- Internet Geography
advertisement

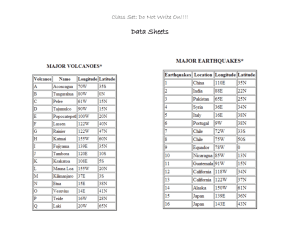
Year 9 Geography – Internet Earthquakes and Virtual Volcanoes Lesson Plans Key Stage 3 Group Date Period Year 9 Unit number: 13 Course Title: Internet Earthquakes and Virtual Volcanoes Lesson Plan – 1 Key Question – What do we already know about volcanoes and earthquakes? Learning Objectives: To be able to work co-operatively with others Time Main activities of lesson 2 1. Register 3 2. Introduction to Geography in Year 9 Internet Earthquakes and Virtual Volcanoes [7 weeks] The Global Fashion Industry [7 weeks] What is development?/Comparing Countries [6 weeks] Tourism [6 weeks] Local Actions, Global Effects [3 weeks] Limestone Environments (Malham Fieldtrip) [3 weeks] 5 10 1 4 5 10 5 5 3. Discuss expectations etc / classroom rules 4. Students to number their pages and outline the classroom rules 5. ITT – What do we know about volcanoes and earthquakes? 6. PW – What do we already know about volcanoes and earthquakes? 7. Envoying – What do we already know about volcanoes and earthquakes? 8. Groups to prepare a 2 minute presentation on Volcanoes and Earthquakes 9. 30 second group presentation on Volcanoes and Earthquakes Conclusion/consolidation & recap (Q&A) Homework: Resources: Exercise Books Differentiation: Extension: Extension Teacher assist lower ability students Differentiated resources CSA work with targeted students (where applicable) Mixed ability pairs and groups Literacy Numeracy Identifying and understanding key curriculum vocabulary. Use of a variety of Calculation of time to manage time targets strategies to identify unfamiliar words. for each task. Using language of comparison ICT SMSC Working co-operatively in pairs and groups Evaluation Internet Geography – http://www.internetgeography.co.uk 1 Year 9 Geography – Internet Earthquakes and Virtual Volcanoes Lesson Plans Key Stage 3 Group Date Year 9 Unit number: 13 Course Title: Internet Earthquakes and Virtual Volcanoes Lesson Plan – 2a – Internet Lesson Key Question – What is a real volcano like? Learning Objectives: Time 5 2 3 10 5 1 19 5 Period 1. To be able to locate a volcano in an atlas 2. To be able to extract a range of information from a web site 3. To be able to ask geographical questions and suggest an appropriate sequence of investigation Main activities of lesson 1. Lesson starter 2. Register 3. Lesson recap and outline: Explain to students that they are to carry out a ‘virtual’ field visit to Stromboli. Inform the students that by using an internet website at www.educeth.ethz.ch/stromboli/ they are to visit the volcano. The purpose of the ‘visit’ is to gather relevant information to produce an A4-size brochure of Stromboli’s geographical features for tourists who visit the volcano, or a web page for the same purpose (G&T). 4. The students are to locate the volcano using an atlas. The students are to produce an annotated sketch map to show the location of the volcano and a brief description 5. Ask students to discuss in groups what sort of questions they will need to ask to find out about the volcano. Ask them to brainstorm headings under which they could find information e.g. details of altitude, relief, Mediterranean vegetation, hazards, eruption evidence, settlements and other human features. 6. Compare these headings to the headings in Geography Matters Book 3 – Resource sheet – 6.1a 7. Students use the web site to find out key geographical information about the volcano and its geography Conclusion/consolidation & recap (Q&A) Homework: Resources: Atlases Computers Internet Differentiation: Extension: Extension Search for further information about the Teacher assist lower ability students volcano using a range of other sources e.g. Differentiated resources CD Rom (Encarta) or search engines on the CSA work with targeted students (where Internet. They should also seek images and applicable) save them into their “My Work/Documents” Mixed ability pairs and groups area Literacy Numeracy Identifying and understanding key curriculum vocabulary. Use of a variety of Calculation of time to manage time targets strategies to identify unfamiliar words. for each task. Using language of comparison ICT SMSC Use of ICT to extract information Working co-operatively in pairs and groups Use of a search engine Evaluation Internet Geography – http://www.internetgeography.co.uk 2 Year 9 Geography – Internet Earthquakes and Virtual Volcanoes Lesson Plans Key Stage 3 Group Date Year 9 Unit number: 13 Course Title: Internet Earthquakes and Virtual Volcanoes Lesson Plan – 2b – Non - Internet Lesson Key Question – What is a real volcano like? Learning Objectives: Time 5 2 3 10 1 2 7 15 5 Period 1. To be able to locate a volcano in an atlas 2. To be able to extract a range of information from a video 3. To be able to ask geographical questions and suggest an appropriate sequence of investigation Main activities of lesson 1. Lesson starter 2. Register Lesson recap and outline: Explain to students that they are to investigate the volcano Mount St Helen’s (locate on an atlas map). The purpose of the ‘investigation’ is to gather relevant information from a video and text to produce an A4-size brochure of Mount St Helen’s geographical features for tourists who visit the volcano. 4. The students are to locate the volcano using an atlas. The students are to produce an annotated sketch map to show the location of the volcano and a brief description 5. ITT – brainstorm 3 questions they would need to answer to complete their brochure 6. Ask students to discuss in A/B pairs what sort of questions they will need to ask and find answers to, e.g. details of altitude, relief, vegetation, hazards, eruption evidence, settlements and other human features. Remind them that they should keep a note of potential dangers that tourists will need to be warned about. 7. Snowballing – two’s become fours – share ideas for questions. Fours become eights and share ideas for questions 8. Data Collection: Students to watch video about Mount St Helen’s. Students attempt to answer geographical questions which they brainstormed in the preparation session. Students then use resources materials e.g. text books and newspaper articles and information downloaded from the internet. Students can also used CDROM’s and the internet to research the topic. Conclusion/consolidation & recap (Q&A) Homework: Resources: Atlases Video Differentiation: Extension: Extension Search for further information about the Teacher assist lower ability students volcano using a range of other sources e.g. Differentiated resources text book (Investigating Geography) or on CSA work with targeted students (where the Internet. applicable) Mixed ability pairs and groups Literacy Numeracy Identifying and understanding key curriculum vocabulary. Use of a variety of Calculation of time to manage time targets strategies to identify unfamiliar words. for each task. Using language of comparison ICT SMSC Use of ICT to extract information Working co-operatively in pairs and groups Use of a search engine Evaluation 3. Internet Geography – http://www.internetgeography.co.uk 3 Year 9 Geography – Internet Earthquakes and Virtual Volcanoes Lesson Plans Key Stage 3 Group Date Period Year 9 Unit number: 13 Course Title: Internet Earthquakes and Virtual Volcanoes Lesson Plan – 3a – Internet Lesson Key Question – What is a real volcano like? Learning Objectives: 1. To be able to make decisions about appropriate clothing and equipment for a visit to a volcano Time 5 2 3 5 5 5 20 5 2. To be able to select and use secondary sources of evidence 3. To be able to collect, and record available evidence and present it in an appropriate way Main activities of lesson 1. Lesson starter 2. Register 3. Lesson recap and outline: Explain to students that they are to carry out a ‘virtual’ field visit to Stromboli. Inform the students that by using an internet website at www.educeth.ethz.ch/stromboli/ they are to visit the volcano. The purpose of the ‘visit’ is to gather relevant information to produce an A4-size brochure of Stromboli’s geographical features for tourists who visit the volcano, or a web page for the same purpose (G&T). 4. Inform them that they should plan the contents of a visitor’s rucksack for the time of year of the visit and to keep a note of potential dangers that tourists will need to be warned about. Complete sheet 6.1b. First selection is their own. 5. Amended selection to be completed in pairs. 6. Final selection to be completed in groups. Voting is not allowed them must draw conclusions through discussion in groups of 3-4. 7. Virtual fieldtrip: During the visit, at each station, ask students to gather the relevant information (by copying/pasting into a word-processed document) and to draw annotated field sketches, e.g. Station 5 – view across Sciara del Fuoco (standard route) and station 13 – on the Vancori (scenic route). Suggest that students download and save useful images, e.g. maps and field-sketch photographs. Remind them to sign the ‘summit guest book’ to receive an e-mail in return. The students can complete sheet 6.1c from the Geography Matters Photocopiable Resource book (p151) to help guide them through the fieldtrip Conclusion/consolidation & recap (Q&A) Homework: Resources: Atlases Computers Internet Differentiation: Extension: Extension Produce brochure: Discuss with students the Teacher assist lower ability students target audience for the leaflet and the Differentiated resources appropriate layouts, fonts, language, colour CSA work with targeted students (where etc that they might consider and that they applicable) will need to include appropriate illustrations. Mixed ability pairs and groups Lower-attaining students are likely to need more structured guidance, e.g. a brochure template, prompts for writing and map/sketch outlines – they can use 6.1e & 6.1F Literacy Numeracy Identifying and understanding key curriculum vocabulary. Use of a variety of Calculation of time to manage time targets strategies to identify unfamiliar words. for each task. Using language of comparison ICT SMSC Use of ICT to extract information Working co-operatively in pairs and groups Use of a search engine Evaluation Internet Geography – http://www.internetgeography.co.uk 4 Year 9 Geography – Internet Earthquakes and Virtual Volcanoes Lesson Plans Key Stage 3 Group Date Period Year 9 Unit number: 13 Course Title: Internet Earthquakes and Virtual Volcanoes Lesson Plan – 3b – Non - Internet Lesson Key Question – What is a real volcano like? Learning Objectives: 1. To be able to select and use secondary sources of evidence 2. Time 5 2 3 10 25 5 To be able to sort, collect, and record available evidence Main activities of lesson 1. Lesson starter 2. Register 3. Lesson recap and outline: Explain to students that they are to investigate the volcano Mount St Helen’s (locate on an atlas map). The purpose of the ‘investigation’ is to gather relevant information from a video and text to produce an A4-size brochure of Mount St Helen’s geographical features for tourists who visit the volcano. 4. In pairs the students complete the card sort/enquiry (Waugh style) into Mount St Helens which students should complete at this stage. How did Harry Trueman Die? 5. Students complete write up activity Conclusion/consolidation & recap (Q&A) Homework: Resources: Atlases Produce Brochure Computers Internet Differentiation: Extension: Extension Produce brochure: Discuss with students Teacher assist lower ability students possible brochure layouts that they might Differentiated resources consider and that they will need to include CSA work with targeted students (where appropriate illustrations. Lower-attaining applicable) students are likely to need more structured guidance, e.g. a brochure template, prompts Mixed ability pairs and groups for writing and map/sketch outlines. Ask them also to evaluate rucksack contents, to identify good and poor choices and different choices for another time of year. Literacy Numeracy Use language of comparison. Describe events and processes making connections between them. Language of causality/reason, e.g. because, therefore, in Calculation of time to manage time targets the light of, thus, however. Read for each task. increasingly complex non-fiction text, selecting essential points and using inference and deduction. ICT SMSC Use of word processor to produce 2 minute Examine the social implications of the news article. eruption Evaluation Internet Geography – http://www.internetgeography.co.uk 5 Year 9 Geography – Internet Earthquakes and Virtual Volcanoes Lesson Plans Key Stage 3 Group Date Period Year 9 Unit number: 13 Course Title: Internet Earthquakes and Virtual Volcanoes Lesson Plan – 4a Internet Lesson Key Question – Are all volcanoes identical? Learning Objectives: To be able to use secondary sources of evidence, including ICT To be able to identify characteristic features of volcanoes Note to non-specialist staff: Read p96/7 of Geography Matters Book 3 before you teach this lesson. It provides a good over view of what you will be delivering. Any problems see a member of the Geography Department Time 5 2 3 5 1 3 6 20 5 Main activities of lesson 1. Lesson starter – Students to open a document in shared resources and are to identify the main features of a typical volcano using labelled cross-sections, e.g. to show cone, crater, vent. 2. Register 3. Lesson recap and outline: (If available – students to use interactive white board to annotate the image) Explain to students that they are to investigate volcanoes. Ask about the different states they can be in (active, dormant and extinct). Are there any other differences? 4. Show the students two images of volcanoes (Shield and a Strato [composite] volcano) and the students are to identify their similarities and differences. 5. ITT: What are the possible reasons for the differences? 6. A/B Pairs: What are the possible reasons for the differences? 7. Student feedback 8. Ask students to consider the key question and to find similarities and differences between volcanoes, using a range of appropriate web sites textbooks/reference books, and to identify the main features. The students should use sheet 6.2a to complete this activity Conclusion/consolidation & recap (Q&A) Homework: Resources: Collect information from a range of resources about a recent earthquake (this information will be required next lesson) Differentiation: Extension Teacher assist lower ability students Differentiated resources CSA work with targeted students (where applicable) Mixed ability pairs and groups Literacy Use language of comparison. Describe events and processes making connections between them. Language of causality/reason, e.g. because, therefore, in the light of, thus, however. Read increasingly complex non-fiction text, selecting essential points and using inference and deduction. ICT Use of appropriate web sites to extract information Evaluation Annotating a volcano (shared documents) Geography Matters Book 3 – p96/7 Internet Extension: Numeracy Calculation of time to manage time targets for each task. SMSC Working co-operatively in pairs and groups Internet Geography – http://www.internetgeography.co.uk 6 Year 9 Geography – Internet Earthquakes and Virtual Volcanoes Lesson Plans Key Stage 3 Group Date Period Year 9 Unit number: 13 Course Title: Internet Earthquakes and Virtual Volcanoes Lesson Plan – 4b Non - Internet Lesson Key Question – Are all volcanoes identical? Learning Objectives: To be able to use secondary sources of evidence, including ICT To be able to identify characteristic features of volcanoes Note to non-specialist staff: Read p96/7 of Geography Matters Book 3 before you teach this lesson. It provides a good over view of what you will be delivering. Any problems see a member of the Geography Department Time 5 2 3 5 1 3 6 20 5 Main activities of lesson 1. Lesson starter – Students to complete sheet on identifying the main features of a typical volcano using labelled cross-sections, e.g. to show cone, crater, vent. 2. Register 3. Lesson recap and outline: (If available – students to use interactive white board to annotate the image) Explain to students that they are to investigate volcanoes. Ask about the different states they can be in (active, dormant and extinct). Are there any other differences? 4. Show the students two images of volcanoes (Shield and a Strato [composite] volcano) and the students are to identify their similarities and differences. 5. ITT: What are the possible reasons for the differences? 6. A/B Pairs: What are the possible reasons for the differences? 7. Student feedback 8. Ask students to consider the key question and to find similarities and differences between volcanoes, using Geography Matters Book 3 and to identify the main features. The students should use sheet 6.2a to complete this activity Conclusion/consolidation & recap (Q&A) Homework: Resources: Collect information from a range of resources about a recent earthquake (this information will be required next lesson) Differentiation: Extension Teacher assist lower ability students Differentiated resources CSA work with targeted students (where applicable) Mixed ability pairs and groups Literacy Use language of comparison. Describe events and processes making connections between them. Language of causality/reason, e.g. because, therefore, in the light of, thus, however. Read increasingly complex non-fiction text, selecting essential points and using inference and deduction. ICT Use of appropriate web sites to extract information Evaluation Annotating a volcano – work sheet Geography Matters Book 3 – p96/7 Internet Extension: Numeracy Calculation of time to manage time targets for each task. SMSC Working co-operatively in pairs and groups Internet Geography – http://www.internetgeography.co.uk 7 Year 9 Geography – Internet Earthquakes and Virtual Volcanoes Lesson Plans Key Stage 3 Group Date Period Year 9 Unit number: 13 Course Title: Internet Earthquakes and Virtual Volcanoes Lesson Plan – 5a Internet Lesson Key Question – What is an earthquake? Are all earthquakes identical? Learning Objectives: To be able to use an extended geographical vocabulary To be able to use secondary sources of evidence including ICT Note to teacher: It is suggested that you pre-prepare a list of recent earthquakes for the students to choose from to complete their investigation. These should be a mixture of countries at different levels of development. Time Main activities of lesson 5 1. Lesson starter – PowerPoint Activity – Volcanoes: Odd one out 2 2. Register 3 3. Lesson recap and outline: 5 5 20 5 5 4. As a stimulus show students a video/play a selection of eyewitness accounts/pictures of earthquake devastation/seismic trace 5. Discuss with them what phenomenon is being described/demonstrated/occurring (and why they think this) and consider what the experience might feel like. Introduce appropriate terminology, e.g. Richter scale, epicenter, focus, seismic wave, tremor, aftershocks. 6. Ask students, in groups, to investigate the nature and effects of a recent earthquake, using a range of resources (newspaper articles/television reports/textbooks/the internet). Ensure there are examples from countries in different states of economic development. Useful websites include: Kobe at www.city.kobe.jp/index-e.html and San Francisco at http://quake.wr.usgs.gov/more/1906/got_seismogram.htm and www.sfmuseum.org/quake/report.html The students can use Geography Matters Book 3 Resource Pack 6.3a to help structure their research investigation. 7. Ask students to either write up their findings in the style of a newspaper report, emphasising the sequence of events, and the effects on buildings, infrastructure and people. Conclusion/consolidation & recap (Q&A) Homework: Resources: Newspaper articles Television reports Textbooks The internet Complete report ready for next lesson Geography Matters Book 3 Resource Pack – sheet 6.3a PowerPoint Activity – Volcanoes: Odd one out Differentiation: Extension: Extension Teacher assist lower ability students Differentiated resources CSA work with targeted students (where applicable) Mixed ability pairs and groups Literacy Numeracy Use language of comparison. Describe events and processes making connections between them. Language of causality/reason, e.g. because, therefore, in Calculation of time to manage time targets the light of, thus, however. Read for each task. increasingly complex non-fiction text, selecting essential points and using inference and deduction. ICT SMSC Use of appropriate web sites to extract Working co-operatively in pairs and groups information Evaluation Internet Geography – http://www.internetgeography.co.uk 8 Year 9 Geography – Internet Earthquakes and Virtual Volcanoes Lesson Plans Key Stage 3 Group Date Period Year 9 Unit number: 13 Course Title: Internet Earthquakes and Virtual Volcanoes Lesson Plan – 5b Non-Internet Lesson Key Question – What is an earthquake? Are all earthquakes identical? Learning Objectives: To be able to use an extended geographical vocabulary To be able to use secondary sources of evidence including ICT Note to teacher: It is suggested that you pre-prepare a list of recent earthquakes for the students to choose from to complete their investigation. These should be a mixture of countries at different levels of development. It is also advised that you print off a range of additional materials for those students who do not complete their homework as a back up. Time Main activities of lesson 5 1. Lesson starter – PowerPoint Activity – Volcanoes: Odd one out 2 2. Register 3 3. Lesson recap and outline: 5 5 20 5 5 4. As a stimulus show students a video/play a selection of eyewitness accounts/pictures of earthquake devastation/seismic trace 5. Discuss with them what phenomenon is being described/demonstrated/occurring (and why they think this) and consider what the experience might feel like. Introduce appropriate terminology, e.g. Richter scale, epicenter, focus, seismic wave, tremor, aftershocks. 6. Ask students, in groups, to investigate the nature and effects of a recent earthquake, using a range of resources (newspaper articles/television reports/textbooks/the internet). Ensure there are examples from countries in different states of economic development. Useful websites include: Kobe at www.city.kobe.jp/index-e.html and San Francisco at http://quake.wr.usgs.gov/more/1906/got_seismogram.htm and www.sfmuseum.org/quake/report.html The students can use Geography Matters Book 3 Resource Pack 6.3a to help structure their research investigation. 7. Ask students to either write up their findings in the style of a newspaper report, emphasising the sequence of events, and the effects on buildings, infrastructure and people. Conclusion/consolidation & recap (Q&A) Homework: Resources: Complete report ready for next lesson Differentiation: Extension Teacher assist lower ability students Differentiated resources CSA work with targeted students (where applicable) Mixed ability pairs and groups Literacy Use language of comparison. Describe events and processes making connections between them. Language of causality/reason, e.g. because, therefore, in the light of, thus, however. Read increasingly complex non-fiction text, selecting essential points and using inference and deduction. ICT Use of appropriate web sites to extract information Evaluation Newspaper articles Television reports Textbooks The internet Geography Matters Book 3 Resource Pack – sheet 6.3a PowerPoint Activity – Volcanoes: Odd one out Extension: Numeracy Calculation of time to manage time targets for each task. SMSC Working co-operatively in pairs and groups Internet Geography – http://www.internetgeography.co.uk 9 Year 9 Geography – Internet Earthquakes and Virtual Volcanoes Lesson Plans Key Stage 3 Group Date Period Year 9 Unit number: 13 Course Title: Internet Earthquakes and Virtual Volcanoes Lesson Plan – 6 Non-Internet Lesson for all Key Question – What is an earthquake? Are all earthquakes identical? Learning Objectives: To be able to use an extended geographical vocabulary To be able to use secondary sources of evidence including ICT To know how a country’s level of development can affect the impact of earthquakes Note to teacher: It is suggested that you pre-prepare a list of recent earthquakes for the students to choose from to complete their investigation. These should be a mixture of countries at different levels of development. It is also advised that you print off a range of additional materials for those students who do not complete their homework as a back up. Time Main activities of lesson 5 1. Lesson starter – PowerPoint Activity – Key Terminology: Earthquakes Word Game starter 2 2. Register 3 3. Lesson recap and outline: 5 5 10 15 5 Students to brainstorm ways in which they can identify a country’s level of economic development 5. Students to identify what level of development the country they have studied is at (they can use an atlas to identify the country’s level of development using a range of development indicators) . They are to describe and explain their reasoning 6. Rearrange students in groups to share their findings of the impacts of earthquakes in countries in different states of economic development. Students to discuss their findings (level of development against impact). In groups they are to discuss possible reasons for any differences they find. This can be done by writing LEDCs and MEDCs on a large sheet of sugar paper. The students can then identify any similarities they find between the case studies 7. Write a report to the United Nations explaining the requirements of LEDCs to cope with earthquakes. Conclusion/consolidation & recap (Q&A) Homework: Resources: Atlas PowerPoint Activity – Key Terminology: Earthquakes Word Game starter Differentiation: Extension: Extension Teacher assist lower ability students Differentiated resources CSA work with targeted students (where applicable) Mixed ability pairs and groups Literacy Numeracy Use language of comparison. Describe events and processes making connections Calculation of time to manage time targets between them. Language of for each task. causality/reason, e.g. because, therefore, in The use of the Richter Scale to compare the light of, thus, however. Read magnitude of earthquakes increasingly complex non-fiction text, The use of social and economic indicators to selecting essential points and using identify a country’s level of development inference and deduction. ICT SMSC Use of appropriate web sites to extract Working co-operatively in pairs and groups information Evaluation 4. Internet Geography – http://www.internetgeography.co.uk 10 Year 9 Geography – Internet Earthquakes and Virtual Volcanoes Lesson Plans Key Stage 3 Group Date Period Year 9 Unit number: 13 Course Title: Internet Earthquakes and Virtual Volcanoes Lesson Plan – 7a Internet Lesson Key Question – Where do earthquakes and volcanoes occur? Learning Objectives: to be able to use an atlas to plot locations on a world map using latitude and longitude to be able to describe geographical patterns Time 5 2 3 10 10 10 5 5 Main activities of lesson 1. Lesson starter – PowerPoint Activity – Volcanoes and earthquakes word association game 2. Register 3. Lesson recap and outline: 4. Recap longitude and latitude. This can be done using the power point presentation. Demonstrate locating a volcano/earthquake onto the outline map shown on the power point presentation. Discuss use of appropriate symbols 5. Internet Lesson: Ask students to use internet to obtain locations of recent earthquakes and volcanic eruptions and to locate these on a world map using latitude and longitude positions. 6. Students to describe the patterns they see and comment on the relationship between the two (Useful websites are: www.gsrg.nmh.ac.uk/gsrg.html (recent earthquakes in the UK compared with world earthquakes) and www.geo.arizona.edu/tools/seismo (real seismic data). For other websites see ‘Resources’). SEN students to complete Where do volcanoes and earthquakes occur? Work Sheet 7. Students to examine the relationship between volcanoes and earthquakes and plate margins Conclusion/consolidation & recap (Q&A) Homework: Resources: Internet PowerPoint Presentation: location_of_volcanoes_and_earthquakes Atlas World map: world_country.pdf Key Geography Matters Book 3 SEN Work sheet – where do volcanoes and earthquakes occur? Differentiation: Extension: Extension Teacher assist lower ability students Differentiated resources CSA work with targeted students (where applicable) Mixed ability pairs and groups Literacy Numeracy Use language of comparison. Describe events and processes making connections between them. Language of Calculation of time to manage time targets causality/reason, e.g. because, therefore, in for each task. the light of, thus, however. Read The use of longitude and latitude to locate increasingly complex non-fiction text, places selecting essential points and using inference and deduction. ICT SMSC Use of appropriate web sites to extract Working co-operatively in pairs and groups information Evaluation Internet Geography – http://www.internetgeography.co.uk 11 Year 9 Geography – Internet Earthquakes and Virtual Volcanoes Lesson Plans Key Stage 3 Group Date Period Year 9 Unit number: 13 Course Title: Internet Earthquakes and Virtual Volcanoes Lesson Plan – 7b Non-Internet Lesson Key Question – Where do earthquakes and volcanoes occur? Learning Objectives: to be able to use an atlas to plot locations on a world map using latitude and longitude to be able to describe geographical patterns Time 5 2 3 10 10 10 5 5 Main activities of lesson 1. Lesson starter – PowerPoint Activity – Volcanoes and earthquakes word association game 2. Register 3. Lesson recap and outline: 4. Recap longitude and latitude. This can be done using the power point presentation. Demonstrate locating a volcano/earthquake onto the outline map shown on the power point presentation. Discuss use of appropriate symbols 5. Non-Internet Lesson: Using list of recent earthquakes/volcanic eruptions obtained by teacher (with longitude and latitude information included) the students are to locate these on a world map using latitude and longitude positions. 6. Students to describe the patterns they see and comment on the relationship between the two. SEN students to complete Where do volcanoes and earthquakes occur? Work Sheet 7. Students to examine the relationship between volcanoes and earthquakes and plate margins Conclusion/consolidation & recap (Q&A) Homework: Resources: PowerPoint Presentation: location_of_volcanoes_and_earthquakes Atlas World map: world_country.pdf Key Geography Matters Book 3 SEN Work sheet – where do volcanoes and earthquakes occur? Differentiation: Extension: Extension Teacher assist lower ability students Differentiated resources CSA work with targeted students (where applicable) Mixed ability pairs and groups Literacy Numeracy Use language of comparison. Describe events and processes making connections between them. Language of causality/reason, e.g. because, therefore, in Calculation of time to manage time targets the light of, thus, however. Read for each task. increasingly complex non-fiction text, selecting essential points and using inference and deduction. ICT SMSC Use of appropriate web sites to extract Working co-operatively in pairs and groups information Evaluation Internet Geography – http://www.internetgeography.co.uk 12 Year 9 Geography – Internet Earthquakes and Virtual Volcanoes Lesson Plans Key Stage 3 Group Date Period Year 9 Unit number: 13 Course Title: Internet Earthquakes and Virtual Volcanoes Lesson Plan – 8 Key Question – What causes earthquakes and volcanoes? Learning Objectives: to make relationships between patterns on a global scale to understand the causes of and processes involved in plate movements Note to teacher: The tectonics video shows a five minute clip on each plate margin. This can be shown to each of the groups during the lesson Time Main activities of lesson 5 1. Lesson starter – PowerPoint – Classification Starter 2 2. Register 3 3. Lesson recap and outline: 5 20 10 5 Introduce students to the concept of plate tectonics and the ‘nature’ of plates, their movement and types of margins (constructive, destructive and conservative). This can be done by showing the first 2 mins of the tectonics video. Students to get into groups of four as jigsaw groups. Each student should be assigned a number (1-4). 5. The students then get into expert groups (all the ones together, all the twos etc.) Group one are to research destructive plate margins (sheet 6.5a can be used to focus the group), Group two are to research collision plate margins (6.5b), Group 3 are to research conservative plate margins (6.5c) and Group 4 are to research constructive plate margins (6.5d). 6. The students then return to their group and take it in turns to describe and explain what happens at each of the different plate margins. Conclusion/consolidation & recap (Q&A) Homework: Resources: PowerPoint – Classification Starter Internet Video – Tectonics – Video 37 Atlas World map Text books Geography Matters Book 3 p102-104) Geography Matters Book 3 Resource Pack 6.5a-d Differentiation: Extension: Extension Teacher assist lower ability students Differentiated resources CSA work with targeted students (where applicable) Mixed ability pairs and groups Literacy Numeracy Use language of comparison. Describe events and processes making connections between them. Language of causality/reason, e.g. because, therefore, in Calculation of time to manage time targets the light of, thus, however. Read for each task. increasingly complex non-fiction text, selecting essential points and using inference and deduction. ICT SMSC Use of appropriate web sites to extract Working co-operatively in pairs and groups information Evaluation 4. Internet Geography – http://www.internetgeography.co.uk 13 Year 9 Geography – Internet Earthquakes and Virtual Volcanoes Lesson Plans Key Stage 3 Group Date Year 9 Unit number: 13 Course Title: Internet Earthquakes and Virtual Volcanoes Lesson Plan – 9 Period Key Question – How do people live with earthquakes and volcanoes? Learning Objectives: to analyse and evaluate evidence and draw and justify conclusions Note to teacher: Time Main activities of lesson 5 1. Lesson starter – Play the theme tune to Ready, Steady, Cook – provide students with a shopping bag of ingredients (plastacine , lolly pop sticks and string) tell the groups they have five minutes to plan an activity in which they will teach the processes at their plate margin. 2 2. Register 3 3. Lesson recap and outline: Inform students that they are to work in groups to investigate managing natural hazards 35 The activities listed below may be taken on by different groups of students and shared through presentations to the rest of the class. 4. Group 1: students to examine ways of reducing the hazard of earthquakes by preparing for them. Ask them to use textbooks/articles to study building techniques and measures aimed at reducing the likelihood of building collapse. Ask them to compare measures in countries at different states of economic development. 5. Group 2: students to explore the role of aid agencies in emergency care following earthquake disasters – see unit 2 ‘The restless earth’ for listed websites. Geography Matters Book 1 has a good section on Aid and natural disasters. 6. Group 3: students to investigate some strategies aimed at predicting natural hazards eruption, e.g. scientific monitoring (see Stromboli website and other internet websites in ‘Resources’). 7. Group 4: Students to investigate how should volcanoes should be managed in the future. You should also examine the advantages of volcanic activity, e.g. geothermal power, fertile soils. Find evidence of why people choose to live in active zone areas. Ask them to find evidence of why people choose to live in active zone areas. 5 Conclusion/consolidation & recap (Q&A) Homework: Resources: Textbooks Articles Video TV Geography Matters Book 1 & 3 Key Question 7 Resources (instruction sheet) Student self assessment sheets plastacine , lolly pop sticks and string Differentiation: Extension: Extension The Students are then to present their Teacher assist lower ability students findings to the class Differentiated resources CSA work with targeted students (where applicable) Mixed ability pairs and groups Literacy Numeracy Use language of comparison. Describe events and processes making connections between them. Language of causality/reason, e.g. because, therefore, in Calculation of time to manage time targets the light of, thus, however. Read for each task. increasingly complex non-fiction text, selecting essential points and using inference and deduction. ICT SMSC Use of appropriate web sites to extract Working co-operatively in pairs and groups information Evaluation Internet Geography – http://www.internetgeography.co.uk 14 Year 9 Geography – Internet Earthquakes and Virtual Volcanoes Lesson Plans Internet Geography – http://www.internetgeography.co.uk 15 Year 9 Geography – Internet Earthquakes and Virtual Volcanoes Lesson Plans Key Stage 3 Group Date Year 9 Unit number: 13 Course Title: Internet Earthquakes and Virtual Volcanoes Lesson Plan – 10 Period Key Question – How do people live with earthquakes and volcanoes? Learning Objectives: to analyse and evaluate evidence and draw and justify conclusions to be able to present information in an appropriate way Note to teacher: Time Main activities of lesson 5 1. Lesson starter – Alphabet challenge lesson starter 2 2. Register 3 3. Lesson recap and outline: Inform students that they are to work in groups to investigate managing natural hazards 10 4. The groups are to complete preparing their presentations 25 5. Students complete presentations. Other students assess the presentations using assessment sheets 5 Conclusion/consolidation & recap (Q&A) Homework: Resources: Textbooks Articles Video TV Geography Matters Book 1 & 3 Key Question 7 Resources (instruction sheet) Student self assessment sheets PowerPoint Presentation: Alphabet Challenge starter Differentiation: Extension: Extension Teacher assist lower ability students Differentiated resources CSA work with targeted students (where applicable) Mixed ability pairs and groups Literacy Numeracy Use language of comparison. Describe events and processes making connections between them. Language of causality/reason, e.g. because, therefore, in Calculation of time to manage time targets the light of, thus, however. Read for each task. increasingly complex non-fiction text, selecting essential points and using inference and deduction. ICT SMSC Use of appropriate web sites to extract Working co-operatively in pairs and groups information Presenting information to peers Evaluation Internet Geography – http://www.internetgeography.co.uk 16 Year 9 Geography – Internet Earthquakes and Virtual Volcanoes Lesson Plans Key Stage 3 Group Date Year 9 Unit number: 13 Course Title: Internet Earthquakes and Virtual Volcanoes Lesson Plan – 11 Period Key Question – What causes earthquakes, what are the impacts and human responses to these hazards? - Assessment Activity Learning Objectives: to analyse and evaluate evidence and draw and justify conclusions to be able to present information in an appropriate way Note to teacher: Time Main activities of lesson 5 1. Lesson starter – the students are to list five things about volcanoes and earthquakes that they did not know before studying the unit 2 2. Register 3 3. Lesson recap and outline: Inform students that they are to work in groups to investigate managing natural hazards 5 4. Discuss enquiry and go over assessment criteria 35 5. Students to complete an investigation into the causes, effects and human responses into an earthquake of their choice. They should use the assessment criteria to help achieve a good national curriculum level 5 Conclusion/consolidation & recap (Q&A) Homework: Resources: Internet Atlas World map Text books Geography Matters Book 3 Geography Matters Book 3 Assessment mark sheet (p17) Key Question 8 Resources (instruction sheet) Differentiation: Extension: Extension The students should be encouraged to mark Teacher assist lower ability students their own work then each others before a Differentiated resources final teacher assessment is awarded CSA work with targeted students (where applicable) Mixed ability pairs and groups Literacy Numeracy Use language of comparison. Describe events and processes making connections between them. Language of causality/reason, e.g. because, therefore, in Calculation of time to manage time targets the light of, thus, however. Read for each task. increasingly complex non-fiction text, selecting essential points and using inference and deduction. ICT SMSC Use of appropriate web sites to extract Working co-operatively in pairs and groups information Presenting information to peers Evaluation Internet Geography – http://www.internetgeography.co.uk 17