Thermo_ta_answers
advertisement

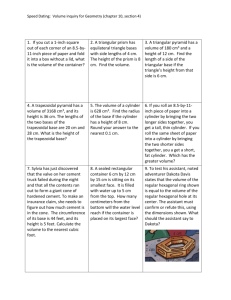
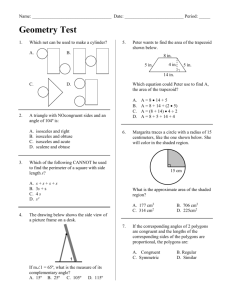
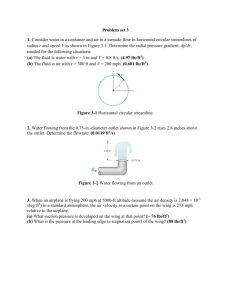
Assignment 1 (From Chapter 1) 1. Problem No. 1.11 When an object of mass 5 kg is suspended from a spring, the spring is observed to stretch by 8 cm. The deflection of the spring is related linearly to the weight of the suspended mass. What is the proportionality constant, in newton per cm, if g = 9.81 m/s2? Solution: Hooke's law of elasticity is an approximation that states that the extension of a spring is in direct proportion with the load added to it as long as this load does not exceed the elastic limit. F=k*x …………………………………… (1) Where, x is the displacement of the end of the spring from its equilibrium position (in SI units: "m"); F is the restoring force exerted by the material (in SI units: "N" or kgms-2); k is the force constant (or spring constant) (in SI units: "N·m-1" or "kgs-2"). Also, F=m*g …………………………………… (2) Where, m is the mass of the spring (5kg) g is the acceleration due to gravity (9.8 m/s2) Equating (1) and (2) and solving for k; k = m*g/x k = (5.0kg)*(9.81m/s2)/(8.0cm) k= 6.131 N/cm 2. Problem No. 1.25 15 kg of carbon dioxide (CO2) gas is fed to a cylinder having a volume of 20 m3 and initially containing 15 kg of CO2 at a pressure of 10 bar. Later a pinhole develops and the gas slowly leaks from the cylinder. (a) Determine the specific volume, in m3/kg, of the CO2 in the cylinder initially. Repeat for the CO2 in the cylinder after the 15 kg has been added. (b) Plot the amount of CO2 that has leaked from the cylinder, in kg, versus the specific volume of the CO2 remaining in the cylinder. Consider v ranging up to 1.0 m3/kg. Solution: Initial mass of CO2; m = 15kg After adding 15kg of CO2; m= 30kg During leaking, if specific volume is v, m = V/v (a) Using v = V/m Initial specific volume v is 20 m3 / 15kg = 1.33 m3/kg After an additional 15kg enters v is 20 m3 / 30kg = 0.67 m3/kg (b) Beginning with 30kg of CO2 in the cylinder, the amount of gas that has leaked is Amount leaked = 30kg – mass in cylinder when specific volume ranges to 1.0 m3/kg Amount leaked = 30kg – 20 m3 / 1.0 m3/kg Amount leaked = 10kg Therefore: Specific volume at initial 30kg = 0.67 m3/kg Specific volume at final 10kg = 0.67 m3/kg 3. Problem No. 1.29 A system consists of nitrogen (N2) in a piston---cylinder assembly, initially at p1 = 20 lbf/in2 and occupying a volume of 2.5 ft3. The nitrogen is compressed to p2 = 100 lbf/in2 and a final volume of 1.5 ft3. During the process the relation between pressure and volume is linear. Determine the pressure in lbf/in2 at an intermediate state where the volume is 2.1 ft3 and sketch the process on a graph of pressure versus volume. Solution: p1 = 20 lbf/in2 p2 = 100 lbf/in2 v1 = 2.5 ft3 v2 = 1.5 ft3 To find P and V (intermediate) (P – p1) / (V-v1) = (p2-p1) / (v2-v1) Solving for P with V = 2.1 ft3 P = 227.5 – 85(V) P = 227.5 – 85(2.1) P = 49 ft3 On the pressure – volume coordinates