Psychiatry ACS Goals and Objectives Goals 1. To enhance
advertisement

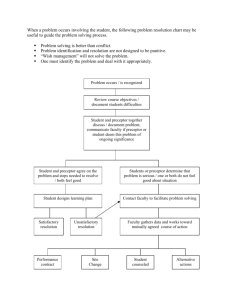
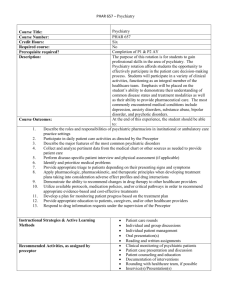
Psychiatry ACS Goals and Objectives Goals 1. To enhance diagnostic and therapeutic skills in the care of patients with primary psychiatric conditions 2. To develop an understanding of the role of the psychiatrist in the community Objectives 1. Medical Knowledge and Skills Objective: Demonstrate knowledge of the diagnosis and management of common psychiatric conditions including adjustment disorders, major depression, anxiety disorders, bipolar disorder, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, substance abuse, dementia, and schizophrenia. 2. Career Development objective: 1.The student should become aware of the rewards and challenges of practicing psychiatry in the community. 2. The student should develop a better appreciation for the scope of practice in the community. 3. The student should become aware of subspecialty choices of practicing psychiatrists. 3. Advocacy Objective: 1. Identify and list local mental health resources available to patients in the community, including organizations that assist with education and advocacy for patients with psychiatric illnesses. 2. Identify and list common barriers to mental health care commonly encountered by patients of all socioeconomic brackets. 3. Write and turn in a resource list that can be used by patients and physicians in the community. 4. Health Care Systems/Practice Management Objective: 1.Describe practice management issues that are important in the practice that you serve. 2. Discover the most common diagnosis and procedure codes for your practice. 3. Learn how the Patient protection and affordable care act is and will impact the practice in which you will be participating. 5. Service Learning Objective: Participate in one or more community service activities in your community. 6. CAM Objective: 1. Identify alternative medicine practices that patients utilize in the practice that you serve. 2. Identify the advantages and disadvantages (including risks) of the alternative medicine practices that you identify. 7. Other Objectives: No information provided. Overview description of Selective activities The student will be assigned a site preceptor who is a practicing Texas psychiatrist. The student will spend a majority of the course working with the preceptor in an office setting, evaluating at least 2 outpatients per day. The patients can be seen either alone or with the preceptor at the discretion of the preceptor. The student will participate in the activities in which the preceptor is involved, including office practice, nursing home care, office management, continuing medical education programs, emergency room call, civic activities, and medical staff meetings. Students will not be assigned to preceptors who are relatives. Students will complete and turn in a comprehensive report of barriers to mental health care encountered by patients in the community, and a list of resources and advocacy groups available to patients. Weekly Schedule of activities: Usual hours: Hours to be determined by preceptor (Note: Call responsibilities at the discretion of the preceptor. Students will have at least one half day per week for independent study/completion of formal course requirements. ) Type of students who would benefit from the course This course is particularly valuable for students interested in a career in psychiatry. It is also of value to any student who is interested in primary care. Method of student evaluation Check all that apply - complete appropriate section(s) only: 1. Clinical Observation A. Frequency - How often are students observed clinically? Daily during the course of clinical activities. B. Format - What method(s) are used to document the student's clinical performance? Daily oral feedback End of period oral feedback Written feedback Other 2. Oral Presentation A. Audience - To whom does the student present? No information provided. B. Frequency / duration of presentation(s)? No information provided. 3. Written Assignments A. Format The student will turn in the following: 1) a comprehensive report of barriers to mental health care encountered by patients in the community, 2) a list of resources and advocacy groups available to patients 3) a list and description of the subspecialty choices of practicing physicians 4) the answers to health care systems questions provided in a syllabus 5) a reflective essay