Classification of rhythm and conduction disorders . • Electrophysiological mechanisms of ectopic arrhythmias (reverse input excitation wavelength , increasing automaticity ) and the possibility of their recognition in the clinic. • Features of hemodynamic , clinics, flow , ECG diagnosis and differential diagnosis of ectopic arrhythmias ( various options extrasystoles , paroxysmal tachycardia ) . • Classification of antiarrhythmic drugs . • Principles of treatment and prevention, especially the treatment of various clinical variants . To Able: • Based on the examination of the patient with heart rhythm disorder formulate the final clinical diagnosis and treatment. Professional orientation of students High prevalence of cardiac arrhythmias , the need to determine their knowledge of the tactics of the examination and treatment of patients with various cardiac diseases. The need to take urgent action in case of emergency . Base level of knowledges and abilities № Discipline To know 1. Anatomy Heart Anatomical structure 2. Histology Structure and function of the myocardium and cardiac conduction system 3. Biochemistry Biochemistry metabolism 4. Pathophysiology Mechanisms disturbances To able myocardial To interpret lipidogramm Rate of rhythm 5. Propedevtik diseases of internal Semiotics arrhythmias of cardiac Evaluate ECG Plan of practical employment № Elements of practical employments Time(minutes) 1. Verification of present's students 5 2. Entrance control and his analysis 10 3. Distributing * patients for Supervision ( card or clinical tasks ) 5 4. Review * patients or study of educational hospital chart 20 5. Discussion of findings, formulation of previous diagnosis, determination of methods of additional inspection of patient, interpretation of their results, formulation of final diagnosis and plan of treatment 15 6. Exercises with clinical formulations for solving clinical situation tasks 10 7. Output control of knowledge and its evaluation 10 8. Results and final assessment of knowledge and skills of students and tasks to self- preparation for the next lesson 5 Note: * - in the case of patients absence in clinical, practice can be made in the form of preparation and decision of situational tasks. List of theoretical questions addressed in class 1. Classification of rhythm and conduction disorders . 2 . Electrophysiological mechanisms of ectopic arrhythmias (reverse input excitation wavelength , increasing automaticity ) and the possibility of their recognition in the clinic. 3 . Features of hemodynamic , clinics , current, ECG - diagnosis and differential diagnosis of ectopic arrhythmias ( extrasystoles different options , paroxysmal tachycardia ) . 4 . Classification of antiarrhythmic drugs . 5 . Principles of treatment and prevention, especially the treatment of various clinical variants . Method of leadthrough of practical employment * On the first employment teacher hold instructing from accident (if there are such terms) which registers in the magazine of teacher's signature of student prevention. * Students answer in writing on the tests of base knowledges entrance control. Then a teacher distributes students for kuration patients and determines them a task. № Task Teasher's students pointing to Teacher's note for students 1. To provide curation of 1. Possible arrhythmias Pay special attention to the patient diagnosed with characteristic clinical manifestations 2 . Signs of underlying with extrabeats, and causes a variety of cardiac disease paroxysmal tachycardia arrhythmias 3 . Characteristic changes in the ECG , Holter ECG monitoring , echocardiography A teacher works in obedience to the plan of organization of employment, in the end - initial control of knowledges. Before completion of employment teacher announce his results with the estimation of every student and declares the theme of next session. Forms and methods of self-control Tests 1. Sign indicates the most likely nature of supraventricular paroxysmal tachycardia ? A. Absence of P wave B. QRS duration less than 0.12 sec. C. Negative prong T. D. Vagal negative samples . E. Tachycardia over 200 min . 2 . Sign indicates the most likely nature of ventricular paroxysmal tachycardia ? A. Absence of P wave B. QRS duration greater than 0.12 seconds. C. Negative prong T. D. Vagal negative samples . E. Tachycardia over 200 min . Situational tasks 1. A young man of 16 years complains of feeling a strong heartbeat , which arose suddenly. OBJECTIVE: Funky . Skin and mucous normal color . Tony loud heart , tachycardia, heart rate = PS = 220 min. , BP - 130/70 mm Hg. Art. On ECG - regular rhythm , QRS = 0,09 s, P wave can be determined. Your preliminary diagnosis . Clinical management of the patient. 2 . Male 67 years with acute myocardial infarction on the first day of the disease complain of general weakness , shortness of breath . OBJECTIVE: Acrocyanosis . RR - 28 min . Tony heart tones , tachycardia, blood pressure - 110/60 mm Hg. Art. On ECG - regular rhythm , RR = 0,3 with , QRS = 0,14 s, P wave can be determined. Your preliminary diagnosis . Clinical management of the patient. Ilustrative material 1. Table and slides classification of cardiac arrhythmias and conduction classification of antiarrhythmic agents . 2 . Educational histories . 3 . Audiocassettes rhythm disorders . 4 . Sets ECG arrhythmia . 5 . Set situational problems with standards responses set of tests with the standards of the responses ( according to the number of students ) . Sources of information (literature) Basic: Therapy. Course of lectures. Simferopol. -2003.- 444p. Additional: 1. Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine 18th edition. .org) 2. ESC Guidelines. Cardiovascular medicine. (Www.escardio.org / guidelines) The program of preparation students to the theme To learn: • Classification of rhythm and conduction disorders . • Electrophysiological mechanisms of ectopic arrhythmias (reverse input excitation wavelength , increasing automaticity ) and the possibility of their recognition in the clinic. • Features of hemodynamic , clinics, flow , ECG diagnosis and differential diagnosis of ectopic arrhythmias ( various options extrasystoles , paroxysmal tachycardia ) . • Classification of antiarrhythmic drugs . • Principles of treatment and prevention, especially the treatment of various clinical variants . draw: • ECG pattern in a paroxysm of supraventricular tachycardia . To Able: • Establish a definitive diagnosis of supraventricular and ventricular arrhythmias , paroxysmal arrhythmias, assign the necessary examination and treatment. Note the use of modern methods of instrumental examination of heart rhythm disturbances . Theme: (4 Cardiac arrhythmias hours) Part 2. Flutter (TA) and atrial fibrillation (AF). Electrophysiological mechanisms. Classification, characteristics of hemodynamic , and clinic flow. ECG diagnosis and differential diagnosis of TP and FP. Clinical management of differentiated therapy and prophylaxis (2 hours) Place Classroom , Department of Cardiology . Purpose Students must know: • Classification of rhythm and conduction disorders . • Electrophysiological mechanisms of TP and FP , the possibility of their recognition in the clinic. • Features of hemodynamic , clinics, flow , ECG diagnosis and differential diagnosis of TP and FP ( different variants of TP and FP , other arrhythmias ) . • Classification of antiarrhythmic drugs . • management tactics , differentiated treatment and prophylaxis of various clinical variants ( with different disease entities , taking into account the patient's condition and hemodynamics ) . To Able: • Based on the examination of the patient with heart rhythm disorder formulate the final clinical diagnosis and treatment. Professional orientation of students Flutter and AF are among the most common cardiac arrhythmia encountered in various disease entities and largely determine the prognosis of the disease . Their knowledge is necessary to determine the tactics of examination and treatment of patients with various cardiac pathology , to take urgent decisions in case of emergency . Base level of knowledges and abilities № Discipline To know 6. Anatomy Heart Anatomical structure 7. Histology Structure and function of the myocardium and cardiac conduction system 8. Biochemistry Biochemistry metabolism To able myocardial To interpret lipidogramm Rate 9. Pathophysiology 10. Propedevtik diseases of Mechanisms disturbances internal Semiotics arrhythmias of of rhythm cardiac Evaluate ECG Plan of practical employment № Elements of practical employments Time(minutes) 9. Verification of present's students 5 10.Entrance control and his analysis 10 11.Distributing * patients for Supervision ( card or clinical tasks ) 5 12.Review * patients or study of educational hospital chart 20 13.Discussion of findings, formulation of previous diagnosis, determination of methods of additional inspection of patient, interpretation of their results, formulation of final diagnosis and plan of treatment 15 14.Exercises with clinical formulations for solving clinical situation tasks 10 15.Output control of knowledge and its evaluation 10 16.Results and final assessment of knowledge and skills of students and tasks to self- preparation for the next lesson 5 Note: * - in the case of patients absence in clinical, practice can be made in the form of preparation and decision of situational tasks. List of theoretical questions addressed in class 1. Classification of rhythm and conduction disorders . 2 . Electrophysiological mechanisms of TP and FP and the possibility of their recognition in the clinic. 3 . Features of hemodynamic , clinics , current, ECG - diagnosis and differential diagnosis of TP and FP ( different options ) . 4 . Classification of antiarrhythmic drugs . 5 . Clinical management , differentiated treatment and prophylaxis of various clinical variants ( with different disease entities , taking into account the patient's condition and hemodynamics ) . Method of leadthrough of practical employment * On the first employment teacher hold instructing from accident (if there are such terms) which registers in the magazine of teacher's signature of student prevention. * Students answer in writing on the tests of base knowledges entrance control. Then a teacher distributes students for kuration patients and determines them a task. № Task 1. To provide curation of 1. Rhythm disturbances , Pay special attention to the patient diagnosed with presence pulse deficit characteristic clinical manifestations AF or Flutter and causes a variety of abnormal 2 . Signs of underlying heart rhythm , timing arrhythmias disease Teasher's students pointing to Teacher's note for students 3 . Characteristic changes in the ECG , Holter ECG monitoring , the dimensions of the walls and chambers of the heart in echocardiography A teacher works in obedience to the plan of organization of employment, in the end - initial control of knowledges. Before completion of employment teacher announce his results with the estimation of every student and declares the theme of next session. Forms and methods of self-control Tests 1. Sign indicates the most likely nature of supraventricular paroxysmal tachycardia ? A. Absence of P wave B. QRS duration less than 0.12 sec. C. Negative prong T. D. Vagal negative samples . E. Tachycardia over 200 min . 2 . Sign indicates the most likely nature of ventricular paroxysmal tachycardia ? A. Absence of P wave B. QRS duration greater than 0.12 seconds. C. Negative prong T. D. Vagal negative samples . E. Tachycardia over 200 min . Situational tasks 1. A young man of 16 years complains of feeling a strong heartbeat , which arose suddenly. OBJECTIVE: Funky . Skin and mucous normal color . Tony loud heart , tachycardia, heart rate = PS = 220 min. , BP - 130/70 mm Hg. Art. On ECG - regular rhythm , QRS = 0,09 s, P wave can be determined. Your preliminary diagnosis . Clinical management of the patient. 2 . Male 67 years with acute myocardial infarction on the first day of the disease complain of general weakness , shortness of breath . OBJECTIVE: Acrocyanosis . RR - 28 min . Tony heart tones , tachycardia, blood pressure - 110/60 mm Hg. Art. On ECG - regular rhythm , RR = 0,3 with , QRS = 0,14 s, P wave can be determined. Your preliminary diagnosis . Clinical management of the patient. Ilustrative material 1. Table and slides classification of cardiac arrhythmias and conduction classification of antiarrhythmic agents . 2 . Educational histories . 3 . Audiocassettes rhythm disorders . 4 . Sets ECG arrhythmia . 5 . Set situational problems with standards responses set of tests with the standards of the responses ( according to the number of students ) . Sources of information (literature) Basic: Therapy. Course of lectures. Simferopol. -2003.- 444p. Additional: 1. Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine 18th edition. .org) 2. ESC Guidelines. Cardiovascular medicine. (Www.escardio.org / guidelines) The program of preparation students to the theme To learn: • Classification of rhythm and conduction disorders . • Electrophysiological mechanisms of ectopic arrhythmias (reverse input excitation wavelength , increasing automaticity ) and the possibility of their recognition in the clinic. • Features of hemodynamic , clinics, flow , ECG diagnosis and differential diagnosis of ectopic arrhythmias ( various options extrasystoles , paroxysmal tachycardia ) . • Classification of antiarrhythmic drugs . • Principles of treatment and prevention, especially the treatment of various clinical variants . draw: • ECG pattern in a paroxysm of supraventricular tachycardia . To Able: • Establish a definitive diagnosis of supraventricular and ventricular arrhythmias , paroxysmal arrhythmias, assign the necessary examination and treatment. Note the use of modern methods of instrumental examination of heart rhythm disturbances .