Ecology & Environment Test
advertisement

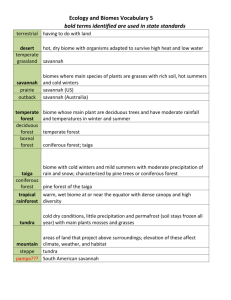
Chapter 49 Student: _________________________________________________________ 1. A lake that is nutrient rich and tends to have large populations of algae is a(n) _____ lake. A. oligotrophic B. eutrophic C. temperate D. stratified 2. Which type of biome would be located at an area where dry air descends? A. temperate forests B. grasslands C. deserts D. tundra 3. Incoming solar radiation affects: A. rise and fall of air masses B. evaporation or precipitation of moisture C. seasons D. all of these choices are directly or indirectly affected by solar radiation 4. The largest communities on land are called A. biospheres. B. estuaries. C. tundras. D. taigas. E. biomes. 5. The earth is actually farther from the sun during the period when the Northern Hemisphere is having summer. How can this be explained? A. The sun grows more powerful on a half-year cycle. B. There is a six-month lag phase between sunlight being absorbed and lost. C. The tilt of the earth presents the Northern Hemisphere in a more perpendicular angle, and this increased sunlight per surface area offsets more than the decrease from added distance. D. There must be some mistake in measuring the earth's orbit because if the earth were farther away, we would be cooler. 6. If the earth was standing still (not rotating), wind directions would A. cease. B. all run north and south. C. all run east and west. D. remain the same since earth rotation does not affect wind directions. 7. Cold and dry air is heavy and sinks; hot and warm air is lighter and rises. A. If the earth were standing still, equatorial air would rise and move toward the poles. B. This would replace heavy polar air that sinks and flows toward the equator. C. This would produce high altitude winds moving toward the poles and surface winds moving toward the equator. D. All of the choices are correct. E. No winds would be produced, merely high altitude warm air and low altitude cold air. 8. In the water cycle, evaporated equatorial water that rises and does not immediately rain back down proceeds to move A. all the way to the poles where it causes snow. B. all the way to the poles if it does not encounter mountain ranges, which it usually does. C. to about 60o north or south and then cool and condense, supporting a band of moist vegetation. D. to about 30o north or south and then cool and condense, supporting a band of moist vegetation. 9. The spinning of the earth A. angles winds away from directly north-south toward east or west. B. causes mountain ranges to spin off moisture. C. is the initial driving force for generating winds. D. causes ocean currents to be directed "out" to the equator. E. causes the tidal ebb and flow. 10. In the wintertime, the air that moves downward from the continental masses of Asia and North America toward the Equator is A. humid. B. warmer. C. bitter cold. D. completely blocked by mountain ranges. 11. Ocean currents A. are generated by friction between winds and ocean surfaces. B. always move clockwise in an ocean basin. C. are important in shipping but have little effect on living environments. D. are driven by the earth's core rotating faster than the ocean water. E. All of the choices are true. 12. In a normal seaside environment, we would expect winds to be A. absent due to the moderating effect of the ocean. B. blowing from land to ocean during the daytime. C. blowing from land to ocean during the nighttime. D. blowing from land to ocean all of the time. E. blowing from ocean to land all of the time. 13. The Gulf Stream A. brings tropical Caribbean water to the east coast of North America and upper western Europe. B. makes local climates uniform so that Great Britain has the same climate as Greenland. C. is the major Atlantic ocean current that warms the eastern coast of South America. D. is the source of "El Nino" and is a major fishing ground. E. All of the choices are true. 14. When a subtropical climate generates wet ocean winds for almost half the year, with the difference in coastal temperature causing a gigantic circulation of air with warm air rising and cooler air continuously coming in off the ocean to replace it, it is called a/an A. rain shadow. B. lake effect. C. upwelling. D. monsoon. E. profundal zone. 15. Based on the graph, if a taiga became substantially warmer, it would next become a A. rain forest. B. temperate forest. C. thorn scrub. D. grasslands. E. savanna. 16. Kansas and Pennsylvania are approximately at the same latitude. Yet why are the potential natural communities in Kansas mostly grassland and in Pennsylvania mostly temperate forest? A. different temperatures B. different levels of moisture C. different soils D. different vegetation due to different seed banks E. different altitudes 17. The deepest A soil horizon occurs in A. rain forests since they are the most diverse. B. deciduous forests since they are the climax community. C. conifer forests since the cold temperature prevents fast decomposition. D. grasslands since the annual grasses are regularly recycled as soil humus. E. All plant communities have equivalent A horizons. 18. The soils of tropical rain forests are reddish colored with different soil profiles than in most parts of the world. Due to the warm weather and the plentiful rainfall, the soil would A. have no leaching of material to lower soil layers. B. have very little litter layer since decay will occur rapidly and leaching is extensive. C. have a very thick "A horizon," often greater than a grassland since growth occurs all year long. D. Both the lack of leaching and the scarce little layer are applicable to tropical rain forest soil. E. None of the choices is correct. 19. The largest biome on earth is the A. tundra. B. taiga. C. temperate deciduous forest. D. desert. E. ocean. 20. Which would be characterized by little rainfall, permafrost, and reindeer? A. grasslands B. temperate deciduous forest C. desert D. taiga E. tundra 21. Which would be characterized by rich soils, insufficient rainfall for trees, and many herbivores? A. grasslands B. chaparral C. desert D. taiga E. tundra 22. Which would be characterized by rainfall under 25 cm/year, hot days, cold nights, and quickly blooming plants? A. grasslands B. temperate deciduous forest C. desert D. taiga E. tundra 23. An African tropical grassland is the A. savanna. B. chaparral. C. prairie. D. taiga. E. tundra. 24. A forest found in a broad belt in northern Eurasia and North America, with conifers and swamps, is called the A. tropical rain forest. B. tundra. C. taiga. D. chaparral. E. temperate deciduous forest. 25. Which would be characterized by poor soil, and animals living in the trees? A. tropical rain forest B. tundra C. taiga D. chaparral E. temperate deciduous forest 26. Trees such as oak and maple and animals such as foxes and deer are found in the A. tropical rain forest. B. tundra. C. taiga. D. chaparral. E. temperate deciduous forest. 27. A treeless region with little rainfall in the far north is the A. grassland. B. tundra. C. taiga. D. chaparral. E. desert. 28. Treeless biomes are treeless primarily because A. there is limited sunlight. B. there is a lack of water or the water is frozen. C. there is no source of seed dispersal in the region. D. trees are dependent upon the animals for support. E. trees cannot withstand hot temperatures or below-freezing cold. 29. Temperate deciduous forests are defined by A. humid climate with seasonal droughts. B. highest variation in day and night length. C. highest amount of organisms living in tree canopy. D. a growing season between 140 and 300 days. E. richest topsoil horizon. 30. The most likely reason(s) for the number of ant species in the table is/are A. greater sunlight. B. variations in soil type. C. different species of predators. D. air pressure, humidity, and resulting rainfall. E. the amount of photosynthetic production, length of the warm season, and diversity of plants. 31. Which of the following aquatic ecosystems has far less primary productivity? A. lake or stream B. agricultural cropland C. saltwater marsh D. open ocean E. tropical rain forest 32. Which vegetation type produces the most carbon and uses the most carbon dioxide per year? A. farmland in grassland biome B. savanna in Africa C. rain forest in South America D. temperate forest in eastern United States E. boreal forest in Canada 33. Freshwater and marine microscopic organisms that freely drift in fresh or salt water are called A. plankton. B. benthic. C. abyssal. D. neritic. E. cryptic. 34. The temperature of the water strata of a lake is/are uniform during the A. winter when the ice forms an insulating cover. B. summer when the sunlight warms the surface and the wind mixes the layers. C. end of the fall and spring overturn. D. The lake has uniform temperatures at all times due to winds causing constant mixing of the layers. E. The lake always has different temperature layers and they are reversed in winter and summer. 35. The important factor(s) in the layering of a lake is/are the A. sunlight input that warms the surface in summer. B. rich nutrients that accumulate on the bottom from the continual rain of detritus. C. temperature gradients that change from summer to winter. D. population of plankton and zooplankton that depends on both sunlight and nutrient levels. E. All of the choices are important factors in the layering of a lake. 36. The Greek root word underlying the term "plankton" means A. wet or moist. B. flat layered, like a "plank." C. plant. D. wandering. E. turnover. 37. The open sunlit layer of the body of a lake is the A. littoral zone. B. limnetic zone. C. profundal zone. D. benthic zone. E. abyssal zone. 38. The bottom of a lake or stream harbors worms, clams, and other organisms in the A. littoral zone. B. limnetic zone. C. profundal zone. D. benthic zone. E. abyssal zone. 39. Which definition is NOT correct? A. littoral–lake zone closest to shore B. benthic–stream, lake or ocean floor C. limnetic–lake zone on surface away from shore D. profundal–surface division of the open ocean E. epipelagic–lower part of open waters of ocean 40. Aquatic plants are rooted in a shallow lake region near the shore called the A. littoral zone. B. benthic division. C. pelagic division. D. profundal zone. E. limnetic zone. 41. The part of a lake where light does not penetrate is the A. littoral zone. B. benthic division. C. pelagic division. D. profundal zone. E. limnetic zone. 42. Dragonfly larvae move about on the bottom of lakes and streams in the soil-water interface called the A. pelagic zone. B. estuarine zone. C. benthic zone. D. limnetic zone. E. littoral zone. 43. There are tubeworms and clams that live at the bottom of the ocean near thermal vents. They derive their energy ultimately from A. the sun by way of burning fossil fuels like we do with coal and oil. B. the sun, but they are deep in the dark ocean and live off dead detritus that sinks to them. C. bacteria that break apart hydrogen sulfide molecules and are therefore not dependent ultimately on sunlight. D. sources not yet known. 44. The ocean region that contains the neritic province and the oceanic province is the A. littoral zone. B. benthic division. C. pelagic division. D. profundal zone. E. limnetic zone. 45. The sunny surface of the middle of a lake is the A. littoral zone. B. benthic division. C. pelagic division. D. profundal zone. E. limnetic zone. 46. The nursery of the sea is the A. rocky beach. B. sandy beach. C. estuary. D. coral reef. E. ocean floor. 47. Which organisms provide most of the nutrient supply in the ocean? A. small fishes B. large fishes C. seaweeds D. phytoplankton E. zooplankton 48. Failure of "El Nino" results in A. excellent fishing. B. no summer weather. C. monsoon climate. D. increased deposits of guano. E. stagnation, poor fishing, and global climate pattern changes. 49. When an ocean current brings rich nutrients to the surface, it is called a/an A. guano. B. lake effect. C. upwelling. D. monsoon. E. profundal zone. 50. Which is NOT strictly a freshwater community? A. lakes B. rivers C. estuaries D. streams E. ponds 51. Which would NOT be a characteristic of an estuary? A. low percentage of immature animals B. high nutrient concentration C. brackish water D. shallow E. good sunlight penetration 52. Climate is affected and/or characterized by all of the following EXCEPT A. temperature. B. variations in solar radiation distribution. C. topography. D. locale. E. rainfall. 53. All of the following affects the distribution of biomes EXCEPT A. temperature. B. soil type. C. rainfall. D. climate. 54. All of the following are terrestrial biomes EXCEPT A. tundra. B. lentic. C. coniferous forests. D. savannas. E. deserts. 55. Which of the following does NOT characterize tundra? A. permafrost B. trees C. shrub D. caribou 56. Which of the following is NOT a location where coniferous forests are found? A. near mountaintops B. in eastern North America and eastern Asia C. the Pacific coast of North America D. the northern part of North America and Eurasia 57. A biome with complex structure, warm weather with plentiful rainfall, and diverse species is A. tropical rain forest. B. savanna. C. taiga. D. tundra. 58. A biome characterized by hot days, cold nights and cacti is the A. tundra. B. desert. C. taiga. D. tropical rain forest. 59. Wetlands perform which of the following for ecosystems? A. provide food and habitats for fish, waterfowl, and wildlife B. purify water by filtering it and breaking down toxic wastes and nutrients C. absorb storm and overflow waters D. All of the choices are functions performed by wetlands. 60. Large forests are maintained by abundant rainfall that occurs as air masses rise and cool around 40o north and south latitude. True False 61. Temperate grasslands are characterized by hot dry summers and cold winters with lots of snow. True False 62. The biosphere is a thin realm of the air, land, and water in which are found living organisms arranged in communities of different populations. True False 63. A rain shadow is the region where heavy condensation precipitates out as warm, moist air rises and cools on the windward side of mountain ranges. True False 64. The early explorers used sailing ships, which were blown by the major winds; therefore, Columbus and other sailors generally traveled from Europe to North America by the mid-latitude westerlies, and returned to Europe by the southern easterlies near the equator. True False 65. Freshwater communities generally have a mix of organisms similar to those in a lake. True False 66. Lakes have some depths that are always dark. True False 67. A sandy beach has the most diversity of life of any of the coastal saltwater communities. True False 68. Oceans cover about one-tenth of the earth's surface. True False 69. Bioluminescence is found in some fishes living in the deepest part of the bathypelagic zone of the ocean. True False 70. There are no trees in the tundra because of the lack of rainfall as well as presence of permafrost and boggy soils. True False 71. The geochemical cycles determine the characteristics of the major biomes. True False 72. Trade winds are so named because sailors depended upon them to fill the sails of their trading ships. True False 73. Why is the Arctic colder than the equatorial region? 74. What causes the seasons to change? 75. What causes ocean currents? 76. Why does it rain so much on the Pacific coastal side of the Rocky Mountains and so little on the leeward side? 77. Describe the relationship between ocean currents and the deposits of phosphorus in guano. 78. Describe the communities found in a freshwater environment, with the organisms living in each. 79. Describe the communities found in a saltwater environment and characteristic organisms living in each. 80. Differentiate between an estuary, a rocky beach, and a sandy beach in terms of the life forms inhabiting each. 81. Compare the levels of rainfall associated with forests, grasslands, and deserts, and explain what requirements this places on the organisms that live in each. 82. Describe desert communities and characteristic organisms living in each. 83. Describe grassland communities and characteristic organisms living in each. 84. Describe forest communities and characteristic organisms living in each. 85. Sometimes it appears as if the distribution of life is a simple matter of climate and soil influencing plant growth, which in turn influences which animals are likely to live there. However, give at least three examples wherein plants affect climate and/or soil formation, and animals affect plant distribution. Chapter 49 KEY 1. B 2. C 3. D 4. E 5. C 6. B 7. D 8. D 9. A 10. C 11. A 12. C 13. A 14. D 15. B 16. B 17. D 18. B 19. E 20. E 21. A 22. C 23. A 24. C 25. A 26. E 27. B 28. B 29. D 30. E 31. D 32. C 33. A 34. C 35. E 36. D 37. B 38. D 39. D 40. A 41. D 42. C 43. C 44. C 45. E 46. C 47. D 48. E 49. C 50. C 51. A 52. D 53. B 54. B 55. B 56. B 57. A 58. B 59. D 60. FALSE 61. TRUE 62. TRUE 63. FALSE 64. FALSE 65. TRUE 66. TRUE 67. FALSE 68. FALSE 69. TRUE 70. TRUE 71. FALSE 72. TRUE 73. Answers will vary. 74. Answers will vary. 75. Answers will vary. 76. Answers will vary. 77. Answers will vary. 78. Answers will vary. 79. Answers will vary. 80. Answers will vary. 81. Answers will vary. 82. Answers will vary. 83. Answers will vary. 84. Answers will vary. 85. Answers will vary.