Additional Genetics Problems
advertisement
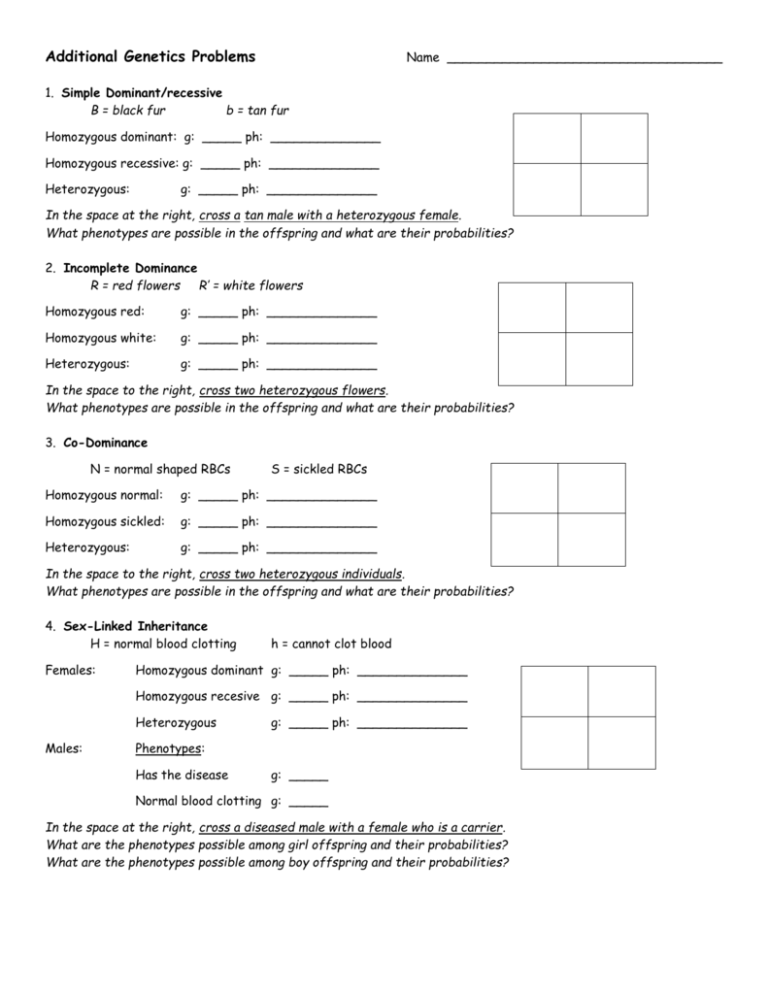
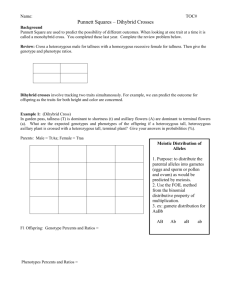
Additional Genetics Problems Name ___________________________________ 1. Simple Dominant/recessive B = black fur b = tan fur Homozygous dominant: g: _____ ph: ______________ Homozygous recessive: g: _____ ph: ______________ Heterozygous: g: _____ ph: ______________ In the space at the right, cross a tan male with a heterozygous female. What phenotypes are possible in the offspring and what are their probabilities? 2. Incomplete Dominance R = red flowers R’ = white flowers Homozygous red: g: _____ ph: ______________ Homozygous white: g: _____ ph: ______________ Heterozygous: g: _____ ph: ______________ In the space to the right, cross two heterozygous flowers. What phenotypes are possible in the offspring and what are their probabilities? 3. Co-Dominance N = normal shaped RBCs S = sickled RBCs Homozygous normal: g: _____ ph: ______________ Homozygous sickled: g: _____ ph: ______________ Heterozygous: g: _____ ph: ______________ In the space to the right, cross two heterozygous individuals. What phenotypes are possible in the offspring and what are their probabilities? 4. Sex-Linked Inheritance H = normal blood clotting Females: h = cannot clot blood Homozygous dominant g: _____ ph: ______________ Homozygous recesive g: _____ ph: ______________ Heterozygous Males: g: _____ ph: ______________ Phenotypes: Has the disease g: _____ Normal blood clotting g: _____ In the space at the right, cross a diseased male with a female who is a carrier. What are the phenotypes possible among girl offspring and their probabilities? What are the phenotypes possible among boy offspring and their probabilities? 5. Multiple Alleles: Fill in the table: Phenotype Genotypes Possible: Type A Type B Type AB Type O In the space at the right, cross a type O parent with a type AB parent. What phenotypes and their probabilities are possible in the offspring? Human Genetics Disorders. Use your text (Ch. 12) or notes to complete the table about the following human genetic disorders. Genetic Disorder How it’s inherited (autosomal dominant/recessive; or sex-linked) Symptoms Other (treatable?, frequency?) Huntington’s Disease Tay-Sachs PKU = ____________________ Cystic Fibrosis Sickle-Cell Disease Hemophilia Try this whooper dihybrid cross on a separate sheet of paper: Woman: carrier for red-green colorblindness and type O blood Man: is red-green colorblind and is heterozygous for type A blood. g: ___________________ g: ___________________