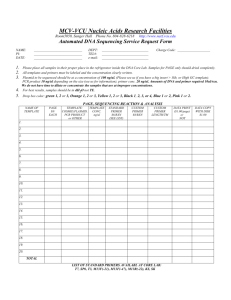
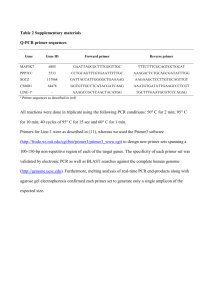
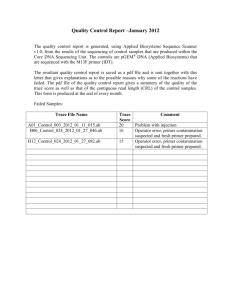
In a cloning experiment a student plans to cut an EcoRI fragment
advertisement

Take home midterm for Molecular Genetics and Biotechnology, 2013 You may refer to notes, books, company catalogs, or the internet. Please cite any information that you consult. It is not necessary to cite the distributed class notes. You may not engage in any interaction with the central nervous system of another person, including conversations, e-mails, e-chat, you posting questions on help boards, calling company help lines, or sharing of answers to these questions among you. Please embed your answers in this file, and return it to Dr. Hardies (hardies@uthscsa.edu) by E-mail before 1:30, Jan 29. You may interject an explanation for your answers to the multiple choice questions. 1) (15 points) After a failed cloning experiment involving EcoRI, the student used the EcoRI to cleave some of the vector. The vector was advertised to be 2 kb. Uncleaved vector ran on a gel consistent with a linear size of 1 kb. After cleavage she killed the EcoRI by heating. One third of the EcoRI treated sample was run on a gel showing a single band that ran slower than the uncut vector, consistent with a linear size of 2 kb. The rest was subjected to ligation, and then the ligase was killed by heating. Half of the ligation product was run on a gel and formed a single slow running band consistent with a linear size of 50 kb. The rest of the religated material was cleaved again with EcoRI, and produced a band consistent with a linear size of 2 kb. Choose one of the following statements to be TRUE, and then write an explanation of what each step in this experiment shows. a) The EcoRI is able to cleave, but must be producing aberrant ends. b) There must be some large DNA contaminating the ligase. c) There is nothing wrong with the EcoRI, but the concentration of vector used in the ligation was too high to use in an actual cloning experiment. d) The apparent 50 kb band is consistent with a ligated circle of vector. e) The experiment shows that the ligation was done at the wrong temperature. 2) (20 points) A postdoc places a cDNA into an expression vector, so that it is expressed with an N-terminal GST fusion affinity tag. Expression was supposed to be heat inducible, but when he heat induced a set of 12 clones derived from the transformation, none of them showed any difference by SDS-PAGE between an induced and uninduced culture. Comment on each of the following diagnostic experiments that he then performed. ALSO answer each of the multiple choice questions that follow. a) Instead of heat inducing, lysing by sonication, spinning out debris, and running the lysate on SDS-PAGE, he heat induced, and then spun the cells down and solubilized all of it in SDS for SDS-PAGE. b) He prepared DNA from the 12 clones and did rudimentary restriction mapping. c) He sequenced a clone across a GST fusion site. d) He sequenced upstream of the N-terminus of the GST. Select one of the following statements about this experiment as a FALSE statement. Provide a better strategy to deal with the specific issue addressed by the false statement. a) If the postdoc had thought ahead to put a second affinity tag of six histidines on the C terminus of the fusion, and if the product had shown up in the insoluble fraction, he would have had the option to switch to an inclusion body preparation and run a denaturing Ni+ column purification. b) If the insert had been prepared as a PCR product with restriction sites added at each end, and the restriction mapping showed that none of the 12 clones had the expected restriction map, it might have helped to also have TA cloned the PCR product so that a fragment that unambiguously had the correct restriction ends could have then been purified from a TA clone. c) Transforming with the uncleaved GST vector and testing if its GST domain could be induced could have uncovered if there was some defect in the vector or the induction protocol before committing to make the construction in this system. d) If the clone expresses 20% of its protein as the fusion in a 2 ml culture, but then shows little expression of the protein when a 2 L culture is grown and induced, the problem would best be addressed by trying a different affinity tag. e) If the clones exhibited a defect in the promoter region upon sequencing, then one should sequence the promoter region of the starting vector. 3) (20 points) An in vitro mutagenesis experiment was planned to change two putative active site residues in an enzyme each to alanine. The gene for the protein was in a pET expression vector. The student designed the following mutagenesis strategy to make both changes at once. Complementary oligos containing the two mutations were synthesized and all four were thrown into a reaction with the wild type plasmid and thermostable DNA polymerase and cycled 20 times. The product was treated with DpnI and transformed into competent cells. This experiment wasn't successful. Give a critique of the flaws in this design. A kit was located that recommended the following alterations. Only oligos 1 and 3 were used. The oligos were reacted with kinase to add 5' phosphates. Before DpnI treatment, the thermal cycled reaction product was treated with a special enzyme mix supplied with the kit. After DpnI treatment, the DNA was transformed into cells and did result in double mutants. Answer the following multiple choice questions about this new design. One enzyme in the 'special' enzyme mixture was probably _____. a) DNA ligase b) 3'->5' exonuclease c) 5'->3' exonuclease d) proofreading thermostable polymerase e) alkaline phosphatase The initial plasmid will have to have been grown in a host with the genotype _____. a) hsdR-M+ b) dam+ c) dutd) unge) dut- ungIn looking at the manifests of several such kits to purchase for this experiment, which of the following components would sway you to choose that kit? a) a tube of special DNA buffer b) a supply of ampicillin c) premade high efficiency competent cells d) a plasmid with two mutations in alpha complementing lacZ and two oligos to revert those mutations e) a catalog of the company's other products 4) (15 points) A PCR primer was designed that had to have its 3' end located in a certain place for its purpose: AspSerAlaLeuLeuArgMetIle GACTCAGCGCTATTGCGCATGATC It was used with its partner at 55C annealing but failed to raise a product. Evaluate the logic behind each of the following attempts to salvage the primer, including whether you think it would be likely to work: a) Change to a two-step cycle with annealing and extension at 72C. b) Increase Mg+2 concentration to 4 mM. c) Increase the primer concentration to 5 uM. d) Change the primer to GCTATTGCGCATGATC and prime at 45C. e) Change the primer to GACTCAGCCCTATTGCGCATGATC, and prime at 60C. 5) (10 points) A student tried to recover an exon from human DNA using primers that included 12 bp 5' extensions including NotI (8 bp) restriction sites. These primer failed to raise a fragment of the correct size, but raised numerous smaller PCR products. How might you fix this experiment? 6) (20 points) In a real time PCR experiment, random hexamers were used to convert cellular RNA to DNA, and the primer pairs for exons of two different genes (gene A and gene B) were applied together with Taqman probes. The object was to measure the relative quantity of transcript from gene A versus gene B. Both primer pair A and B produced an average Ct of 22.5. However a serial dilution of the input cDNA revealed that the slope for primer pair A in Ct vs. log10 starting concentration was -3.322, whereas the slope for primer pair B was -4. State whether you agree with each of the following assertions and why. a) An initial estimate would be that there is 14 times more transcript for gene B than gene A in the starting RNA. b) One should be concerned that primer pair B was exhibiting nonuniform efficiency through the amplification. If performance can't be improved by altering concentration, annealing temperature, or cycle time, one should consider making a new primer pair for exon B. c) Since the slope for primer pair A has a flatter slope than primer pair B, one should be concerned that primer pair A is detecting primer dimer instead of a product originating from the cellular RNA. d) If one of the primer pairs is not giving a clear log linear curve across the Ct threshold it would help to remake the primers so that the PCR product was larger. e) Doubling the cycle time caused the slope for both primers to come to -3.322, but Ct for primer pair B changed for 22.5 to 18.7. This suggests that the primer pairs are no good and should be replaced.