Kinetics Quiz #2 Factors that Change the Reaction Rate 1. Which of
advertisement

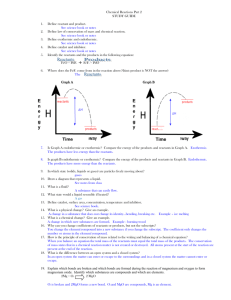
Kinetics 1. High kinetic energy High activation energy Catalytic effect on the reaction Large surface area for the reaction Consider the following reaction: 2H2O2(aq) → 2 H2O(t) + O2(g) When 1.0 g of KI is added to the H2O2, bubbles of O2 are produced at an increased rate. When the reaction is complete, the mass of KI is 1.0 g. The KI is a A. B. C. D. 4. Zn(s) + S(s) → ZnS(s) Ba2+(aq) + SO42-(aq) → BaSO4(s) NH3(g) + HCl(g) → NH4Cl(g) 2 Ag+(aq) + CO32-(aq) → Ag2CO3(s) Dust particles suspended in the air inside unheated grain elevators can sometimes react explosively because the dust particles have a: A. B. C. D. 3. Factors that Change the Reaction Rate Which of the following reactions is the slowest at room temperature? A. B. C. D. 2. Quiz #2 Product Catalyst Reactant Reaction Intermediate Consider the following factors: I. II. III. Concentration of reactants. Temperature of reactants. Surface area of reactants. The factors that affect the rate of a chemical reaction between two gases are A. B. C. D. I and II only I and III only II and III only. I, II, and III 5. Consider the following reactions: I. N2(g) + O2(g) → 2NO(g) II. 2Mg(s) + O2(g) → 2MgO(s) III. CaCO3(s) + 2H+(aq) → Ca2+(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g) Increasing the surface area will increase the reaction rate in A. B. C. D. 6. An untreated sugar cube does not burn when held over a lighted match. A sugar cube coated with cigarette ash readily ignites and burns. All of the cigarette ash remains after the reaction. The factor that caused this change in rate is the A. B. C. D. 7. 9. Nature of reactants Presence of a catalyst Increase in surface area Increase in concentration Which combination of factors will affect the rate of the following reaction? Zn(s) + 2HCl (aq) → ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g) A. B. C. D. 8. II only I and III only II and III only I, II and III Temperature and surfaces only Temperature and concentration only Concentration and surface area only Temperature, concentration, and surface area To increase the rate of a reaction there must be an increase in I II III IV frequency of successful collisions volume of reaction vessel pressure of the system mass of the system A. B. C. D. I only I and III only I, III and IV only I, II, III and IV Consider the following reaction: 2MnO4-(aq) + 5C2O42-(aq) + 16H+(aq) 2Mn2+(aq) + 10CO2(g) + 8H2O(l) The rate of decomposition of the oxalate ion is increased by A. B. Adding NaOH Removing CO2 C. D. 10. Which of the following factors affect the rates of both homogeneous and heterogeneous reactions I. Nature of reactants II. Presence of a catalyst III. Temperature of system IV Concentration of reactants A. B. C. D. 11. Nature of reactants Temperature of system Surface area of reactants Concentration of reactants Consider the following reaction: 2S(s) + 302(g) → 2SO3(g) + heat The rate of this reaction could be increased by A. B. C. D. 13. I and IV only II and III only. II, III and IV only I, II, III and IV Which of the following factors affects the rate of heterogeneous reactions only. A. B. C. D. 12. Adding a catalyst Decreasing the pressure. Decreasing temperature Adding a catalyst Increasing the concentration of S(s) Increasing the concentration of SO3(g) 6.0 g of Mg reacts with some HCl in two different experiments. The reaction for both was: Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) MgCl2(aq) + H2(g) In the first experiment, it took 6.2 minutes for all the Mg to react. In the second experiment, it took 10.8 minutes for all the Mg to react. Which of the following could explain the change in rate in the second experiment? A. B. C. D. A catalyst was added The Mg was powdered The H2 was decreased The temperature was decreased 14. 15. Which of the following reactions is most likely to proceed at the greatest rate? A. Zn(s) + S(s) ZnS(s) B. H2(g) + I2(s) 2HI(g) C. Cu(s) + Cl2(g) D. 2KOH + H2SO4(aq) CuCl2(s) 2H2O(l) + K2SO4(aq) Consider the following reaction: Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) MgCl2(aq) + H2(g) Which of the following would increase the reaction rate? A. B. C. D. 16. an increase in pressure an increase in temperature an increase in the concentration of H2 an increase in the concentration of CaCl2 When a candle C20H42 burns, the following reaction occurs: 2C20H42(s) + 61O2(g) 40CO2 + 42H2O(g) If the rate of production of CO2 is 0.49 g/min, what is the rate of oxygen consumption? A. B. C. D. 17. Which of the following properties could best be monitored in order to determine the reaction rate of the above burning candle? A. B. C. D. 18. 0.24 g/min 0.27 g/min 0.36 g/min 0.54 g/min mass of C20H42 pressure of H2O surface area of C20H42 concentration of C20H42 Which of the following factors only affects the rate of heterogeneous reactions? A. nature of reactants B. C. D. 19. presence of a catalyst temperature of reactants surface area of reactants Consider the following experimental results: Experiment 1 Experiment 2 Reactants Ca(s) + HCl(aq) Zn(s) Temperature 20 0C 40 0C Concentration 1.0 M 2.0 M Rates Fast Slow + HCl(aq) Which factor would account for the faster reaction rate in Experiment 1? A. B. C. D. 20. temperature surface area nature of reactants solution concentration Consider the following reaction: 2NO(g) + O2(g) 2NO2(g) How could the rate of this reaction be increased? A. B. C. D. 21. Which factor explains why coal dust is explosive? A. B. C. D. 22. Reduce the pressure Increase the volume Remove some NO2(g) Increase the temperature temperature surface area concentration addition of catalyst Which factor explains why potassium generally reacts faster than magnesium? A. surface area B. C. D. 23. temperature concentration nature of reactants Which factor explains why gasoline vapour is explosive? A. B. C. D. temperature surface area concentration nature of the reactant