Biology 121 – Molecular Cell Biology
advertisement
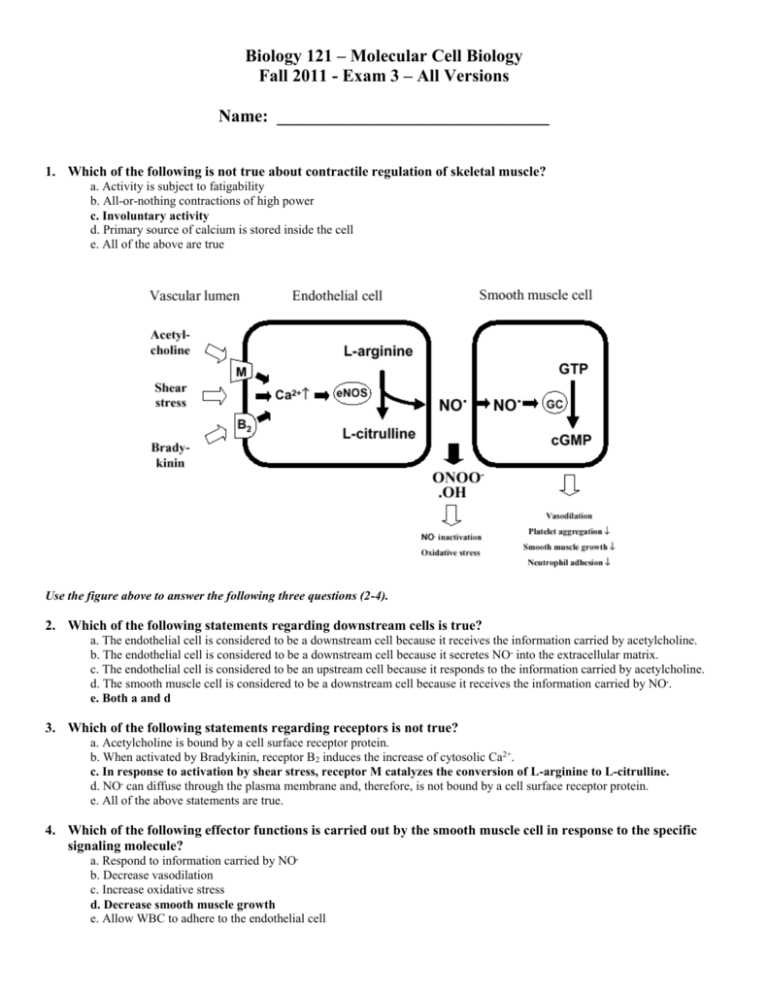
Biology 121 – Molecular Cell Biology Fall 2011 - Exam 3 – All Versions Name: _______________________________ 1. Which of the following is not true about contractile regulation of skeletal muscle? a. Activity is subject to fatigability b. All-or-nothing contractions of high power c. Involuntary activity d. Primary source of calcium is stored inside the cell e. All of the above are true Use the figure above to answer the following three questions (2-4). 2. Which of the following statements regarding downstream cells is true? a. The endothelial cell is considered to be a downstream cell because it receives the information carried by acetylcholine. b. The endothelial cell is considered to be a downstream cell because it secretes NO . into the extracellular matrix. c. The endothelial cell is considered to be an upstream cell because it responds to the information carried by acetylcholine. d. The smooth muscle cell is considered to be a downstream cell because it receives the information carried by NO.. e. Both a and d 3. Which of the following statements regarding receptors is not true? a. Acetylcholine is bound by a cell surface receptor protein. b. When activated by Bradykinin, receptor B 2 induces the increase of cytosolic Ca2+. c. In response to activation by shear stress, receptor M catalyzes the conversion of L-arginine to L-citrulline. d. NO. can diffuse through the plasma membrane and, therefore, is not bound by a cell surface receptor protein. e. All of the above statements are true. 4. Which of the following effector functions is carried out by the smooth muscle cell in response to the specific signaling molecule? a. Respond to information carried by NO. b. Decrease vasodilation c. Increase oxidative stress d. Decrease smooth muscle growth e. Allow WBC to adhere to the endothelial cell 5. Which of the following is not true about contractile regulation of cardiac muscle? a. Activity is not subject to fatigability b. All-or-nothing contractions of moderate power c. Involuntary activity d. Primary source of calcium is stored inside the cell e. All of the above are true 6. Which of the following statements is a reason why contraction in cardiac muscle is spontaneous and not fatiguable? a. The neurotransmitter acetylcholine starts its action potential and it uses calcium stored in the endoplasmic reticulum. b. Calcium is not needed in cardiac muscle because tropomyosin is not blocking myosin from binding the troponin complex. c. A regulatory system allows for spontaneous depolarization and the Calcium channels located directly on the Ttubules allow for a potentially unlimited source of calcium from the extracellular matrix. d. Neurons continuously send signals to the heart muscle and large amount of sarcoplasmic reticulum keeps it from fatiguing. e. Cardiac muscle is voluntary and high powered at the cost of fatiguability. 7. The complexity of the mitotic cell cycle is necessary to __________. a. Ensure that all cell will eventually undergo apoptosis b. Ensure that all second messenger cascades perform their functions c. Control cell migration in the ovary d. Control cell number, quality, and cell type e. Create four daughter cells to deliver the parents DNA to its offspring 8. How is the G-protein [of the G-protein linked receptor] activated? a. Once a ligand binds to the receptor, the receptor undergoes conformational change and that leads to conformational change of the G-protein; thereby allowing the removal of a GDP in exchange for a GTP molecule. b. Once a ligand binds to the receptor, the receptor undergoes conformational change that leads to conformational change of the ligand; thereby allowing the removal of a GDP in exchange for a GTP molecule. c. Once a ligand binds to the receptor, the receptor undergoes conformational change that leads to conformational change of the G-protein; thereby allowing the removal of a GTP in exchange for a GDP molecule. d. The G-protein is constitutively activated. There is a mechanism to inactivate a G-protein, but not activating it. e. Once a ligand binds to the receptor, the receptor undergoes conformational change that leads to the phosphorylation of the G-protein, thereby activating it. 9. A single ligand activating two or more pathways is an example of __________. a. Divergent crosstalk b. Convergent crosstalk c. Integration d. Amplification e. Desensitization 10. What is the function of diacylglycerol (DAG) in the G-protein linked-Phospholipase C pathway? a. Activates the gated calcium ion channel in the ER membrane allowing calcium ions to flow into the cytosol. b. Recruits protein kinase C (PKC) c. Recruits phospholipase C (PLC) d. Acts as a digestive enzyme e. Catalyzes the exchange of PKC for PLC 11. Which of the following is not true about contractile regulation of smooth muscle? a. Activity not subject to fatigability b. All-or-nothing contractions of low power c. Involuntary activity d. Activity depends on the amount of Ca2+ in the cytosol e. All of the above are true 12. Which of the following statements is not true about small hydrophobic signaling molecules? a. They mostly require carrier proteins to reach the target cell. b. They can readily diffuse across the target cell plasma membrane to bind to receptors in the cytosol. c. They are molecules commonly found in the bloodstream secreted during autocrine signaling. d. Many hormones are small hydrophobic signaling molecules. e. All of the above statements are correct. 13. How is a cell regulated to shut off DNA repair mechanisms in the presence of too many DNA mutations? a. p21 binding to APC/C b. p21 binding to BH123 c. p21 binding to p53 d. p21 binding to PCNA e. p21 binding to cyclin or cdk 14. In synaptic signaling, the system has elements of both paracrine and endocrine systems because __________. a. Nerve cells communicate at long distances via axons b. Ligands are secreted at the axon terminal, which is a short (local) distance from the target cell c. It involves the bloodstream d. All of the above e. Both a and b 15. Which of the following signaling involves adaptation for systemic regulation in Animalia? a. Endocrine signaling b. Synaptic signaling c. Paracrine signaling d. All of the above 16. Which of the following is not true about contractile regulation of smooth muscle cells? a. Low number of gap junctions are used b. Actin filaments run in all directions c. Ca2+ binds to calmodulin at up to 4 sites d. Calcium-calmodulin solubizes caldesmon e. Hormones, neurotransmitters, metabolites, and growth factors all affect Ca 2+ levels 17. Which statement is MOST true? a. Growth phase 2 (G2) is when the cell gets ready for DNA synthesis, this is when kinetochores are refined and finalized. b. Growth phase 2 (G2) is when cells get ready for cell division and requires DNA synthase complexes, repair enzymes as well as histones. c. S-phase is after the chromosomes have been proof read and edited. d. Growth phase 2 (G2) requires construction of organelles, cytoskeletal proteins, molecular motors, and metabolic enzymes as the cell prepares for cell division. 18. Which of the following statements best describes the process of desensitization? a. The receptor has low affinity for the ligand; therefore, the ligand is not able to bind. b. A ligand is not able to bind to the receptor because there is such a low amount of receptors or no receptors at all present in the plasma membrane. c. Once the ligand binds to the receptor the half-life of the ligand is reduced, and the receptor will not activate. d. A receptor is bound by a ligand, thereby, activating the receptor. However, there is a lack of effector enzyme to be activated. e. A receptor is bound by a ligand, thereby, activating the receptor. However, a protein binds to the cytosolic domain of the receptor, therefore, preventing activation of the intracellular signaling pathway. 19. Levels of importance for signaling pathways are described in what order? (From low to high) a. Divergent cross-talk, daily activities, convergent cross-talk. b. Daily activities, divergent cross-talk, convergent cross-talk. c. Daily activities, convergent cross-talk, divergent cross-talk. d. Convergent cross-talk, divergent cross-talk, daily activities. e. Divergent cross-talk, convergent cross-talk, daily activities. 20. Phosphorylated CREB can bind to __________ to __________ in __________. a. A promoter; regulate gene expression; the nucleus b. A promoter; regulate translation; the cytosol c. cAMP; regulate gene expression; the nucleus d. PKA catalytic subunit; regulate gene expression; the nucleus e. Nuclear membrane; regulate transport of a transcription factor; the nucleus 21. What is the sequence of events that occurs during the regulation of cardiac muscle contraction? a. Neuron, acetylcholine, action potential, dihydropyradine in T-tubule membrane, influx of Ca2+ from extracellular matrix b. Spontaneous action potential, dihydropyradine in T-tubule membrane, ryanodine in sarcoplasmic reticular (SR) membrane, Ca2+ from SR lumen flow into cytosol c. Neuron, acetylcholine, action potential, dihydropyradine in T-tubule membrane, ryanodine in sarcoplasmic reticular (SR) membrane, Ca2+ from SR lumen flow into cytosol d. Spontaneous action potential, dihydropyradine in T-tubule membrane, influx of Ca2+ from extracellular matrix e. Hormones, action potential, Calcium-calmodulin solubizes caldesmon, Ca2+ binds to calmodulin at up to 4 sites, Ca2+ from SR lumen flow into cytosol 22. If p53 is mutated and can’t perform its normal function, which of the following would most likely occur? a. Cells cannot pass through the G1/S checkpoint. b. Cells are marked for apoptosis. c. Cells cannot pass through the M checkpoint, no matter what. d. Cells with damaged DNA may proliferate in an uncontrollable manner. e. The G0 checkpoint would not work properly. 23. During G1, a cell can either be told to “go” and progress through the cell cycle or told to “stop” and perhaps go back into the G0 phase. Which of the following is not a determining factor to tell the cell to “go”? a. Enough nutrients are available b. The cell is anchored (anchorage dependence) c. External signals such as growth hormones, cytokines, and hormones are available d. The cell is crowded with other cells in the area (density-dependent inhibition) e. All these are necessary to tell the cell to “go”. 24. Apoptosis is characterized by __________. a. Cessation of DNA repair mechanisms, cell shrinkage, DNA mutation, and reduced transcription b. Cell shrinkage, DNA fragmentation, and nuclear membrane blebbing c. Nuclear membrane blebbing, DNA replication, cell shrinkage, and cessation of DNA repair mechanisms d. Cell shrinkage, increased DNA repair mechanisms, nuclear membrane blebbing, and reduced transcription e. All of the above 25. Which is not a function of M-cdk-cyclin? a. Phosphorylation of Rb protein b. Phosphorylation of histones c. Phosphorylation of lamins d. Phosphorylation of myosin e. All of the above are functions of M-cdk-cyclin 26. List the 4 components of a signaling system in order of activity. a. Ligand, bloodstream, second messenger cascade, target mechanism b. Signaling cell, membrane receptor, second messenger protein, target mechanism c. Ligand, membrane receptor, gene expression, signal transduction pathway d. Ligand, receptor, second messenger cascade, target mechanism e. Paracrine signaling, endocrine signaling, synaptic signaling, contact-dependent signaling 27. Which of the following statements is not true? a. In synaptic signaling, both the signaling cell and target cell must be neurons. b. In autocrine signaling, the target cell and signaling cell are the same cell type in the same vicinity. c. In paracrine signaling, the target cell and signaling cell are in the same vicinity but may not be the same cell type. d. In endocrine signaling, hormones released by the endocrine glands travel through the bloodstream to their target cells. e. All these statements are true. 28. Which of the following is an example of convergent cross-talk? a. Glycogen breakdown in the liver can be induced by both glucagon from the pancreas acting through cAMP and vasopressin from neural pituitary acting through PLC-. b. Both adenylyl cyclase and phospholipase C can be activated by a G-protein linked receptor. c. Regulation of skeletal muscle contraction by acetylcholine and of smooth muscle contraction by hormones. d. The control of cell proliferation in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. e. All of the above are examples of convergent cross-talk. 29. Which of the following sets contain molecules that act only in second messenger cascades? a. Calcium ions, IP3, and cAMP b. Ras, Raf, MEK, Erk c. Amphipathic signaling molecules and cAMP d. G-protein linked receptor, Receptor tyrosine kinase, Ion channel receptor e. None of the above 30. Which statement is most accurate? a. Dinoflagellates don’t contain microtubules but they contain a nuclear envelope that remains intact all throughout division. b. Eukaryotes utilize kinetochore microtubules while maintaining an intact nuclear envelope all throughout the process. c. Diatoms and yeasts have multiple sets of microtubules and their chromosomes remain inside of the intact nuclear envelope during cell division. d. Bacteria exhibit mitosis and while the nuclear envelope splits into fragments, the kinetochore microtubules are very involved and intact. 31. Most drugs that are developed act on which type of receptor? a. G-protein linked receptor b. Receptor Tyrosine Kinase c. Receptor Serine/Threonine Kinase d. Ion-channel Receptor e. Enzyme-linked Receptor 32. Which of the following facts about ligand is true? a. Active concentration of most ligands is astoundingly high b. Most ligands have very short half-life c. Ligands bind directly to the phospholipid bilayer d. Low affinity is described as the interaction between a ligand and its affiliated receptor at very low ligand concentration. e. Both a and b 33. Which phase of the cell cycle is the key to differentiation events? a. G0 b. G1 c. S d. G2 e. M 34. Cell survival and cell proliferation are regulated by __________. a. Inhibitory, but not activating signals b. Activating, but not inhibitory signals c. Multiple required signals d. Protein cleavage e. Phosphorylation of proteins 35. If any kinetochores are not attached to spindle microtubules during metaphase they send a molecular signals that delays cycle progression during? a. APC/C b. M checkpoint regulation c. Cyclins and securing d. Apoptosis 36. At the point of ER construction, what protein(s) are responsible for the accumulation of phosphatidyl inositol in the cytosolic phase of the plasma membrane for Phospholipase C to attack? a. The G protein-linked receptor. b. The G protein. c. The Phospholipase C. d. A and C. e. None of the above. 37. Which of the following reaction occur during the Adenylyl cyclase catalysis? a. cAMP is converted to ATP b. CREB-binding protein is activated c. GTP is converted to GDP d. GTP inactivate α subunit of stimulatory G protein e. None of the above 38. Which of the following signal molecules cause a change of gene expression within the target cell? a. Progesterone b. Growth factors c. Lipid hormones d. Vitamin D e. All of the above 39. When the intrinsic apoptosis cascade when it passes which point will be only allowed to proceed to apoptosis and not return to normal cell cycle? a. When all PCNA is bound by p21 and at a concentration five times that of p21 b. When the cell begins to transcribe p21 c. When the p53 is activated d. When GTP is hydrolyzed to GDP e. None of the above 40. Which of the following statements about apoptic pathway is true? a. The intrinsic apoptotic pathway is activated by an anti-apoptotic molecule. b. The intrinsic apoptotic pathway can be activated by Fas ligand. c. The intrinsic apoptotic pathway is activated by the M-phase cdk-cyclin complex. d. The extrinsic apoptotic pathway may occur in the extracellular matrix only if the Fas Death Receptor is soluble. e. The extrinsic apoptotic pathway can be activated by an extracellular signaling molecule. 41. Which of the following is the correct sequence of events in an intrinsic apoptotic pathway? a. Fas ligand, Fas Death Receptor, cleavage of procaspase-8, activation of caspase cascade b. Activation of anti-apoptic molecule, inactivation of BH123 proteins, synthesis of cytochrome C, activation of APAF-1, cleavage of procaspase-8, activation of intrinsic apoptotic pathway c. Inactivation of anti-apoptotic molecule, aggregation of BH123 proteins, leakage of cytochrome C into cytosol, activation of APAF-1, cleavage of procaspase-9, activation of caspase cascade d. Activation of APC/C, digestion of securin, activation of separase, digestion of cohesins, intrinsic apoptotic pathway e. DNA mutation, activation of ATM/ATR, phosphorylation of caspase-9, activation of caspase cascade 42. Which of the following statements about the induction of cell cycle checkpoint arrest is true? a. Phosphorylated p53 acts as a transcription factor to activate the expression of p21. b. Unphosphorylated p53 acts as a transcription factor to activate the expression of p21. c. Unphosphorylated p53 activates p21. d. p21 binds to PCNA when the concentration of p21 is 5X that of PCNA. e. Both c and d 43. Which of the following is an important process during cytokinesis? a. Microtubule depolymerization pulling sister chromatids apart b. Actin filament depolymerization pulling the plasma membrane inward c. Actin filament polymerization occurs in the middle of the cell d. Myosin pulls actin filaments within the contractile ring e. Membranes forming around the separated chromosomes forming 2 new nuclei 44. Total number of cells in an organism is regulated by __________. a. A balance between cell division and cell death b. A balance between necrosis and apoptosis c. A balance between symmetric and asymmetric cell division d. Even separation of RNA molecules, proteins, cytoskeletal components, and organelles during cell division e. A balance in cell size increase 45. Which of the following signaling systems does not require a receptor? a. Paracrine system b. Endocrine system c. Synaptic system d. Contact dependent signaling e. Signaling through a gap junction 46. Which of the following molecules is not a transmembrane protein? a. Ras b. Receptor tyrosine kinase c. Soluble gas receptor d. Ion-channel linked receptor e. Both a and c 47. Which of the following is an example of divergent cross-talk? a. Both skeletal and smooth muscles can be induced to undergo contraction. b. G-protein linked receptor can activate both adenylyl cyclase and phospholipase C. c. PLC induces the production of DAG and IP3. d. Ras activates Raf, which in turn activates MEK. e. There are multiple sources where Ca2+ can be retrieved. 48. Which of the following is true about the TGF-Smad pathway? a. Very few levels of regulation involving only a couple of reactions and enzymes b. Quick cellular and physiological changes c. Ensures that effector function is induced quickly d. All of the above e. None of the above 49. What is the complete molecular pathway for the activation of PKC after G protein activation? a. Active GTP alpha and beta/gamma subunits activate phospolipase C, which breaks down phosphatidyl inositol into DAG and IP3. The DAG then binds PKC, but it’s inactive until the complex binds Ca 2+ which was released from the ER by IP3. b. Active GTP alpha and beta/gamma subunits activate phospholipase E, which breaks down phosphatidyl serine into DAG and IP3.The DAG binds PKC, but it’s inactive until the complex binds Ca2+ which was released from IP3. c. Active GTP alpha and beta/gamma subunits activate phospolipase C, which breaks down phosphatidyl inositol into DAG and IP3. The IP3 binds PKC, but it’s inactive until the complex binds Ca2+ which was released from DAG. d. Active GDP alpha and beta/gamma subunits activate phospolipase C, which breaks down phosphatidyl inositol into DAG and IP3. The DAG binds PKC, but it’s inactive until the complex binds Ca2+ which was released from IP3. e. None of the above. 50. Upon entering the cell, lipid soluble hormones bind to a specific receptor present in the cytoplasm. The receptor-hormone complex, in turn, __________. a. Adds lipid components to membrane-destined proteins b. Binds to DNA in the nucleus and acts as a transcription factor c. Activates adenyl cyclase, allowing it to begin cAMP creation d. Causes the cell to release nitric oxide e. Activates a receptor serine/threonine receptor