Competencies
advertisement

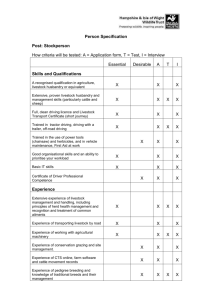
LIVESTOCK MANAGEMENT ACTIVITY/COURSE CODES 5646, 5647 COURSE DESCRIPTION: Livestock Management courses are designed to teach technical knowledge and skills for entrylevel positions in an animal production enterprise by developing competencies concerning the selection, breeding, physiology, nutrition, health, housing, feeding, and marketing of farm and companion animals. Typical instructional activities include hands-on experiences with the principles and practices essential in the production and management of animals and animal products for economic, recreational, and therapeutic uses; participating in personal and community leadership development activities; planning and implementing a relevant school-to-work transition experience; and participating in FFA activities. OBJECTIVE: Given the necessary equipment, supplies, and facilities, the student, upon completion of the prescribed number of instructional hours, will be able to successfully complete the following core competencies. Credit: 1/2 - 1 - 2 units 1 Competency/Objective A. ORIENTATION 1. Prepare in outline form a plan for integrating the FFA program into the course in livestock management. 2. Prepare in outline form a supervised occupa-tional experience program that will enrich and complement the course. 3. Identify occupational opportunities and educa-tional requirements for employment. 4. Identify the functions of livestock management. 5. Describe the economic importance of livestock. B. MARKETING 1. Plan a marketing schedule. 2. Calculate seller’s return, commission, and total price of livestock given weight and price per pound. 3. List five methods of marketing livestock. 4. Demonstrate how to use the livestock futures market and hedging. 5. List the market classes for different livestock. 6. Describe the price, supply, and demand trends of livestock products. 7. List and describe the different types of dairy products. 8. Describe the quality checks and weight grades of eggs. 9. Give USDA standard grades for each type of livestock. 10. Describe the function and selection of market. 11. Describe the factors that affect shrinkage when marketing. 12. Describe the methods of loading and handling livestock going to market. C. ANIMAL BREEDING 1. Plan and outline a breeding schedule for live-stock. 2. Evaluate performance records to select a sire and dam. 3. Identify breeds of various groups of livestock. 4. Describe advantages and disadvantages of various breeding systems. 5. Describe artificial insemination of livestock. 6. Make sire selections based on progency data. 7. Plan and outline a heat synchronization program. 8. Identify types of heat synchronization drugs. 9. Describe palpation for pregnancy testing. 10. List the expected percentages of parental stock in the offspring resulting from various systems of breeding. D. FEEDS AND FEEDING 1. Prepare livestock feeding records. 2. Balance and feed ration to livestock. 3. Determine required forage and grain crops. 4. Describe the proper feeding practices for feed-ing animals during the lactation period. 5. List and define the different feed components and their sources. 2 6. Do a feed inventory of a farm, and list three reasons why it is important. 7. Identify feed requirements of livestock at various stages of development. 8. Interpret feed tags/labels. E. PASTURE MANAGEMENT 1. Take soil sample. 2. Determine fertilizer and lime needs, and figure costs given on soil test results. 3. Till soil using chisel plow, moldboard, disc, spring tooth harrow, tandem disc, disc harrow, spike tooth harrow, and/or field cultivator. 4. Prepare seedbed using plow, disc harrow, and drag or power tiller. 5. Plant seed using cyclone seeder, grain drill, and/or conventional row crop planter. 6. Calibrate a chemical sprayer. 7. Apply chemicals using a sprayer. 8. Clean brush and weeds with rotary mower. 9. Cut hay with mower-conditioner, bar mower, and/or rotary cutter. 10. Rake hay into windows using a side-delivery, finger wheel rake or a buncher attached to the mower. 11. List and categorize sixteen essential elements for plant growth. 12. Describe legumes and their importance. 13. List the factors to consider in selecting pasture grasses and/or hay crops for livestock. F. FARM MANAGEMENT AND RECORD KEEPING 1. Appraise farm and ranch properties to determine the total value. 2. Plan goals for the farm. 3. Plan a cash flow for a livestock operation. 4. Inventory cattle, equipment, etc. 5. Purchase and/or lease land. 6. Manage labor and plan daily work schedules. 7. Establish and maintain ledger record system and filing system. 8. Prepare production performance records, marketing records, and purchase orders. 9. Order fuel and petroleum supplies as determined by the farming operation, storage facility, and delivery schedule. 10. Prepare federal and state income tax returns, and describe the estate tax. 11. Demonstrate use of electronic equipment for maintaining and interpreting records. 12. Prepare a net worth statement. 13. Prepare a financial statement. 14. Plan an effective insurance program for equip-ment, livestock, etc. 15. Describe lending methods. G. MAINTAINING ANIMAL HEALTH 1. Plan a livestock health program. 2. Restrain livestock using a squeeze chute or rope/chain restrainer. 3. Give subcutaneous and intramuscular injec-tions. 4. Castrate cattle and swine. 5. Dehorn cattle. 3 6. Administer growth stimulants. 7. Brand, tattoo, notch, and nose print livestock. 8. Trim a calf’s hooves. 9. Give birth assistance to livestock. 10. Plan and perform parasite and insect control program. 11. Clean livestock pens and housing. 12. Treat cattle for scours, foot rot, internal parasites, maggots, pinkeye, pneumonia, shipping fever, and mastitis. 13. Identify livestock health equipment, and describe the use and effectiveness of each. 14. Perform methods of relieving bloat. H. FACILITIES AND EQUIPMENT 1. Construct and maintain livestock fencing. 2. Construct and maintain livestock gaps and gates. 3. Construct and maintain livestock housing, hay barns/sheds, and equipment facilities. 4. Construct and maintain livestock facilities: corrals, chutes, head gates, and scales. 5. Construct and maintain feeding facilities: feed troughs, self-feeders, creep feeders, etc. 6. Join plastic, copper, aluminum, and steel pipe. 7. Install a water system for a typical farm build-ing. 8. Wire a typical 110 circuit consisting of at least two receptacles, two lights, and two switches. 9. Arc weld steel to steel. 10. Cut stock metal using an oxyacetylene torch. 11. Sharpen equipment using a grinder. 12. Make adjustments on a combine or hay baler. 13. Service farm machinery using the equipment owner’s manual. 14. Carry out operator maintenance on farm machinery. 15. Construct calf puller. 16. Identify types of fencing. I. SELECTING, FITTING, AND SHOWING 1. Cut animals for sale. 2. Groom animals for showing. 3. Halter break animals for showing. 4. Describe the external parts of an animal, and list factors that should be considered in judging livestock. 5. Give an oral set of reasons for selection of a class of animals. 6. Describe how to use performance records in selection of animals. 7. List terms used in judging and fitting. 8. Identify and describe show equipment. 9. List factors to consider in selecting an animal for showing. 4 J. CARCASS EVALUATION 1. Define marbling, muscle thickness, and frame size. 2. Grade animals based on cutability and quality grades. 3. List and describe the steps in slaughtering an animal. 4. Define the role of the USDA in the slaughter process. 5. Slaughter animals. K. COMPUTERS IN AGRICULTURE 1. Demonstrate proper care of equipment and materials. 2. Identify various input/output devices and media associated with information processing systems. 3. Perform power on/off or log on/off procedures. 4. Use the keyboard and/or other input devices to operate the computer. 5. Load and run programs. 6. Define basic computer terminology. 7. Identify the ways computers are used in agri-cultural business and industry. 8. Demonstrate the basic features of an agri-cultural software package. L. LEADERSHIP/COMMUNICATION/FFA 1. Lead a group discussion for five minutes. 2. Define leadership. 3. Identify various leadership styles. 4. Identify qualities of successful leaders. 5. Define communication. 6. Explain the relationship between communi-cation and leadership. 7. Explain the communication process. 8. Identify three suggestions for improving each of the following skills: listening, reading, writing, and speaking. 9. Recite the FFA Creed. 10. Demonstrate knowledge of history, activities, and purposes of FFA. 11. Identify the basic principles of public speaking. 12. Demonstrate the basic procedures of parlia-mentary procedure. 13. Conduct a simulated meeting. 14. Identify the function and purposes of a committee. 15. List the basic steps in problem solving/decision making. 16. Identify the major reasons for setting goals. 17. Identify the steps in developing a positive self-concept. 5