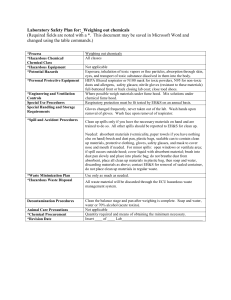
Hydrochloric Acid
advertisement
SAFETY OPERATING PROCEDURE TEMPLATE By signing and dating here the Principal Investigator/ or a designee certifies that the Safety Operating Procedure (SOP) for Hydrochloric Acid is accurate and effectively provides safe operating procedures for employees and students in this lab who will handle this hazardous chemical. _________________________________________________________________________ Signature Printed Name Date I affirm that I have read and understand the Safety Operating Procedure for Hydrochloric Acid and have undergone the EH&S Laboratory & Research training and any lab specific training regarding this SOP. Printed Name Page 1 of 5 Signature Date CONTACT INFORMATION: Chemical Name: Hydrochloric Acid Building/Room Number: Date of Creation/Revision Principal Investigator: (The PI, Lab Supervisor, or Autonomous Researcher) Emergency Phone number: HAZARD SUMMARY List all physical and health hazards associated with the chemical in this SOP. Examples of potential hazards include: toxicity, reactivity, flammability, corrosivity, pressure, etc. Potential physical and health hazards associated with the use of this chemical include: Inhalation May be harmful if inhaled. Material is extremely destructive to the tissue of the mucous membranes and upper respiratory tract. Skin May be harmful if absorbed through skin. Causes skin burns. Eyes Causes eye burns. Ingestion May be harmful if swallowed. SPECIAL HANDLING AND STORAGE REQUIREMENTS Describe special handling and storage requirements for this hazardous chemical in your laboratory, i.e. restricted access to chemical, inclusion of designated areas to limit and minimize possible sources of exposure to these materials. The entire laboratory, a portion of the laboratory, or a laboratory fume hood or bench may be considered a designated area. Special handling and storage requirements for this chemical include: Avoid contact with skin and eyes. Avoid inhalation of vapor or mist. Always use inside a chemical fume hood. Note: In case you need to dilute the concentration of HCl, always add acid to water. Always transfer from container to the receptacle by using an appropriate funnel. DO NOT mouth-pipette HCl. Conditions for safe storage Do not store in/with combustible packing material; such as cardboard, Styrofoam, plastic and paper. Keep container upright & tightly closed in a dry and well-ventilated place. Containers which are opened must be carefully resealed and kept upright to prevent leakage. Always store HCl in a secondary container. Note: Nalgene/polypropylene tray or a tub is the best suited secondary containment. Store segregated from – Organic Acids, Bases, Amines, Alkali metals, Metals, permanganates, e.g. potassium permanganate, sodium hypochlorite (bleach), Fluorine, metal acetylides, hexalithium disilicide. Page 2 of 5 ENGINEERING AND VENTILATION CONTROLS Include requirements for specific engineering/ventilation controls for this specific chemical, i.e. fume hood. If the process does not permit the handling of such materials in a fume hood, the lab personnel should contact Environmental Health and Safety at x4-4036 for review the adequacy of ventilation measures. Handling processes should be designed to minimize the potential for splash, splatter, or other likely scenarios for accidental contact. The handling of this chemical must be conducted in a fume hood. Additional engineering/ventilation controls for the handling of this chemical include: All operations involving Hydrochloric acid must be carried out in a certified chemical fume hood (certified once every year by EH&S). Laboratory rooms must be at negative pressure with respect to the corridors and external environment. To achieve this, the laboratory/room door must be kept closed at all times. PERSONAL PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENT Include specific personal protective equipment required for the handling of this chemical. See the following references: 1. The USF Hazardous Inventory Tracking System (HITS) provides access to MSDS. 2. A glove compatibility chart provides specific information on the type of safety gloves that should be used based on the hazards of specific chemicals. 3. The following EH&S webpage provides links to glove manufacturers as well as other PPE selection resources, http://usfweb2.usf.edu/eh&s/labsafety/links.html. At minimum, safety glasses, lab coat, and gloves are to be worn when using this hazardous chemical. Additional PPE Requirements for the handling of this chemical include: Respiratory protection Respirators should be used only under any of the following circumstances: • As a last line of defense (i.e., after engineering and administrative controls have been exhausted). • When Permissible Exposure Limit (PEL) has exceeded or when there is a possibility that PEL will be exceeded. • Regulations require the use of a respirator. • An employer requires the use of a respirator. • There is potential for harmful exposure due to an atmospheric contaminant (in the absence of PEL) • As PPE in the event of a chemical spill clean-up process Lab personnel intending to use/wear a respirator mask must be trained and fit-tested by EH&S. This is a regulatory requirement. If the use of an N95, half mask, or full face respirator is requested, the individual and/or their supervisor must first contact Environmental Health & Safety for a consultation to determine if respirator use is necessary. If EH&S determines the use of a respirator is necessary, the individual must participate in the University’s respirator program. This includes a medical evaluation; respirator fit test, and training. Hand protection Type of gloves recommended for Hydrochloric acid: Nitrile Note: Consult with your preferred glove manufacturer to ensure that the gloves you plan on using are compatible with Hydrochloric acid. Page 3 of 5 Eye protection Type of eye protection used to handle the chemical: Splash goggles. If used in large quantities, please use appropriate face shield. Skin and body protection Lab coat, long pants, closed-toed shoes Hygiene measures Avoid contact with skin, eyes and clothing. Wash hands before breaks and immediately after handling Hydrochloric acid. EMERGENCY PROCEDURES If a there is a spill involving an extremely hazardous chemical, emergency responders should be contacted immediately. Dial 911 during and after normal business hours to contact the local emergency responders for your area and provide detail information to the emergency responders including chemical name, volume, hazards, spill location, and any injuries incurred. Building occupants can be notified of a building evacuation through the activation of a fire alarm pull station. Personnel: If lab personnel are exposed to an extremely hazardous chemical, call 911 immediately. Remove any contaminated clothing, and IMMEDIATELY flush contaminated skin with water for at least 15 minutes following any skin contact. For eye exposures, IMMEDIATELY flush eyes with water for at least 15 minutes. Consult MSDS for guidance on appropriate first aid. Where medical attention is required, ensure to bring along MSDS(s) of chemical(s) to aid medical staff in proper diagnosis and treatment. Fire and Emergency Evacuation Procedures: In case of fire or emergency situation, call 911 and or use emergency blue phone immediately to notify the fire emergency services and campus police. Immediately evacuate the building via the nearest exit when the fire alarm is activated. If unable to evacuate due to a disability, shelter in the area of rescue / refuge, typically a stairwell landing, and wait for assistance from drill volunteers or emergency responders. Instruct visitors and students to evacuate and assist them in locating the nearest exit. Do not use elevators to exit the building during an evacuation as they may become inoperable. Carry only those personal belongings that are within the immediate vicinity. Close doors to limit the potential spread of smoke and fire. Terminate all hazardous operations and power off equipment. Close all hazardous materials containers. Remain outside of the building until the building is released for reentry. Do not restrict or impede the evacuation. Convene in the designated grassy gathering area and await instruction from emergency responders or drill volunteers. Avoid parking lots. Report fire alarm deficiencies, (e.g., trouble hearing the alarm) to facilities personnel for repair. Notify evacuation drill volunteers or emergency responders of persons sheltering in the areas of rescue/ refuge. Never assume that an alarm is a “false alarm”. Treat all fire alarm activations as emergencies. Get out of the building! The Laboratory/Studio and Field Incident Report form is to be completed by the Lab Manager/Teaching Assistant/Instructor for any incident that occurs in any University of South Florida affiliated teaching or research laboratory/studio or field research project. An incident means Page 4 of 5 any unplanned event within the scope of a procedure that causes, or has the potential to cause, an injury or illness and/or damage to equipment, buildings, or the natural environment. Please fill out the online Laboratory/Studio and Field Incident Report form below and submit to Environmental Health & Safety within 24 hours of the incident. Due to medical privacy concerns, no personal identifying information of the person involved in the incident shall be entered or submitted with the form. http://usfweb2.usf.edu/eh&s/labsafety/LabIncident.html WASTE DISPOSAL All chemical waste generated within USF System laboratories are considered hazardous waste and must be disposed of as hazardous waste in accordance with USF Hazardous Waste Management Procedure, the EPA, and the DEP. The USF Hazardous Waste Management Procedure can be found using the following link, http://compass.custhelp.com/app/answers/detail/a_id/1118/kw/hazardous%20waste. TRAINING REQUIREMENTS All individuals working with chemicals in USF laboratories must take EH&S’s Laboratory & Research Safety Training. To register for Laboratory & Research Training, please use the following link, http://usfweb2.usf.edu/eh&s/labsafety/tmaterials.html. However, the use of this chemical may warrant additional safety training per the PI, EH&S, or an authorizing unit such as the Biosafety or Radiation Safety programs. Additional training requirements are listed below. Training Requirements: X Laboratory & Research Safety Training (EH&S) X Research-specific Training (PI) □ Other _____________________________________________________________ PRIOR APPROVALS □ The handling of this chemical requires prior approval from the PI/designee. □ The handling of this chemical does not require prior approval from the PI/designee. Approval Signature (if required by PI) _________________________________________________________ Page 5 of 5