Part 2 - cosee now
advertisement

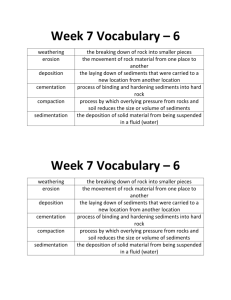
Student Learning Map for Unit: Voyage to the Bottom of the Sea (4.2) Key Learning(s): The Earth is made up of different layers that are dynamic. There is a connection between the features of the Earth and the rock cycle. Phenomena such as earthquakes and volcanoes result from tectonic activity. The current location of the continents is the result of past plate movement and is continually changing. Sand forms in many different ways. There are differences between active/passive and primary/secondary coasts. Humans make modifications to the coastline for many reasons. Unit Essential Question(s): How is Earth’s inside different from its outside? What is Continental Drift and Seafloor Spreading? What can sediments tell you about biological productivity and ecological concerns? How do we classify sediment? How do sedimentation processes differ based on their location? How are coasts classified and how do they change over time? Concept: Concept: Concept: Concept: The Study of Sediments Continental Shelf Sediments Deep Ocean Sediments Sediments as Economic Resources Lesson Essential Question(s): Lesson Essential Question(s): Lesson Essential Question(s): Lesson Essential Question(s): What techniques do scientists use to study ocean sediments? (A) How do scientists use ocean sediments to study the past? (A) How are sediments classified by origin? (ET) What processes affect sedimentation on the Continental Shelf? (A) What are recent and relict sediments? (A) How does the rate of Continental Shelf sedimentation compare to the rate of deep ocean sedimentation? (A) What processes affect sedimentation in the deep ocean? (A) What is the carbonate compensation depth? (A) Why do siliceous deposits dominate sediments below the carbonate compensation depth? (A) How do scientists think ferromanganese and phosphorite nodules form? (A) How does the study of ocean sediments relate to the economic importance of sediments? (ET) What are the characteristics and relative abundance of sediments? (A) How are sediments classified by size? (A) What are the effects of erosion and deposition? (A) KEY: (A) – Acquisition Lesson (ET) – Extended Thinking Vocabulary: Bottom profiling Clamshell sampler Grab sampler Paleoceanography Seismic profile Seismic reflection Siliceous oozes Stratrigraphy Why does deep ocean sediment tend to have the same particle composition as surface water above it? (A) Vocabulary: Biogenous Cosmogenous Hydrogenous Lithogenous Meteorite Meteors Microtektites Model from Learning-Focused Strategies. Thompson, M., Thompson, J. (2008) Vocabulary: Recent sediments Relict sediments Turbidites Turbidity currents Vocabulary: Calcareous Ferromanganese nodules Hydrogenous sediment Ooze Radiolarians Siliceous zone Tests Ooids Ooliths