Chest drain insertion in children
advertisement

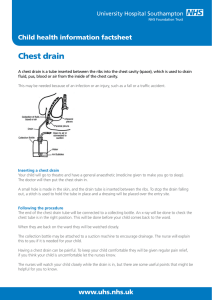
Chest Drain Insertion In Children Emergency Indications Tension Pneumothorax after initial needle thoracocentesis Traumatic Haemothorax or Haemopneumothorax This will be usually be inserted as part of a trauma team in A&E according to APLS and ATLS guidelines, using a large bore Argyll chest tube as described in the APLS manual. This procedure must be carried out by an appropriately trained and experienced doctor. This will be a doctor with current APLS or ATLS training. Equipment Skin prep and surgical drapes Scalpel Large clamps x 2 Suture local anaesthetic scissors chest drain tube underwater seal system In general, the largest tube which will pass between the ribs should be used The trocar must not be used to introduce the drain tube due to the high risk of lung perforation. Procedure If haemothorax is suspected large bore IV access and fluid resuscitation must be commenced prior to drain insertion. Identify insertion site :- 5th intercostal space, mid-axillary line Swab chest wall with surgical prep Give local anaesthetic Make 2-3 cm skin incision along the line of the intercostals space, just above the rib below Bluntly dissect through the subcutaneous tissues just over the top of the rib below, and puncture the parietal pleura with the tip of the clamp. Put a gloved finger into the incision to clear a path into the pleura (this will not be possible in small children) Advance the chest drain tube into the pleural space during expiration Ensure the tube is in the pleural space by listening for air movement, and by looking for fogging of the tube during expiration Connect the chest drain to the underwater seal Suture the drain in place and secure with tape Obtain chest X-ray Purse string suture must not be used due to the risk of unsightly scarring Elective Indications Pleural effusion or empyema Chest drain for any indication other than emergency as above should be inserted by appropriately trained personnel in a tertiary respiratory centre. The child must therefore be discussed with and transferred to the paediatric respiratory team in Leicester (Leicester Royal Infirmary) or Oxford (Oxford Children’s Hospital, John Radcliffe). References Advanced Paediatric Life Support Manual . Fourth Edition 2005 Guidance for the implementation of local Trust policies for the safe insertion of chest drains in children, following the NPSA Rapid Response Report – NPSA/2008/RRR003 British Paediatric Respiratory / Society British Thoracic Society 2008