Earth Layers & Earthquakes Study Guide Draft
advertisement

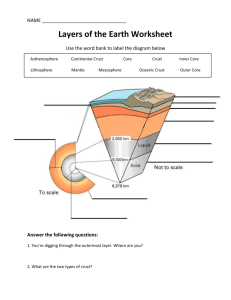
Earth Layer Test Study Guide Answers REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. List the five layers of the Earth. Inner Core, Outer Core, Mesosphere, Asthenosphere, and Lithosphere. 2. Draw a picture of each of the 5 Earth layers below. Make sure that you write the types of rocks found in both types of crust and the temperature of each layer. Lithosphere, Asthenosphere, Mesosphere, Outer Core, and Inner Core Ocean Crust – Basalt Continental Crust – Granite Lithosphere – 0 to 870 Asthenosphere – 879 to approximately 1,500 Mesosphere – Approximately 1,500 to 4,400 Outer Core – 4,400 to 7,000 Inner Core – 7,000 to 8,000 3. What layer(s) of the Earth are liquid? Outer Core. 4. The inner core is composed primarily of Iron while the outer core is composed of Iron and Nickel. 5. There are two types of crust. The oceanic crust is heavier and more dense and it is made primarily of basalt. 6. The continental crust is lighter and it is made primarily of granite. 7. Why is there different density between the types of crust? The oceanic crust is squeezed by the immense pressure of the ocean above and the granite is transformed into basalt. 8. The hottest layers of the Earth are found at the center of the Earth. 9. The hottest layer of the Earth is the inner core and the coldest layer of the Earth is the lithosphere. 10. The consistency of the second layer of the Earth is similar to hot tar/pudding/clay. 11. Hot rocks rising and falling in the asthenosphere is called convection. 12. The lithosphere is the smallest layer of the Earth and it comprises 1% of the Earth’s total mass. 13. The mesosphere and the asthenosphere make up the mantle and this layer is the largest Earth layer. This layer comprises 66% of the Earth’s total mass. 14. The inner core and the outer core are the hottest two layers of the Earth and together they represent 33% of the Earth’s total mass. 15. Geologists can see inside the Earth by analyzing earthquake waves (seismic waves). 16. A machine that measures earthquakes is called a seismograph and the picture that this machine draws is called a seismogram. 17. The focus is the exact location where an earthquake begins while the epicenter is the spot on the Earth’s surface immediately above where the earthquake hit. 18. Scientists that study earthquakes are called seismologists and they studied seismology in college. 19. There are 3 main types of earthquake waves. The wave that lets geologists know that the Earth has a liquid layer is the S wave. They know this because the S wave is blocked by liquid and seismographs on the opposite side of the Earth do not receive any S waves. 20. The P wave is the fastest wave and the least destructive. 21. The Surface wave is the slowest wave and the most destructive. 22. The Richter scale measures the strength of earthquakes. 23. A 5.0 earthquake is approximately 32 times stronger than a 4.0 earthquake. 24. Earthquakes occur in the lithosphere. 25. Earthquakes occur where tectonic plates are moving. They can move towards each other, away from each other, or horizontally beside each other. 26. If you are inside a building, the best thing to do when an earthquake occurs is immediately hide under a desk or chair. 27. A shadow zone is formed on the opposite side of the Earth from where the earthquake occurred because S waves are blocked by liquid. 28. Since the lithosphere is the least dense layer of the Earth, the lightest rocks are found in this layer. Vocabulary (Review the following terms prior to the test) Seismogram Seismograph Seismologist P Wave S Wave Surface Wave Asthenosphere Mesosphere Lithosphere Granite Basalt Richter Shadow Zone Epicenter Focus