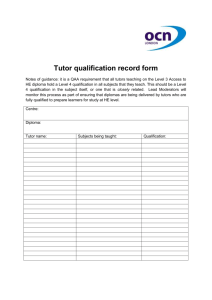
Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training
advertisement

Teaching and Training Qualifications for the Further Education and Skills Sector in England (2013) Guidance for higher education institutions Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training (QCF) Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training including specialist pathway (QCF) Level 5 integrated specialist Diplomas in Education and Training (QCF) Level 5 standalone specialist Diplomas (QCF) Updated May 2013 Level 5 Diplomas Contents Glossary ..................................................................................................................................... Section 1 Introduction 1.1 Purpose of this document ......................................................................................................... 4 1.2 How to use this document ........................................................................................................ 4 1.3 Background..................................................................................................................................... 4 Section 2 Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training 2.1 Purpose of qualification ............................................................................................................. 6 2.2 Entry requirements ...................................................................................................................... 6 2.3 Level, size and GLH ...................................................................................................................... 8 2.4 Content ............................................................................................................................................ 8 2.5 Minimum core of literacy, language, numeracy and ICT ............................................... 8 2.6 Links to other qualifications ...................................................................................................10 2.7 Practice requirement .................................................................................................................10 2.8 Requirements for those delivering units and/or observing and assessing practice 11 Section 3 Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training including a specialist pathway 3.1 Purpose of the qualification ...................................................................................................13 3.2 Entry requirements ....................................................................................................................14 3.3 Level, size and GLH ....................................................................................................................14 3.4 Content ..........................................................................................................................................15 3.5 Minimum core of literacy, language, numeracy and ICT .............................................15 3.6 Links to other qualifications ...................................................................................................16 3.7 Practice requirement .................................................................................................................16 3.8 Requirements for those delivering units and/or observing and assessing practice 18 Section 4 Integrated specialist Level 5 Diplomas in Education and Training 4.1 Purpose of the qualifications .................................................................................................20 4.2 Entry requirements ....................................................................................................................20 Guidance for higher education institutions Page 1 of 51 3 Level 5 Diplomas 4.3 Level, size and GLH ....................................................................................................................21 4.4 Content ..........................................................................................................................................21 4.5 Minimum core of literacy, language, numeracy and ICT .............................................21 4.6 Links to other qualifications ...................................................................................................23 4.7 Practice requirement .................................................................................................................23 4.8 Requirements for those delivering units and/or observing and assessing practice 25 Section 5 Standalone specialist Level 5 Diplomas 5.1 Purpose of the qualifications .................................................................................................26 5.2 Entry requirements ....................................................................................................................26 5.3 Level, size and GLH ....................................................................................................................27 5.4 Content ..........................................................................................................................................27 5.5 Links to other qualifications ...................................................................................................27 5.6 Practice requirement .................................................................................................................28 5.7 Requirements for those delivering units and/or observing and assessing practice 29 Annex 1 Overview of the Education and Training qualifications (2013) ................... 30 Annex 2 Common mandatory content for the Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training (QCF) and equivalent HEI qualifications in the FHEQ ............ 33 Annex 3 Summary of qualification practice, including observed and assessed practice, requirements ...................................................................................... 45 Annex 4 Links between the specialist standalone qualifications and Level 5 Diplomas in Education and Training including those with a specialist pathway ........ 49 Guidance for higher education institutions Page 2 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas Glossary This table gives definitions for the terms and acronyms used in this document. Acronym / Definition Term BIS Department for Business, Innovation and Skills Credit One credit equates to ten notional hours of learning (QCF) CTLLS Certificate in Teaching in the Lifelong Learning Sector DTLLS Diploma in Teaching in the Lifelong Learning Sector GLH Guided learning hours (as defined by the Skills Funding Agency) HEI Higher education institution ITE Initial teacher education LLUK Lifelong Learning UK LSIS Learning and Skills Improvement Service QCF Qualifications and Credit Framework Guidance for higher education institutions Page 3 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas Section 1 1.1 Introduction Purpose of this document This document provides guidance for higher education institutions wishing to develop qualifications within the Framework for Higher Education Qualifications (FHEQ) equivalent to: Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training (QCF); Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training (QCF) including specialist pathways; integrated specialist Level 5 Diplomas in Education and Training (QCF); and standalone specialist Level 5 Diplomas (QCF). These qualifications replace the Qualifications and Credit Framework (QCF) qualifications introduced in 2007 and updated in 2011. 1.2 How to use this document The document is arranged as follows: Section 1 provides background to the introduction of the 2013 qualifications. Section 2 gives details of the qualification requirements for the Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training and equivalent qualifications in the FHEQ. Section 3 gives details of the qualification requirements for the Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training including a specialist pathway and equivalent qualifications in the FHEQ. Section 4 gives details of the qualification requirements for the integrated specialist Level 5 Diplomas in Education and Training and equivalent qualifications in the FHEQ. Section 5 gives details of the qualification requirements for the standalone specialist Level 5 Diplomas and equivalent qualifications in the FHEQ. 1.3 Background An LSIS review of qualifications for teachers and trainers in the further education and skills sector was undertaken in 2012. The proposal for a diploma at Level 5 was supported as part of a suite of generic teaching and training qualifications including award and certificate qualifications. The development of specialist qualifications was also supported. More information about the findings of the review can be found in the report, Further Education and Skills in England: New Qualifications for Teachers and Trainers, Phase Two Findings Report (LSIS, 2013). Guidance for higher education institutions Page 4 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas The Professional Standards for Teachers, Tutors and Trainers in the Lifelong Learning Sector (LLUK, 2006) were outside the scope of the review. These standards will continue to underpin practice in the sector alongside the 2013 teaching qualifications. LSIS has agreed with the Department for Business, Innovation and Skills (BIS) that there should be a phased introduction of the 2013 qualifications as this will respect the different development cycles of awarding organisations and higher education institutions. As with previous qualifications, the 2013 qualifications can be offered by awarding organisations or higher education institutions. The titles of the qualifications may differ between awarding organisations and higher education institutions. An awarding organisation will always use the QCF titles and levels as stated above whereas higher education institutions do not have to use the QCF titles, as their qualifications are validated by their own institution and have to comply with the FHEQ. Some higher education institutions may also offer the Level 5 qualifications at a higher, postgraduate level. However, whether offered by higher education institutions or awarding organisations, the qualifications have common content and teaching practice requirements. An overview of the 2013 qualifications is included in Annex 1. Guidance for higher education institutions Page 5 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas Section 2 2.1 Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training Purpose of qualification The Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training prepares trainee teachers to teach in a range of contexts. There is a significant practice requirement as this qualification will assess, and provide evidence of, competence when undertaking teaching and/or training responsibilities. It can meet the needs of a range of trainee teachers, including: individuals who are not currently teaching and training but who can meet the practice requirements, including the observed and assessed practice requirements, of the qualification; individuals who are currently teaching and training, including those who have just begun teaching and training, who can meet the practice requirements, including the observed and assessed practice requirements, of the qualification; individuals who are currently working as assessors and who wish to achieve a teaching qualification. 2.2 Entry requirements All trainee teachers joining the generic qualification programme should undertake an initial assessment of skills in English, mathematics and ICT. They should record their development needs and, where applicable, agree an action plan to address them. If trainees join the qualification programme having already undertaken an initial assessment of their English, mathematics and ICT skills, their record of development needs and any previous action taken to address them should be reviewed and updated as required. Entry requirement for specialist optional units Potential teacher trainees wishing to take any of the specialist optional units will need to evidence Level 3 personal skills in English or mathematics, as appropriate. This entry requirement applies to all Level 5 QCF diplomas and FHEQ qualifications for teachers of English (literacy and/or ESOL) and mathematics (numeracy) detailed in this and other LSIS qualification guidance documents. The entry criteria, and how they may be evidenced, are detailed in the separate document, Criteria for entry to mathematics (numeracy) and English (literacy and ESOL) teacher training in the lifelong learning sector (LLUK, June 2007, amended 2010). Guidance for higher education institutions Page 6 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas In addition to these national entry requirements, individual higher education institutions are able to set their own entry requirements. Guidance for higher education institutions Page 7 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas 2.3 Level, size and GLH The minimum requirements for the Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training, and equivalent qualifications in the FHEQ, are: Level 5 120 credits at Level 4 or 5 (a minimum of 20 credits and a maximum of 60 credits at Level 4) 360 GLH (minimum). 2.4 Content Qualifications in the FHEQ are not required to use the QCF unit structure for the Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training or equivalent qualifications. However, the qualifications must cover the minimum mandatory content that underpins the QCF units as specified in Annex 2. They must also reflect the emphasis on practice in the QCF qualifications where 40 credits are linked to units in which trainee teachers must demonstrate practice and the application of theory, principles, and models to their practice. 2.5 Minimum core of literacy, language, numeracy and ICT The minimum core of literacy, language, numeracy and ICT details the knowledge, understanding and personal skills in English, mathematics and ICT expected of all teachers in the sector. The minimum core document comprises three sections: Language and literacy Numeracy Information and communication technology (ICT). Each of these sections comprises two parts: Part A – knowledge and understanding Part B – personal skills. Knowledge, understanding and personal skills requirements for literacy, language, numeracy and ICT are included in the teaching qualifications. Details can be found in the document, Addressing Literacy, Language, Numeracy and ICT needs in education and training: Defining the minimum core of teachers’ knowledge, understanding and personal skills. A guide for initial teacher education programmes (LLUK 2007; updated LSIS, 2013). Requirements for knowledge and understanding elements Guidance for higher education institutions Page 8 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas Elements of the minimum core should be selected appropriate to the context and needs of each cohort of trainee teachers. The selected elements should be delivered and assessed across the mandatory content. Guidance for higher education institutions Page 9 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas Requirements for personal skills in English, mathematics and ICT elements All trainee teachers joining this qualification programme should undertake an initial assessment of skills in English, mathematics and ICT. If trainees join the qualification programme having already completed a Level 3 Award in Education and Training or a Level 4 Certificate in Education and Training, their record of development needs and any previous actions taken to address them should inform opportunities to continue to develop their skills as required by the appropriate minimum core elements. Opportunities to develop these personal skills should be made available across the mandatory units as a minimum. LSIS supports opportunities to develop these skills throughout a teacher education programme. Teacher education teams should ensure that the personal skills developed by trainees are those most appropriate for their professional role as teachers. 2.6 Links to other qualifications Individuals who have completed the Level 4 Certificate in Education and Training (QCF) who are progressing to HEI-validated qualifications at Level 5 or above may have their Level 4 credit recognised in line with each higher education institution’s arrangements for the recognition of prior learning. Individuals who have completed the Level 4 Certificate in Education and Training (QCF) may also use the evidence of practice, including observed and assessed practice, towards the overall minimum practice requirements, including observed and assessed practice requirements, for the Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training. Further details are provided in Section 2. 7. Individuals who have already achieved one of the standalone specialist qualifications can also use some of their evidence of practice, including observed and assessed practice, towards the overall minimum practice, including observed and assessed practice requirements, for the Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training. Further information on credit transfer and the transfer of practice between the Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training, the Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training including a specialist pathway and the standalone specialist qualifications is given in Annex 4. 2.7 Practice requirement There is a requirement for a minimum of 100 hours of practice and a requirement to evidence working with groups of learners to achieve this qualification. The practice requirements for individual qualifications are detailed in Annex 3. LSIS recognises that an effective teaching practice experience should ideally include: Guidance for higher education institutions Page 10 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas different teaching practice locations/settings/contexts; teaching across more than one level; teaching a variety of learners; teaching individuals and groups; experience of non-teaching roles; and gaining subject-specialist knowledge through workplace mentoring. LSIS supports any endeavour of ITE providers to ensure that trainee teachers have access to as many of these elements as possible during their teaching practice. Observed and assessed practice requirements There must be a minimum of eight observations, totalling a minimum of eight hours. This excludes any observed practice completed as part of the Level 3 Award in Education and Training. Any single observation must be a minimum of half an hour. Observations should be appropriately spaced throughout the whole programme and take into account a trainee teacher’s progress. The higher education institution will decide the sufficiency of evidence required to make a judgment about the standard of practice. These are minimum requirements for whatever combination of units is undertaken by the trainee to achieve the qualification. Higher education institutions may make additional requirements if they so wish. Transfer of practice There is no transfer of practice, including observed and assessed practice, from a previously achieved Level 3 Award in Education and Training. Details of arrangements for the transfer of practice, including observed and assessed practice, from the Level 4 Certificate in Education and Training are given in Annex 3. Details of arrangements for the transfer of practice, including observed and assessed practice, from the standalone specialist qualifications are given in Annex 4. 2.8 Requirements for those delivering units and/or observing and assessing practice All those delivering units and/or observing and assessing practice for the Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training (QCF) and equivalent qualifications in the FHEQ must have all of the following: a teaching qualification equivalent to QCF Level 5 or above; Guidance for higher education institutions Page 11 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas evidence of teaching experience in an education and training context; access to appropriate guidance and support; and on-going participation in related programme quality assurance processes. Guidance for higher education institutions Page 12 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas Section 3 Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training including a specialist pathway 3.1 Purpose of the qualification A Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training including a specialist pathway prepares trainee teachers to teach in a range of generic and specialist contexts and provide an opportunity to spend part of the qualification developing knowledge and skills in the following specialist areas: English (ESOL) English (Literacy) English (Literacy and ESOL) Mathematics (Numeracy) Teaching Disabled Learners. There is a significant practice requirement as these qualifications assess, and provide evidence of, competence when undertaking teaching and/or training responsibilities. A Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training including a specialist pathway can meet the needs of a range of trainee teachers, including: individuals who are not currently teaching and training but who can meet both the generic and specialist practice requirements, including the observed and assessed practice requirements, of the qualification; individuals who are currently teaching and training, including those who have just begun teaching and training, who can meet both the generic and specialist practice requirements, including the observed and assessed practice requirements, of the qualification; individuals who have already achieved one of the standalone diplomas for English (Literacy), English (ESOL), English (Literacy and ESOL), Mathematics (Numeracy) or for teaching Disabled Learners. Such individuals are entitled to exemption from the units they have already achieved as part of their standalone qualification. Individuals who take a specialist pathway through the optional credit will be awarded one of the following qualifications: Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training (including teaching English: ESOL) (QCF) Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training (including teaching English: Literacy) (QCF) Guidance for higher education institutions Page 13 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training (including teaching English: Literacy and ESOL) (QCF) Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training (including teaching Mathematics: Numeracy) (QCF) Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training (including teaching Disabled Learners) (QCF). Each of these specialist pathways enables trainee teachers to achieve all three of the units included within the relevant standalone diplomas for teaching English (Literacy), English (ESOL), English (Literacy and ESOL), Mathematics (Numeracy) or teaching Disabled Learners. 3.2 Entry requirements All trainee teachers should undertake an initial assessment of skills in English, mathematics and ICT. They should record their development needs and, where applicable, agree an action plan to address them. Where trainee teachers have already undertaken an initial assessment of their English, mathematics and ICT skills, their record of development needs and any previous action taken to address them should be reviewed and updated as required. Entry requirement for specialist optional units Potential teacher trainees wishing to take any of the specialist pathways will need to evidence Level 3 personal skills in English or mathematics, as appropriate. This entry requirement applies to all Level 5 QCF diplomas and FHEQ qualifications for teachers of English (literacy and/or ESOL) and mathematics (numeracy) detailed in this and other LSIS qualification guidance documents. The entry criteria, and how they may be evidenced, are detailed in the separate document, Criteria for entry to mathematics (numeracy) and English (literacy and ESOL) teacher training in the lifelong learning sector (LLUK, June 2007, amended 2010). In addition to these national entry requirements, individual higher education institutions are able to set their own entry requirements. 3.3 Level, size and GLH The minimum requirements for the Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training including a specialist pathway in English: Literacy, English: ESOL, Mathematics (Numeracy) and teaching disabled learners, and equivalent qualifications in the FHEQ are: Level 5 Guidance for higher education institutions Page 14 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas 120 credits – Level 4 and 5 (a maximum of 20 credits at Level 4) 135 credits – Level 4 and 5 (a maximum of 20 credits at Level 4) for the combined pathway in English (Literacy and ESOL) 360 GLH (minimum) for a single specialist pathway diploma 420 GLH (minimum) for the combined pathway in English (Literacy and ESOL). 3.4 Content Qualifications in the FHEQ are not required to use the QCF unit structure for the Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training including a specialist pathway. However, the qualifications must cover the minimum mandatory and specialist content that underpins the QCF units as specified in Annex 2. They must reflect the emphasis on practice in the QCF qualifications where 55 credits (60 credits for the combined pathway) are linked to units where trainee teachers must demonstrate practice and the application of theory, principles, and models to their practice. 3.5 Minimum core of literacy, language, numeracy and ICT The minimum core of literacy, language, numeracy and ICT details the knowledge, understanding and personal skills in English, mathematics and ICT expected of all teachers in the sector. The minimum core document comprises three sections: Language and literacy Numeracy Information and communication technology (ICT). Each of these sections comprises two parts: Part A – knowledge and understanding Part B – personal skills. Knowledge, understanding and personal skills requirements for literacy, language, numeracy and ICT are included in the teaching qualifications. Details can be found in the document, Addressing Literacy, Language, Numeracy and ICT needs in education and training: Defining the minimum core of teachers’ knowledge, understanding and personal skills. A guide for initial teacher education programmes (LLUK 2007; updated LSIS, 2013). Requirements for knowledge and understanding elements Elements of the minimum core should be selected appropriate to the context and needs of each cohort of trainee teachers. The selected elements should be delivered and assessed across the mandatory content. Guidance for higher education institutions Page 15 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas Requirements for personal skills in English, mathematics and ICT elements All trainee teachers joining this qualification programme should undertake an initial assessment of skills in English, mathematics and ICT. If trainees join the qualification programme having already completed a Level 3 Award in Education and Training or a Level 4 Certificate in Education and Training, their record of development needs and any previous actions taken to address them should inform opportunities to continue to develop their skills as required by the appropriate minimum core elements. Opportunities to develop these personal skills should be made available across the mandatory units as a minimum. LSIS supports opportunities to develop these skills throughout a teacher education programme. Teacher education teams should ensure that the personal skills developed by trainees are those most appropriate for their professional role as teachers. 3.6 Links to other qualifications Individuals who have completed the Level 4 Certificate in Education and Training (QCF) who are progressing to HEI-validated qualifications at Level 5 or above may have their Level 4 credit recognised in line with each higher education institution’s arrangements for the recognition of prior learning. Individuals who have completed the Level 4 Certificate in Education and Training (QCF) may also use the evidence of practice, including observed and assessed practice, towards the overall minimum practice requirements, including observed and assessed practice requirements for the Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training. Further details are provided in section 3. 7. Individuals who have already achieved one of the standalone specialist qualifications can also use some of their practice and their observed and assessed practice towards the overall minimum practice, including observed and assessed practice requirements for the Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training including a specialist pathway. Further information on credit transfer and the transfer of practice between the Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training, the Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training with a specialist and the standalone specialist qualifications is given in Annex 4. 3.7 Practice requirement For the four single specialist pathways listed below, there is a requirement for a minimum of 100 hours of practice and a requirement to evidence working with groups of learners to achieve the qualification. Of the 100 hours, 50 hours must be in the context of the chosen specialist area: Guidance for higher education institutions Page 16 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training (including teaching English: ESOL) Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training (including teaching English: Literacy) Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training (including teaching Mathematics: Numeracy) Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training (including teaching Disabled Learners). For the combined specialist pathway Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training (including teaching English: Literacy and ESOL), there is a requirement for a minimum of 120 hours of practice with 70 hours in the context of the specialist areas. The practice requirements for individual qualifications are summarised in Annex 3. LSIS recognises that an effective teaching practice experience should ideally include: different teaching practice locations/settings/contexts; teaching across more than one level; teaching a variety of learners; teaching individuals and groups; experience of non-teaching roles; and gaining subject-specialist knowledge through workplace mentoring. LSIS supports any endeavour of ITE providers to ensure that trainee teachers have access to as many of these elements as possible during their teaching practice. Guidance for higher education institutions Page 17 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas Observed and assessed practice requirements For the four single specialist pathways listed below, there must be a minimum of eight observations totalling a minimum of eight hours with at least four of the observations in the specialist context: Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training (including teaching English: ESOL) Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training (including teaching English: Literacy) Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training (including teaching Mathematics: Numeracy) Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training (including teaching Disabled Learners). For the combined specialist pathway Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training (including teaching English: Literacy and ESOL), there must be a minimum of ten observations totalling a minimum of ten hours, six in the specialist contexts. Any single observation must be a minimum of half an hour. Observations should be appropriately spaced throughout the whole programme and take into account a trainee teacher’s progress. The higher education institution will decide the sufficiency of evidence required to make a judgment about the standard of practice. These are minimum requirements for whatever combination of units is undertaken by the trainee to achieve the qualification. Higher education institutions may make additional requirements if they so wish. Transfer of practice There is no transfer of practice, including observed and assessed practice, from a previously achieved Level 3 Award in Education and Training. Details of arrangements for the transfer of practice, including observed and assessed practice, from the Level 4 Certificate in Education and Training are given in Annex 3. Details of arrangements for the transfer of practice, including observed and assessed practice, from the standalone specialist qualifications are given in Annex 4. 3.8 Requirements for those delivering units and/or observing and assessing practice All those delivering units and/or observing and assessing practice for the Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training including a specialist pathway (QCF) and equivalent qualifications in the FHEQ must have all of the following: Guidance for higher education institutions Page 18 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas a teaching qualification equivalent to QCF Level 5 or above; a Level 4 specialist qualification or Level 5 Additional Diploma or equivalent qualification in the relevant specialist area(s); evidence of teaching experience in the relevant specialist context(s); in-depth knowledge of the relevant specialist area(s); access to appropriate guidance and support; and on-going participation in related programme quality assurance processes. Guidance for higher education institutions Page 19 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas Section 4 Integrated specialist Level 5 Diplomas in Education and Training Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training (English: Literacy) Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training (English: ESOL) Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training (English: Literacy and ESOL) Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training (Mathematics) Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training (Disabled Learners) 4.1 Purpose of the qualifications In these qualifications, units from the Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training (QCF) and units from the standalone Level 5 Diplomas (QCF) have been combined to provide specialist training in specialist areas. The mandatory generic credit in this qualification should be contextualised in the specialist area as far as possible. There is a significant practice requirement in the specialist area as this qualification will assess, and provide evidence of, competence when undertaking teaching and/or training responsibilities. They can meet the needs of a range of trainee teachers, including: individuals not currently teaching and training but who can meet the practice requirements, including the observed and assessed practice requirements, of the qualification; individuals who are currently teaching and training, including those who are new to teaching and training, who can meet the practice requirements, including the observed and assessed practice requirements, of the qualification. 4.2 Entry requirements All trainee teachers should undertake an initial assessment of skills in English, mathematics and ICT. They should record their development needs and, where applicable, agree an action plan to address them. Where trainee teachers have already undertaken an initial assessment of their English, mathematics and ICT skills, their record of development needs and any previous action taken to address them should be reviewed and updated as required. Entry requirement for specialist optional units Potential teacher trainees wishing to take any specialist qualification will need to evidence Level 3 personal skills in English or mathematics, as appropriate. Guidance for higher education institutions Page 20 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas This entry requirement applies to all Level 5 QCF diplomas and FHEQ qualifications for teachers of English (literacy and/or ESOL) and mathematics (numeracy) detailed in this and other LSIS qualification guidance documents. The entry criteria, and how they may be evidenced, are detailed in the separate document, Criteria for entry to mathematics (numeracy) and English (literacy and ESOL) teacher training in the lifelong learning sector (LLUK, June 2007, amended 2010). In addition to these national entry requirements, individual higher education institutions are able to set their own entry requirements. 4.3 Level, size and GLH The minimum requirements for the Level 5 integrated specialist diplomas and equivalent qualifications in the FHEQ, are: Level 5 120 credits at Level 4 and5 for a single specialist pathway (a minimum of 20 credits and a maximum of 35 credits at Level 4) 135 credits at Level 4 and 5 for the combined specialist pathway in English (Literacy and ESOL) Diploma (a minimum and maximum of 20 credits at Level 4) 360 GLH 420 GLH for the combined English (Literacy and ESOL) Diploma. 4.4 Content Qualifications in the FHEQ are not required to use the QCF unit structure for the Level 5 integrated specialist diplomas. However, the qualifications must cover the minimum mandatory generic and specialist content that underpins the QCF units as specified in Annex 2. They must reflect the emphasis on practice in the QCF qualifications where 40 credits (60 credits for the combined specialist pathway qualification) are linked to units for which trainee teachers must demonstrate practice and the application of theory, principles, and models to their practice. 4.5 Minimum core of literacy, language, numeracy and ICT The minimum core of literacy, language, numeracy and ICT details the knowledge, understanding and personal skills in English, mathematics and ICT expected of all teachers in the sector. The minimum core document comprises three sections: Language and literacy Numeracy Guidance for higher education institutions Page 21 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas Information and communication technology (ICT). Each of these sections comprises two parts: Part A – knowledge and understanding Part B – personal skills. Knowledge, understanding and personal skills requirements for literacy, language, numeracy and ICT are included in the teaching qualifications. Details can be found in the document, Addressing Literacy, Language, Numeracy and ICT needs in education and training: Defining the minimum core of teachers’ knowledge, understanding and personal skills. A guide for initial teacher education programmes (LLUK 2007; updated LSIS, 2013). Guidance for higher education institutions Page 22 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas Requirements for knowledge and understanding elements Elements of the minimum core should be selected appropriate to the context and needs of each cohort of trainee teachers. The selected elements should be delivered and assessed across the mandatory content. Requirements for personal skills in English, mathematics and ICT elements All trainee teachers joining these qualification programmes should undertake an initial assessment of skills in English, mathematics and ICT. If trainees join a qualification programme having already completed a Level 3 Award in Education and Training or a Level 4 Certificate in Education and Training, their record of development needs and any previous actions taken to address them should inform opportunities to continue to develop their skills as required by the appropriate minimum core elements. Opportunities to develop these personal skills should be made available across the mandatory units as a minimum. LSIS supports opportunities to develop these skills throughout a teacher education programme. Teacher education teams should ensure that the personal skills developed by trainees are those most appropriate for their professional role as teachers. 4.6 Links to other qualifications Individuals who have completed the Level 4 Certificate in Education and Training (QCF) who are progressing to HEI-validated qualifications at Level 5 or above may have their Level 4 credit recognised in line with each higher education institution’s arrangements for the recognition of prior learning. Individuals who have completed the Level 4 Certificate in Education and Training (QCF) may also use the evidence of practice, including observed and assessed practice, towards the overall minimum practice requirements, including observed and assessed practice requirements, for the Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training. Further details are provided in section 4.7. 4.7 Practice requirement There is a requirement for a minimum of 100 hours of practice (120 hours for the combined specialist pathway qualification) and a requirement to evidence working with groups of learners to achieve these qualifications. All of the hours of practice must be in the specialist area. Further details of the practice requirements for each qualification are given in Annex 3. LSIS recognises that an effective teaching practice experience should ideally include: Guidance for higher education institutions Page 23 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas different teaching practice locations/settings/contexts; teaching across more than one level; teaching a variety of learners; teaching individuals and groups; experience of non-teaching roles; and gaining subject specialist knowledge through workplace mentoring. LSIS supports any endeavour of ITE providers to ensure that trainee teachers have access to as many of these elements as possible during their teaching practice. Observed and assessed practice requirements There must be a minimum of eight observations, totalling a minimum of eight hours (ten observations, totalling a minimum of ten hours for the combined specialist pathway qualification), all of which must in the specialist area(s). This excludes any observed practice completed as part of the Level 3 Award in Education and Training. Any single observation must be a minimum of half an hour. Observations should be appropriately spaced throughout the whole programme and take into account a trainee teacher’s progress. The higher education institution will decide the sufficiency of evidence required to make a judgment about the standard of practice. These are minimum requirements for whatever combination of units is undertaken by the trainee to achieve the qualification. Higher education institutions may make additional requirements if they so wish. Transfer of practice There is no transfer of practice, and no transfer of observed and assessed practice hours from a previously achieved Level 3 Award in Education and Training or Level 4 Certificate in Education and Training. Details of arrangements for the transfer of practice, including observed and assessed practice, from the Level 4 Certificate in Education and Training are given in Annex 3. Details of arrangements for the transfer of practice, including observed and assessed practice, from the standalone specialist qualifications are given in Annex 4. Guidance for higher education institutions Page 24 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas 4.8 Requirements for those delivering units and/or observing and assessing practice All those delivering units and/or observing and assessing practice for the integrated specialist Level 5 Diplomas in Education and Training (QCF) and equivalent qualifications in the FHEQ must have all of the following: a teaching qualification equivalent to QCF Level 5 or above; a Level 4 specialist qualification or Level 5 Additional Diploma or equivalent qualification in the relevant specialist area(s); evidence of teaching experience in the relevant specialist context(s); in-depth knowledge of the relevant specialist area(s); access to appropriate guidance and support; and on-going participation in related programme quality assurance processes. Guidance for higher education institutions Page 25 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas Section 5 Standalone specialist Level 5 Diplomas Level 5 Diploma in Teaching English: Literacy Level 5 Diploma in Teaching English: ESOL Level 5 Diploma in Teaching English: Literacy and ESOL Level 5 Diploma in Teaching Mathematics: Numeracy Level 5 Diploma in Teaching Disabled Learners 5.1 Purpose of the qualifications These qualifications have been developed for teachers who hold a generic teaching qualification or trainee teachers who require, or wish to obtain, a specialist teaching qualification. They can meet the needs of a range of trainee teachers, including: individuals not currently teaching and training but who can meet the practice requirements, including the observed and assessed practice requirements, of the qualification; individuals who are currently teaching and training (including those who are new to teaching and training) who can meet the practice requirements, including the observed and assessed practice requirements, of the qualification. 5.2 Entry requirements All trainee teachers should undertake an initial assessment of skills in English, mathematics and ICT. They should record their development needs and, where applicable, agree an action plan to address them. Where trainee teachers have already undertaken an initial assessment of their English, mathematics and ICT skills, their record of development needs and any previous action taken to address them should be reviewed and updated as required. Entry requirement for specialist optional units Potential teacher trainees wishing to take any specialist qualification will need to evidence Level 3 personal skills in English or mathematics, as appropriate. This entry requirement applies to all Level 5 QCF diplomas and FHEQ qualifications for teachers of English (literacy and/or ESOL) and mathematics (numeracy) detailed in this and other LSIS qualification guidance documents. Guidance for higher education institutions Page 26 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas The entry criteria, and how they may be evidenced, are detailed in a separate document, Criteria for entry to mathematics (numeracy) and English (literacy and ESOL) teacher training in the lifelong learning sector (LLUK, June 2007, amended 2010). In addition to these national entry requirements, individual higher education institutions are able to set their own entry requirements. 5.3 Level, size and GLH The minimum requirements for the Level 5 standalone specialist diplomas and equivalent qualifications in the FHEQ, are: Level 5 45 credits at Level 5 60 credits at Level 5 for the combined English (Literacy and ESOL) Diploma 120 GLH 180 GLH for the combined English (Literacy and ESOL) Diploma. 5.4 Content Qualifications in the FHEQ are not required to use the QCF unit structure for the Level 5 standalone specialist diplomas. However, the qualifications must cover the minimum mandatory specialist content that underpins the QCF units as specified in Annex 2. They must reflect the emphasis on practice in the QCF qualifications where 15 credits (20 for the combined qualification) are linked to units where trainee teachers must demonstrate practice and the application of theory, principles, and models to their practice. 5.5 Links to other qualifications Individuals who achieve one of the standalone specialist qualifications can also use some of their practice and their observed and assessed practice towards the overall minimum practice, and observed and assessed practice, requirements for the Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training and the Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training including a specialist pathway. Further information on credit transfer and the transfer of practice between the Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training, the Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training including a specialist pathway and the standalone specialist qualifications is given in Annex 4. Guidance for higher education institutions Page 27 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas 5.6 Practice requirement There is a requirement for a minimum of 50 hours of practice (75 hours for the combined Literacy and ESOL qualification) and a requirement to evidence working with groups of learners to achieve this qualification. All of the hours of practice must be in the specialist area(s). Further details of the practice requirements for each qualification are given in Annex 3. LSIS recognises that an effective teaching practice experience should ideally include: different teaching practice locations/settings/contexts; teaching across more than one level; teaching a variety of learners; teaching individuals and groups; experience of non-teaching roles; and gaining subject specialist knowledge through workplace mentoring. LSIS supports any endeavour of ITE providers to ensure that trainee teachers have access to as many of these elements as possible during their teaching practice. Observed and assessed practice requirements There must be a minimum of four observations, totalling a minimum of four hours (six observations, totalling a minimum of six hours for the combined Literacy and ESOL qualification), all of which must be in the specialist area(s). This excludes any observed practice completed as part of the Level 3 Award in Education and Training. Any single observation must be a minimum of half an hour. Observations should be appropriately spaced throughout the whole programme and take into account a trainee teacher’s progress. The higher education institution will decide the sufficiency of evidence required to make a judgment about the standard of practice. These are minimum requirements for whatever combination of units is undertaken by the trainee to achieve the qualification. Higher education institutions may make additional requirements if they so wish. Transfer of practice There is no transfer of practice, and no transfer of observed and assessed practice hours from a previously achieved Level 3 Award in Education and Training or Level 4 Certificate in Education and Training. Guidance for higher education institutions Page 28 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas Details of arrangements for the transfer of practice, including observed and assessed practice, from the standalone specialist qualifications to the Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training and the Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training including a specialist pathway are given in Annex 4. 5.7 Requirements for those delivering units and/or observing and assessing practice All those delivering units and/or observing and assessing practice for the standalone specialist Level 5 Diplomas (QCF) and equivalent qualifications in the FHEQ must have all of the following: a teaching qualification equivalent to QCF Level 5 or above; a Level 4 specialist qualification or Level 5 Additional Diploma or equivalent qualification in the relevant specialist area(s); evidence of teaching experience in the relevant specialist context(s); in-depth knowledge of the relevant specialist area(s); access to appropriate guidance and support; and on-going participation in related programme quality assurance processes. Guidance for higher education institutions Page 29 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas Annex 1 Overview of the Education and Training qualifications (2013) Level 3 Award in Education and Training (QCF) – 12 credits 15 optional credits Level 4 Certificate in Education and Training (QCF) – 36 credits 3 mandatory credits 9 optional credits Level 3 Level 3 15 optional credits No minimum teaching practice requirement, but there is a minimum microteaching requirement 21 mandatory credits 15 optional credits Level 3 and 4 Level 3 and 4 A minimum practice requirement of 30 hours teaching 3 assessed observations of teaching Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training (QCF) – 120 credits 75 mandatory credits 45 optional credits Level 4 and 5 Level 4 and 5 Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training (QCF) including a specialist pathway – 120 credits1 75 mandatory credits Level 4 and 5 A minimum practice requirement of 100 hours teaching 45 credits in one of: English (Literacy) English (ESOL) English (Literacy and ESOL) Mathematics (Numeracy) Teaching Disabled Learners Level 5 A minimum practice requirement of 100 hours teaching, 8 assessed observations of teaching 50 of which must be in the specialist area 1 assessed observations teaching, 4 in the The 8English (Literacy and ESOL)of pathway, covering twospecialist specialist areas, is 135area credits with 60 credits in the specialist pathway. It has different practice requirements. Guidance for higher education institutions Page 30 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas Level 5 integrated specialist diplomas – 120 credits Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training (English: Literacy) Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training (English: ESOL) Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training (English: Literacy and ESOL)2 Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training (Mathematics: Numeracy) Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training (Disabled Learners) 105 mandatory credits 15 optional credits Level 4 and 5 Level 4 and 5 A minimum practice requirement of 100 hours teaching 8 assessed observations of teaching, all in the specialist area 2 This qualification, covering two specialist areas, is 135 credits. All of the credits are mandatory. It has different practice requirements. Guidance for higher education institutions Page 31 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas Level 5 standalone specialist diplomas – 45 credits Level 5 Diploma in Teaching English: Literacy Level 5 Diploma in Teaching English: ESOL Level 5 Diploma in Teaching English: Literacy and ESOL3 Level 5 Diploma in Teaching Mathematics: Numeracy Level 5 Diploma in Teaching Disabled Learners 45 credits Level 5 A minimum practice requirement of 50 hours teaching, all of which must be in the specialist area 4 assessed observations of teaching, all in the specialist area 3 This qualification, covering two specialist areas, is 60 credits. It has different practice requirements. Guidance for higher education institutions Page 32 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas Annex 2 Common mandatory content for the Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training (QCF) and equivalent HEI qualifications in the FHEQ Explanatory notes 1. The areas of content in the left hand column have largely been drawn from an analysis of learning outcomes from a sample of HEI DTLLS equivalent programmes. 2. The following documents were also consulted: New overarching professional standards for teachers, tutors and trainers in the lifelong learning sector (LLUK , not dated) Teachers’ Standards (Department for Education, 2011) The UK Professional Standards Framework for teaching and supporting learning in higher education (Higher Education Academy, 2011) Common inspection framework for further education and skills 2012 (Ofsted, 2012a) The framework for the inspection of initial teacher education 2012 (Ofsted, 2012b). 3. The proposed mandatory content detailed below mostly reflects the content of HEI DTLLS equivalent programmes. There is some additional content reflecting key aspects of some of the above documents. 4. LSIS recognises that HEIs may wish to categorise and/or group the proposed topic areas differently when designing their Level 5 Diploma or equivalent programmes. This is acceptable providing that all of the proposed mandatory content is covered within an equivalent FHEQ qualification. Guidance for higher education institutions Page 33 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas Mandatory content for Level 5 Diploma and equivalent HEI programmes Area of content Topics Roles, responsibilities and professional relationships in Education and Training Legislation, regulatory requirements and codes of practice Teacher related roles Own role and responsibilities Relationships between teachers and other professionals Role boundaries Points of referral Area of specialism Pedagogical principles and their implications for teaching and learning Innovative and creative approaches and their application Working with other professionals in own area of specialism Learners and their individual needs Theories, models and principles of learning Learning preferences Inclusion and inclusive teaching Learner support needs Involving learners in learning and assessment Agreeing learning targets/goals/outcomes Planning Delivery models Role and use of initial and diagnostic assessment Programmes/sessions/lessons Schemes of work Teaching and learning plans Individual learning plans Learning related to learning outcomes/curriculum requirements Differentiation Integrating English, Mathematics, ICT and wider skills (enterprise, employability, sustainability, citizenship) Inclusive learning environment Safe, supportive and motivating learning environment Creating and maintaining an inclusive learning environment Behaviour management Theories of behaviour management Promoting and maintaining appropriate behaviour Communication Theories and models of communication Principles of communication Methods of communication Communicating with learners, other learning professionals and other relevant parties Guidance for higher education institutions Page 34 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas Area of content Topics Resources, including learning technologies Practice of teaching Assessment of, for and as learning Using teaching and learning approaches/strategies/methods/techniques and resources, including learning technologies to meet individual learning needs Promoting equality and valuing diversity in own teaching/delivery Applying knowledge and understanding of literacy, language, numeracy and ICT in own teaching/delivery Demonstrating flexibility and adaptability in using teaching and learning approaches/strategies/methods/techniques in response to individual learning needs Taking risks in own teaching/delivery Theories and models of assessment Principles of assessment Types of assessment Methods of assessment Developing and designing assessments Role and use of questioning and feedback in assessment Conducting assessments Using assessment approaches/strategies/ methods/techniques to meet individual learning needs Demonstrating flexibility and adaptability in using assessment approaches/strategies/methods/techniques in response to individual learning needs Achievement, attainment and progress Using assessment data in monitoring of progress, setting targets and planning subsequent sessions Recording and reporting on assessments Awarding organisation requirements for assessments Theories and models of reflection Theories and models of evaluation Methods of evaluation Using feedback from learners and others Identifying areas for improvement in own practice Reflection and evaluation Types of resources including learning technologies Identifying/selecting/adapting/preparing/using resources including learning technologies in teaching learning and assessment Evaluating resources, including learning technologies Guidance for higher education institutions Page 35 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas Area of content Topics Curriculum development and evaluation Theories and models of curriculum development Impact of social/political/economic context on curriculum development Evaluating curriculum Guidance for higher education institutions Page 36 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas Area of content Topics Wider professional practice Professionalism and professional values Dual professionalism Social/political/economic context of education and training Contemporary issues in education and training Roles of external bodies and stakeholders and stakeholders in education and training Accountability of education and training organisations to external bodies and stakeholders Organisational policies, codes of practice and guidelines Quality assurance and quality improvement arrangements Minimum core of literacy, language, numeracy and ICT Knowledge and understanding of literacy, language, numeracy and ICT Own personal skills in literacy, language, numeracy and ICT Research and scholarship Evidence based practice Carrying out research Guidance for higher education institutions Page 37 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas Specialist content for the Level 5 standalone Diplomas and equivalent HEI qualifications English: Literacy Area of content Topics Knowledge of Literacy and Language Learners and their needs Literacy and language planning and Theories and principles relating to literacy learning and development How written and spoken language can be described and analysed Use of key discoursal, grammatical, lexical and phonological terms Processes involved in the development of speaking Processes involved in the development of listening Processes involved in the development of reading Processes involved in the development of writing Mutual dependence of speaking, listening, reading and writing in literacy and language teaching and learning Implications of theories, principles and processes for teaching and learning approaches Ways in which spoken and written language can change over time and vary according to context Impact of language change and variety for language and literacy learners Language and social processes Personal, social and cultural factors influencing learners' language acquisition, learning and use Impact of learning difficulties and disabilities on literacy and language teaching and learning Use of initial and diagnostic assessment to identify the literacy and language skills of learners Use of assessment tools in literacy and language teaching and learning Boundaries between specialist role and those of other professionals Sharing teaching and support needs between learning professionals Including literacy and language development in vocational and other subject areas Planning teaching and learning to meet the needs of learners and curriculum requirements Selecting and using specialist teaching approaches and Guidance for higher education institutions Page 38 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas delivery Reflecting, evaluating and improving own practice resources to meet the individual needs of learners Use of initial and diagnostic assessment to identify learners’ existing literacy and language skills, knowledge and understanding Involving learners in the processes of assessment and target setting Use of specialist assessment tools to measure the development of learners’ language and literacy skills Use of research and feedback to evaluate and improve own practice. English: ESOL Area of content Topics Knowledge of Literacy and Language Learners and their needs Theories and principles relating to first and second language acquisition and learning Theories and principles relating to literacy learning and development How written and spoken language can be described and analysed Impact of phonological features of spoken English on the communication of ESOL learners Differences between the description and conventions of English and other languages Use of key discoursal, grammatical, lexical and phonological terms Impact of phonological features of spoken English on the communication of ESOL learners Processes involved in the development of speaking Processes involved in the development of listening Processes involved in the development of reading Processes involved in the development of writing Mutual dependence of speaking, listening, reading and writing in literacy and language teaching and learning Implications of theories, principles and processes for teaching and learning approaches Ways in which spoken and written language can change over time and vary according to context Impact of language change and variety for ESOL learners Language and social processes Personal, social and cultural factors influencing ESOL learners' language acquisition, learning and use Impact of learning difficulties and disabilities on literacy and Guidance for higher education institutions Page 39 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas ESOL planning and delivery Reflecting, evaluating and improving own practice language teaching and learning The skills, knowledge and understanding that can be assessed in ESOL Use of initial and diagnostic assessment to identify the literacy and language skills of learners Use of assessment tools in literacy and language teaching and learning Boundaries between specialist role and those of other professionals Sharing teaching and support needs between learning professionals Including literacy and language development in vocational and other subject areas Planning teaching and learning to meet the needs of ESOL learners and curriculum requirements Selecting and using specialist teaching approaches and resources to meet the individual needs of ESOL learners Use of initial and diagnostic assessment to identify learners’ existing literacy and language skills, knowledge and understanding Involving learners in the processes of assessment and target setting Use of specialist assessment tools to measure the development of learners’ language and literacy skills Delivering inclusive learning and teaching Promote inclusion of literacy and language and wider skills (embedding) Specialist tools for assessment Use of research and feedback to evaluate and improve own practice. Guidance for higher education institutions Page 40 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas Mathematics: Numeracy Area of content Topics Knowledge of Mathematics and Numeracy Historic and cultural development of mathematics. Language and concepts associated with number systems Common errors and misconceptions in mathematics Techniques used in mathematics and numeracy for conceptual linkages Activities, processes and stages within mathematical problems and investigations Written, mental and diagrammatic mathematical strategies, and associated meta language Use, interpretation and representation of data Use of measurement systems within problem solving The effect of the origins and status of mathematics knowledge on mathematics and numeracy curriculum development The role of mathematics and numeracy within society Perceptions of mathematics and numeracy Learners and their needs The impact of personal, social, economical and political factors on the development and progression of numeracy learners. The impact of learners’ literacy and language skills on the development and progression of their numeracy skills Use of communication approaches can affect the learning of numeracy processes and skills. The numeracy skills and knowledge needed by learners across contexts and subjects, and for progression purposes Links between learners’ mathematical and numeracy development and other personal development Boundaries between specialist area and those of other professionals Sharing teaching and support needs between learning professionals Including numeracy in vocational and other subject areas Planning numeracy teaching and learning to meet the needs of Numeracy Identification of the skills, knowledge and understanding that can be assessed in numeracy Approaches to initial and diagnostic assessment Use of assessment tools in numeracy teaching and learning. Use of numeracy teaching approaches and numeracy resources, including technologies Guidance for higher education institutions Page 41 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas planning and delivery Reflecting, evaluating and improving own practice numeracy learners and curriculum requirements Selecting and using numeracy teaching approaches and resources to meet the individual needs of numeracy learners Use of initial and diagnostic assessment to identify learners’ existing mathematical and numeracy skills, knowledge, understanding and aspirations Involving learners in the processes of assessment and target setting Use of numeracy assessment tools to measure the development of learners’ numeracy skills Devising and using communication strategies to enable learners to develop numeracy language and vocabulary and to develop the literacy and language skills needed to by learners to develop their numeracy and problem solving skills Maintaining a supportive and challenging numeracy-learning environment that motivates learners and meets their needs Use of collaborative learning techniques to improve numeracy learning and problem solving. Use of research and feedback to evaluate and improve own practice. Guidance for higher education institutions Page 42 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas Disabled learners Area of content Topics Knowledge of Disabilities Learners and their needs The social model of disability and its impact on inclusive learning opportunities for disabled young people and adults Definitions of inclusive learning and importance for disabled learners Application of theories of teaching and learning to teaching practice in relation to disabled learners Approaches to communication and language development in relation to disabled learners Ways of adjusting practice for learners with a specific impairment Whole organisational approach to inclusive learning The influence of national, regional and local policy, guidance and regulatory frameworks on provision for , rights and wellbeing of disabled young people and adults Legal requirements and national policies and guidance promote the rights and well being of learners Influence of attitudes to disability, including social, cultural, and faith and belief on learning opportunities for disabled young people and adults Risk assessments and the curriculum Planning and delivery Specific impairments and the related support needs of disabled learners. The impact of dual or multiple impairments on inclusive practice. Use of augmentative and alternative forms of communication are used by disabled learners. Role of organisations and networks that can offer services and support to disabled people Maintaining relationships with parents, carers and others with an interest in the learner Skills needed to work collaboratively for the benefit of disabled learners Planning personalised programmes of learning to meet the individual learning and support needs of disabled learners. Planning for learning opportunities in real life contexts Use of differentiated assessment approaches to support learning and measure achievement. Guidance for higher education institutions Page 43 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas Planning support activities with learning support practitioners. Use of differentiated approaches, methods, activities and resources to meet the individual learning and support needs of disabled learners. Adapting own communication to meet the individual learning needs and skills of learners. Use of differentiated assessment approaches that involve learners. Feedback to learners Action research methods Ethical considerations when involving disabled learners Use of research and feedback to evaluate and improve own practice Reflecting, evaluating and improving own practice Guidance for higher education institutions Page 44 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas Annex 3 Summary of qualification practice, including observed and assessed practice, requirements Qualification Notes on requirements Level 5 Diploma in Trainee teachers must complete a minimum of 100 hours of practice to achieve this qualification. Education and Trainee teachers must have evidence of a minimum of eight assessed observations of practice, at the required standard, Training totalling a minimum of eight hours Trainee teachers who have previously completed a Level 4 Certificate in Education and Training or a Level 4 CTLLS qualification can use 20 hours of practice and two hours of observed and assessed practice towards meeting the overall practice requirements for this qualification. Guidance for higher education institutions Page 45 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas Qualification Notes on requirements Level 5 Diploma in Trainee teachers must complete a minimum of 100 hours (120 for the combined Literacy and ESOL pathway) hours of Education and practice to achieve this qualification, 50 in the specialist area. (70 for the combined Literacy and ESOL pathway). Training including a Trainee teachers must have evidence of a minimum of eight assessed observations of practice, at the required standard, specialist pathway totalling a minimum of eight hours, four in the specialist area (ten assessed observations for the combined pathway, totalling a minimum of ten hours, six in the specialist area). Practice must be in teaching and learning environments in specialist context, and should involve working with groups of learners. For the ESOL pathway, practice must be undertaken within at least two of the three levels of the ESOL curriculum – Entry Level and one other level. Assessed observations should include at least one ESOL observation at Entry Level. For the Literacy pathway, practice must be undertaken within at least two of the three levels of the literacy curriculum – Entry Level and one other level. Assessed observations should include at least one literacy observation at Entry Level. For the Literacy and ESOL pathway, a minimum of 25 hours of practice must be undertaken in a literacy context and 25 hours in an ESOL context. The remaining hours can be in either context. Practice must also be undertaken within at least two of the three levels of both the literacy and the ESOL curriculum. – Entry Level and one other level (Level 1or Level 2). Assessed observations should include at least one literacy and one ESOL observation at Entry Level, and at least one literacy and one ESOL observation at Level 1 or 2. The remaining observations can be at either level and in either context. For the Numeracy pathway, practice must be undertaken within at least two of the three levels of the numeracy curriculum – Entry Level and one other level. Assessed observations should include at least one numeracy observation at Entry Level. For the Teaching Disabled Learners pathway, practice must be undertaken with groups of learners. Trainee teachers who have previously completed a Level 4 Certificate in Education and Training or a Level 4 CTLLS qualification can use 20 hours of practice and two hours of observed and assessed practice towards meeting the overall practice requirements for this qualification. Guidance for higher education institutions Page 46 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas Qualification Notes on requirements Level 5 integrated Trainee teachers must complete a minimum of 100 hours (120 for the combined Literacy and ESOL pathway) hours of specialist practice to achieve this qualification, all in specialist area. qualifications Trainee teachers must have evidence of a minimum of eight assessed observations of practice, at the required standard, totalling a minimum of eight hour, all in the specialist area. (a minimum of ten assessed observations, totalling ten hours for the combined Literacy and ESOL qualification). Practice must be in teaching and learning environments in specialist context, and should involve working with groups of learners. For the ESOL Diploma, practice must be undertaken within at least two of the three levels of the ESOL curriculum – Entry Level and one other level. Assessed observations should include at least one ESOL observation at Entry Level. For the Literacy Diploma, practice must be undertaken within at least two of the three levels of the literacy curriculum – Entry Level and one other level. Assessed observations should include at least one Literacy observation at Entry Level. For the Literacy and ESOL Diploma, a minimum of 50 hours of practice must be undertaken in an literacy context and 50 hours in ESOL context. The remaining practice hours can be in either context. Practice must be undertaken within at least two of the three levels of both the literacy and the ESOL curriculum – Entry Level and one other level (Level 1or Level 2). Assessed observations should include at least two literacy and two ESOL observation at Entry Level, and at least two literacy and two ESOL observations at Level 1 or 2. The remaining observations can be at either level and in either context. For the Numeracy Diploma, practice must be undertaken within at least two of the three levels of the numeracy curriculum – Entry Level and one other level. Assessed observations should include at least one numeracy observation at Entry Level. For the Teaching Disabled Learners pathway, practice must be undertaken with groups of learners. Guidance for higher education institutions Page 47 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas Qualification Notes on requirements Level 5 standalone Trainee teachers must complete a minimum of 50 hours (75 for the combined Literacy and ESOL pathway) hours of practice specialist to achieve this qualification, all in specialist area. qualifications Trainee teachers must have evidence of a minimum of four assessed observations of practice, at the required standard, totalling a minimum of four hours, all in the specialist area. (a minimum of assessed observations, totally six hours for the combined Literacy and ESOL qualification). Practice must be in teaching and learning environments in the specialist context, and should involve working with groups of learners. For the ESOL Diploma, practice must be undertaken within at least two of the three levels of the ESOL curriculum – Entry Level and one other level. Assessed observations should include at least one ESOL observation at Entry Level. For the Literacy Diploma, practice must be undertaken within at least two of the three levels of the literacy curriculum – Entry Level and one other level. Assessed observations should include at least one Literacy observation at Entry Level. For the Literacy and ESOL pathway, a minimum of 25 hours of practice must be undertaken in a literacy context and 25 hours in an ESOL context. The remaining hours can be in either context. Practice must be undertaken within at least two of the three levels of both the literacy and the ESOL curriculum – Entry Level and one other level (Level 1or Level 2). Assessed observations should include at least one literacy and one ESOL observation at Entry Level, and at least one literacy and one ESOL observation at Level 1 or 2. The remaining observations can be at either level and in either context. For the Numeracy Diploma, practice must be undertaken within at least two of the three levels of the numeracy curriculum – Entry Level and one other level. Assessed observations should include at least one numeracy observation at Entry Level. For the Teaching Disabled Learners pathway, practice must be undertaken with groups of learners. Guidance for higher education institutions Page 48 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas Annex 4 Links between the specialist standalone qualifications and Level 5 Diplomas in Education and Training including those with a specialist pathway This annex explains the links between the Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training, the Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training including a specialist pathway and the following standalone specialist qualifications: Level 5 Diploma in Teaching Disabled Learners Level 5 Diploma in Teaching English: Literacy Level 5 Diploma in Teaching English: ESOL Level 5 Diploma in Teaching English: Literacy and ESOL Level 5 Diploma in Teaching Mathematics: Numeracy. Potential trainee teachers should understand that, since 2007, they have been able to undertake one of the above standalone specialist qualifications before a generic teaching qualification alongside it (concurrently), or afterwards. Units from the above standalone specialist qualifications are available as specialist pathways within the Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training including a specialist pathway. The knowledge units from the above standalone specialist qualifications are also available as optional units with the Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training. Trainee teachers achieving one or both units from a standalone qualification that are included as optional units within a Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training relating to a particular area of specialism can go on to take the additional unit(s) to complete one of the standalone qualifications identified above. Recognition of prior learning from the Level 5 standalone specialist qualifications In line with each higher education institution’s arrangements for the recognition of prior learning, individuals who have already achieved a standalone specialist qualification can use the units to meet the optional credit requirements for the relevant specialist pathway in the Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training including a specialist pathway. For example, a trainee teacher who has already achieved the Level 5 Diploma in Teaching Disabled Learners would be given exemption from the units in the specialist pathway for teaching disabled learners. Guidance for higher education institutions Page 49 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas Transfer of practice from the Level 5 standalone specialist qualifications Individuals who have completed one of the standalone specialist qualifications may transfer a maximum of 50 hours of practice from one of these qualifications towards the overall minimum practice requirement of 100 hours for the Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training including a specialist pathway (120 hours for the combined specialist pathway). Guidance for higher education institutions Page 50 of 51 Level 5 Diplomas Transfer of observed and assessed practice from the Level 5 standalone specialist qualifications Individuals who have completed one of the standalone specialist qualifications may transfer a maximum of two observed assessments of practice towards the overall minimum of eight observed assessments of practice required for the Level 5 Diploma in Education and Training including a specialist pathway (ten observed assessments for the combined specialist pathway). Guidance for higher education institutions Page 51 of 51 © Learning and Skills Improvement Service 2013 Registered Office: Friars House, Manor House Drive Coventry CV1 2TE Company number 06454450 May 2013 Registered charity number 1123636