DynamicsII

the Physics Classroom Summarized
2
Dynamics
Much of the following has been taken directly from the Physics Classroom website and the Physics
Classroom Summarized-Dynamics , although there are some differences.
Newton's First Law
an object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force
objects tend to "keep on doing what they're doing", unless acted upon by an unbalanced force
Inertia and Mass
inertia is resistance an object has to a change in its state of motion, aka velocity
more inertia an object has, the more mass it has
a more massive object has a greater tendency to resist changes in its state of motion
Balanced and Unbalanced Forces
if two individual forces are of equal magnitude and opposite direction, then forces are balanced
The Meaning of Force
push or pull upon an object resulting from the object's interaction with another object
contact forces; when interacting objects are in contact o frictional, tensional, normal, air resistance, applied
action-at-a-distance forces; when interacting objects are not in contact o gravitational, electric, magnetic
unit of measure is the Newton, abbreviated by N
one Newton is the amount of force required to give a 1-kg mass an acceleration of 1 m/s/s
force is a vector; has a direction, common to represent with arrows using free-body diagrams
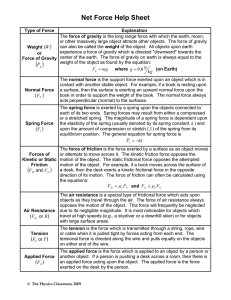
Types of Forces
applied force is force applied to an object by a person or another object
force of gravity is force with which the Earth, or other large object attracts another object towards itself. The size of force of gravity is weight of the object. Force of gravity on earth found by the equation: F g
mg . Mass refers to amount of matter that is contained by the object.
normal force is support force exerted upon object in contact with another stable object
friction force is force exerted by a surface as an object moves across it or makes an effort to move across it. Usually opposes motion of an object. Two types: sliding and static friction.
Magnitude of maximum amount can be calculated using: F f
F
N
air resistance is a special type of frictional force that acts upon objects as they travel through air
tension force is force is transmitted through a string, rope, cable or wire
spring force is the force exerted by a compressed or stretched spring
Last updated June 24, 2015
1.
Drawing Free-Body Diagrams
diagrams used to show the forces acting with arrows
each arrow indicates approximate size and direction of force
force arrows are labeled to indicate the exact type of force
dot at center of the object and the force arrows outward from the center
Determining the Net Force
net force is vector sum of all the forces acting
Newton’s Second Law
F net
ma
Free Fall and Air Resistance
only force acting is gravity
all objects will fall with the same rate of acceleration, regardless of mass
Double Trouble
situations involving two objects are often referred to as two-body situations
system analysis: two objects are considered to be a single object moving together
individual object analysis; either object is isolated and considered as separate
Newton’s Third Law
for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction
Resolution of Forces
vector directed at an angle to customary coordinate axis can be resolved into components
each component being directed along one of the axes - either horizontally or vertically
trigonometric functions can be used to determine components
Equilibrium and Statics
when all forces acting on an object are balanced, then object is in equilibrium; Fnet = 0 N
Inclined Planes
normal force acts perpendicular to surface
perpendicular component of force of gravity is equal and opposite to normal force
Last updated June 24, 2015
2.