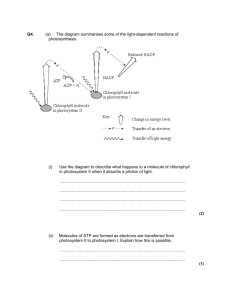
11 - Photosynthesis
advertisement
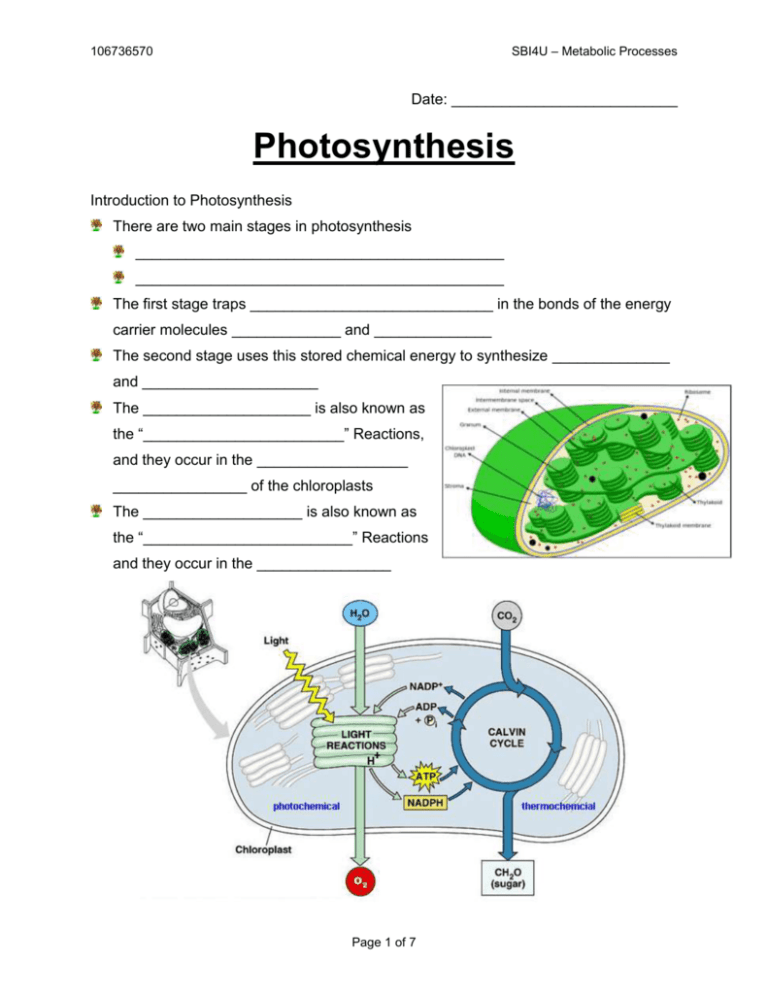
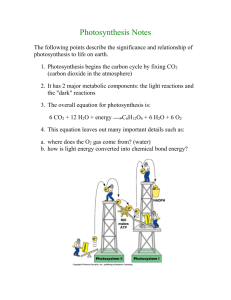
SBI4U – Metabolic Processes 106736570 Date: ___________________________ Photosynthesis Introduction to Photosynthesis There are two main stages in photosynthesis ____________________________________________ ____________________________________________ The first stage traps _____________________________ in the bonds of the energy carrier molecules _____________ and ______________ The second stage uses this stored chemical energy to synthesize ______________ and _____________________ The ____________________ is also known as the “________________________” Reactions, and they occur in the __________________ ________________ of the chloroplasts The ___________________ is also known as the “_________________________” Reactions and they occur in the ________________ Page 1 of 7 SBI4U – Metabolic Processes 106736570 Historical Background In early experiments on photosynthesis, Joseph Priestley found that a green plant sealed in a jar with a candle or a mouse could “______________” the air in the jar He was the first to observe the _______________ of plants Van Helmont did an experiment in which he weighed a small tree, the soil in the pot in which the tree was planted and the water given to the tree over a five year period He found that the tree changed its __________ significantly over the five years while the mass of the _____________________________ Van Helmont concluded that the mass gained did not come from the ___________, but rather from the ______________________________ Pigments Pigments are molecules that can absorb certain _______________ of ___________ The primary pigment of photosynthesis is chlorophyll Chlorophyll is green in colour because it _____________ green light while it ______________ red and blue colours Additional pigments called __________________ pigments absorb most colours of the visible spectrum to some extent Most leaves appear green because chlorophyll is much more ________________ than the accessory pigments Page 2 of 7 SBI4U – Metabolic Processes 106736570 Chlorophyll ______________ in short daylight allowing the colours of the accessory pigments to become visible in the fall Chlorophyll Although there is only a slight difference in the ___________________________ of Chlorophyll A and B, Chlorophyll A is located in the __________________________ where radiant energy is transferred for the production of energy carrier molecules The characteristics chemical structure of chlorophyll is a series of alternating ___________ and ______________ bonds The electrons of the double bonds are held _______________________ than the electrons of the single bonds Light energy is ________________ by the loosely held electrons, freeing them from the bond and enabling them to enter a series of reactions similar _______________ _________________________ of aerobic respiration Photosystems Some chlorophyll and accessory pigments are grouped into two types of light gathering complexes called ____________________ ___________ (PSII) and ______________ ____________ (PSI) These light gathering complexes are embedded in the __________________ ____________ of the chloroplast Photosystem II is also called _________, because the reaction center of this type of photosystem best absorbs light photons at a wavelength of ____________ Photosystem I is also referred to as ___________ because the reaction center of this type of photosystem best absorbs light photons at a wavelength of ____________ The photons absorbed in Photosystem II have ___________________ because the ___________________ of light have the higher energy Page 3 of 7 SBI4U – Metabolic Processes 106736570 Each photosystem is composed of several hundred __________________________ molecules They are called _______________________________ because they collect and channel energy to the ___________________________ Accessory pigments can be molecules of chlorophyll A and a variety of other accessory pigments such as: _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ These other types of pigment molecules help absorb some light at wavelengths not absorbed by chlorophyll Photosynthesis is broken into two reactions Page 4 of 7 SBI4U – Metabolic Processes 106736570 Light Dependent Stage (Photo Stage) When a _______________ of light energy eventually reaches the chlorophyll A molecule at the __________________, ________ electrons from the chlorophyll A molecule are bounced out of the _________________ This means that the chlorophyll molecule has been ___________________ The energized electrons are quickly absorbed by an electron acceptor called “____” embedded in the ____________________ membrane The electrons lost by the chlorophyll A molecule in the reaction center of the Photosystem II are immediately ___________________ with two electrons released in the _____________________ or splitting of one molecule of water In addition to the two electrons, photolysis also produces two _______ and _______ that is released in to the atmosphere The two electrons from Photosystem II that were absorbed by electron acceptor “Q” are then transferred to ___________________ and on to several other molecules in a series of ___________________________ reactions This electron transport chain is very similar to that found in mitochondria The production of ATP is similar to that in _______________________ in that H+ are pumped into the ______________________ and large electrochemical gradient is established Page 5 of 7 SBI4U – Metabolic Processes 106736570 At the end of the first electron transport chain, the pair of electrons move to _____________________, where they again become energized by another ______________ of light The newly energized electrons are quickly passed to _________________ and then they go on to combine with NADP+ and H+ to produce ______________ The ATP and NADPH molecules then move to the ______________ where they are used to power the _______________________________ Light Independent Stage Sometimes known as the _____________________ or the ____________________ This is the ____________________ stage The role of the dark reactions is to fix ___________________ into ______________ using ___________ energy transformed from ___________ energy in the thylakoids The dark reactions occur in the stroma of the chloroplasts Although the dark reactions do not require _______________ or use ___________, it cannot take place in the absence of light because it needs _______________ from the light reaction Although _______________ is the primary product of photosynthesis, more complex ___________________ as well as ____________ and _____________ can be synthesized as byproducts of the dark reactions The Calvin Cycle The Calvin Cycle (or C3 Cycle) begins with a molecule of _____________________ ________________ and results in the production of one molecule of ____________ 3 molecules of ________________________ are reacted with 3 molecules of ________, which are then immediately broken into 6 molecules of _________________________ Page 6 of 7 SBI4U – Metabolic Processes 106736570 Each of the six 3-phosphoglycerates is phosphorylated by ____________ into six ___________________________ which are then converted to _________________ _______________ using NADPH as energy One glyceraldehyde -3-phosphate is removed from the cycle, leaving 5 molecules of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, which are converted to _________________________ The three ribulose-5-phosphates are then _________________________________ back to ____________________________________ to start the cycle again Each turn of the cycle “fixes” one molecule of CO2 Therefore, 6 turns of the cycle are necessary to fix the carbon in one molecule of glucose since glucose has ___________________ A total of 18 molecules of ATP and 12 molecules of NADPH are provided as energy by the light reaction Page 7 of 7